- What is a poppet valve and what does it do ?
- What is the difference between the Poppet valve and spool valve ?
- How does a poppet valve work ?
- How to do the selection, installation, and maintenance of a poppet valve?
- What are the types of the poppet valve?
- How ball seat poppet valve is different from disk seat poppet valve?
- What are the advantages of the poppet valve?
- What are the disadvantages of the poppet valve?
- Poppet or Spool Which Will Work Best for Your Application?
- Comparing Poppet Valves vs. Spool Valves
- What are the applications of the poppet valve?
- What is a Poppet Valve Used For?
- What is the Function of the Poppet?
- What Opens a Poppet Valve?
- What is the Difference Between a Poppet Valve and a Check Valve?
What is a poppet valve and what does it do ?
The poppet valve is used to control the flow, it could use a disc, ball, or cone to control the flow. Poppet valves are directional control valves and these valves would act very quickly. These valves are composed of movable poppet which would close against a valve seat. The ball, cone or disc in the poppet valve is used to close the seating area. In a certain type of poppet valve, the actuation force is depended on the pressure and area so in order to avoid this pressure compensation is done. Most of the poppet valves have this problem and poppet valves cannot be constructed for pressure compensation, because of this the actuation of the poppet valve is done by high switching force. So the actuation is done with the help of pilot control or lever transmission.
A poppet valve, also known as a mushroom valve, is typically used to regulate the timing and amount of fuel or vapor flowing into or out of an engine, though it has many other applications as well.
Poppet valves, though the most expensive, are highly efficient, offering approximately 50% more effective lift area compared to concentric ring valves of the same size. They can operate with lifts up to ¼ inch and are commonly used in natural gas pipeline booster applications. As pressure increases above the poppets, they open, allowing gas to flow through, with greater lift reducing flow resistance.
These valves feature a mushroom-shaped element, with material selection determining application range. Metallic poppets, capable of withstanding pressures up to 3000 psi and temperatures up to 500°F, are rarely used due to inertia. Nonmetallic poppets, made from materials like Nylon, Torlon, and PEEK, can handle up to 450°F and 800 psi, with speeds up to 1800 rpm.
The Dresser-Rand “Magnum” valve stands out for its ability to operate at high compressor speeds. Its unique design reduces tensile stresses, optimizes flow path, and is more tolerant of particles and liquids, making it suitable for high molecular weight applications at varying compressor speeds.

What is the difference between the Poppet valve and spool valve ?
Poppet valves are able to cover the internal passage by using a ball or disc and it is held by using air pressure and a spring. So when the poppet valves are actuated the poppet will be pushed away by the stem from the seat so that the flow could occur. While in case of a spool valve a spool is used to block the flow so when the spool valve is actuated then the spool will move and that could cause the seal to be close to the bore and the ports will be opened for the airflow
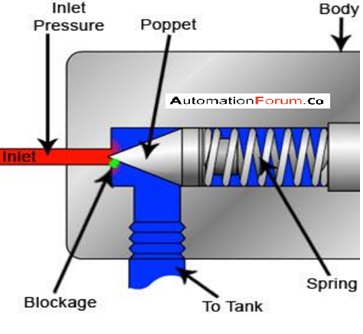
How does a poppet valve work ?
The poppet valve has a poppet that is movable and it would close against a valve seat the valve would be tightly closed by the pressure from the inlet. When we apply a small force to the poppet stem then the poppet would open. The stem of the poppet valve has an O-ring seal so that it can reduce the leakage. In most of the poppet valves, the poppet is held down with the help of a spring. According to the purpose of the valve, the number of poppets will vary.
How to do the selection, installation, and maintenance of a poppet valve?
- Check if the disk is centered within 3mm on the seat
- During the stroke, we must check the shaft alignment and the valve must be straight between the cylinder and guide by 1mm, if it is more than this then it would cause problems
- During the closed position, the valve disc must not have more than 1mm clearance to seat
- Cylinder end stroke must be varied to soften final seat speed so that hard hit to the seat can be avoided
- The disc deflection must be checked when it touches the seat, it must not be in the range of 4-6mm and this will provide proper pressure for the seal
- Check the center hole of the disc, it should be cut, round with no edging or rough cuts
- The washers used in the top and bottom part of the disc and nut must be checked and the diameter of the washer should be proper for the disc
- Check if the PRV is installed and the pressure setting is correct
- Check the solenoid and air tubing
- Exhaust air pressure must be checked
- Check if the poppet valve shaft guides have Teflon bushing
- Check if dry air is used for poppet air supply
What are the types of the poppet valve?
Mostly there are two poppet valves and they are ball seat poppet valve and disc seat poppet valve
Ball seat poppet valve
Disk seat poppet valve
How ball seat poppet valve is different from disk seat poppet valve?
Ball seat valves are not expensive and they are small, it can resist dirt and it can be operated manually or mechanically. While the disk seat poppet valve requires more area but a small lift is needed. Quick response time and they are resistive to dirt, and these valves can be actuated manually, mechanically, electrically and pneumatically.
What are the advantages of the poppet valve?
- It has a high flow rate because of the larger internal surface
- The controlling of the positions can be done properly because the exhaust port is covered by the poppet before the flow
- The product life would be high because of less wear
- The response time of poppet valve is really fast, during the actuation the port will open quickly
- We would get a larger opening in a small stroke
- These valves are resistive to dust and dirt
- Less maintenance and economical
What are the disadvantages of the poppet valve?
- These valves are unbalanced and pressure compensation is required
- It is not used with vacuum
- Actuation is done by higher force because the spring and air pressure must be overcome for the flow
- If there is no supply pressure then the back pressure may open the valve, so these valves cannot be used to hold the pressure downstream.
- Pitting can happen due to the opening impact
- Because of buckling, the spring could wear
What are the Benefits of Poppet Valves?
A poppet valve features a valving element that seals against a valve seat, with a return spring and inlet pressure aiding in the sealing process. Compared to spool valves, poppet valves offer specific advantages and disadvantages, making them ideal for applications requiring precise control, high flow rates, long life, low leak rates, fast response times, or cost-effectiveness.
Poppet or Spool Which Will Work Best for Your Application?
When deciding between a poppet valve and a spool valve, consider the key factors most critical for your application. Poppet valves are ideal for applications requiring precise control, as they avoid transitional states between functions, ensuring closed crossover. They also excel in situations where fast response times are essential, as they open immediately upon actuation with a shorter stroke. However, if your application demands consistent response times or operates under a vacuum, a spool valve would be the better choice. The chart below can help guide your decision.
Comparing Poppet Valves vs. Spool Valves
This below table outlines the key differences between poppet valves and spool valves, helping to determine which type is more suitable for specific applications.
| Feature | Poppet Valves | Spool Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Utilizes a mushroom-shaped element (poppet) that seals or opens the flow path. | Features a cylindrical spool that slides within a bore to control flow. |
| Efficiency | Highly efficient with a larger effective lift area. | Generally less efficient compared to poppet valves. |
| Response Time | Faster response due to direct movement of the poppet. | Slower response time due to the sliding motion of the spool. |
| Pressure and Temperature | Can handle high pressures (up to 3000 psi) and temperatures (up to 500°F for metallic poppets). | Typically handles lower pressures and temperatures compared to poppet valves. |
| Application | Commonly used in engines, natural gas pipelines, and high-pressure systems. | Widely used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems for directional control. |
| Durability | Nonmetallic poppets are lightweight and reduce wear, but metallic versions can withstand higher pressures. | Generally durable but may wear out faster due to the sliding action. |
| Flow Characteristics | Provides direct flow with minimal resistance when open. | Flow is controlled by the position of the spool, which can introduce some resistance. |
| Maintenance | Typically requires less maintenance due to fewer moving parts. | May require more frequent maintenance due to wear on the spool and seals. |
| Tolerance to Contaminants | More tolerant to particles and liquids in the flow. | Less tolerant to contaminants, which can cause wear or blockage. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to complex design and high efficiency. | Typically less expensive, making them cost-effective for many applications. |
What are the applications of the poppet valve?
- It can be used for gas transport because it has a low opening impact, high lift, and good efficiency
- They are also used for process applications
What is a Poppet Valve Used For?
A poppet valve is commonly used in internal combustion engines, hydraulic systems, and pneumatic systems. It controls the flow of fluid or gas by opening and closing ports, ensuring that fluids or gases move in the desired direction or are blocked when necessary.
What is the Function of the Poppet?
The poppet, which is the valve’s movable element, functions as a gatekeeper that either seals the valve port to stop the flow or lifts away to allow flow. When seated, the poppet prevents fluid or gas from passing through; when lifted, it permits flow.
What Opens a Poppet Valve?
A poppet valve is typically opened by mechanical force, such as a camshaft in engines, hydraulic or pneumatic actuators, or manually through levers or switches. In some designs, pressure from the fluid or gas can also open the valve if it exceeds a certain threshold.
What is the Difference Between a Poppet Valve and a Check Valve?
The primary difference between a poppet valve and a check valve is their function. A poppet valve is a control valve, which can be manually or automatically operated to control the flow direction or stop flow. In contrast, a check valve is a type of one-way valve that allows flow in one direction only and automatically prevents reverse flow, operating based on the pressure difference without external control.
Check the following links to get more info about control valves
- Types of pressure control valves
- Directional control valve
- Unloading valve
- Bleed valve
- Breather valve
- Control valve troubleshooting
- Air valve
- Float valve
- Control valve positioner
- Control valve actuator
- Pressure control valve
- Safety valve
- Solenoid valve
- Hydraulic valve
- Pressure relief valve
- Pneumatic valve
- Shuttle valve
- Foot valve
- Check valve
- Spool valve
- Piston valve
- Pinch valve
- Plug valve
- Ball valve
- Gate valve
- Butterfly valve
- Globe valve
- Needle valve
- Diaphragm valve
- Control valve installation





