- What is a piston valve?
- What are the parts of piston valves and how are they constructed
- Piston Valve Symbol
- What are the types of piston valves?
- Other Types of Piston Valve
- What are the applications of piston valves
- Typical Applications of Piston Valves:
- Piston Valve Function
- What is a Piston Valve used for?
- Why Is a Piston Valve Used in a Steam Line?
- Purpose of Piston Valve Relief
- Piston Valve vs. Globe Valve
- What is the difference between globe valve and piston valve?
- Top Piston Valve Manufacturers
- Glandless Piston Valve:
- 3-Way Piston Valve:
What is a piston valve?
A piston valve is a device that is used to control the motion of a fluid along a tube or pipe by means of the linear motion of a piston within a chamber or cylinder. Piston valves are used for fully open or fully closed for on/off regulation on steam, gas, and other fluid services. These valves are mostly used on fluids that cause excessive seat wear. Piston valves are mostly actuated manually, but sometimes other actuation modes such as hydraulic and electric are used. Piston valves are usually used where the valve body is permanently installed to reduce maintenance. Piston valves are not designed for throttling applications and they must be used in fully opened or closed positions. When the valve is fully opened, only the bottom face of the piston is exposed to fluid and the rest of the body is protected by the upper sealing rings. So the sealing surfaces are protected from erosion by the fluid flow.
piston valve is a device designed to regulate the flow of fluid or gas through a pipe by utilizing the linear movement of a piston within a chamber or cylinder.
Common examples of piston valves include:
- Valves in brass musical instruments
- Valves in pneumatic cannons
- Valves in stationary steam engines and steam locomotives
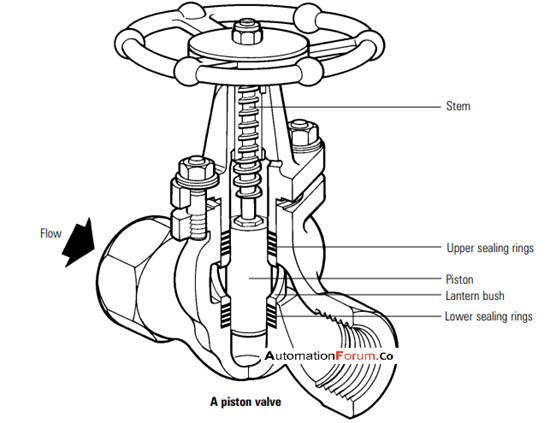
What are the parts of piston valves and how are they constructed
Piston valve parts
- Body
- Bonnet
- Piston
- Valve rings
- Lantern bush
- Spindle
- Gland
- Packing
- Handwheel
- Yoke bush
- Bonnet stud
- Gland eyebolt
Piston valves are the variant of the conventional globe valve, with the traditional seat and cone is replaced by a piston and lantern bush. The piston is of chrome steel and perfectly machined, the sealing rings are often self-lubricating Teflon. Mostly the body is constructed by the cast and they could have screwed ends, flanged ends, or butt welding ends. The bonnet is also the same material as that of the body and it is of bolted construction. Proper sealing is done by a piston with the help of two resilient seats. The piston is connected to the valve stem and hand-wheel and passes through two sealing rings which are separated by a lantern bush. When assembled the two sets of the sealing rings are compressed around the piston by the load exerted along the stem. The upper set of the sealing rings acts as conventional gland packing, and the lower set acts as the seat. High-level shut-off tightness is assured by the large sealing area between the piston and rings. If the valve needs maintenance, all the internals can be easily removed by undoing the cover nuts and withdrawing the piston. The rings and the lantern bush can be removed by using an extractor tool. This operation can be conducted without removing the valve from the pipeline. Piston valves have a long life, but the sealing ring could damage after being used for so long.
How does a piston valve work
The construction of a piston valve is similar to a globe valve and they are used to shut off and regulate. These valves provide positive shut-off. The shut-off assembly comprises the metal piston, two resilient valve rings, and a metal lantern bush. The sealing surface consists of the outer vertical surface of the piston and the corresponding inner surfaces of the sealing rings. This provides a sealing surface compared to the globe valves of conventional design. At the beginning of the opening, a displacement uncovers the small flow section. Which controls the low rate of flow.
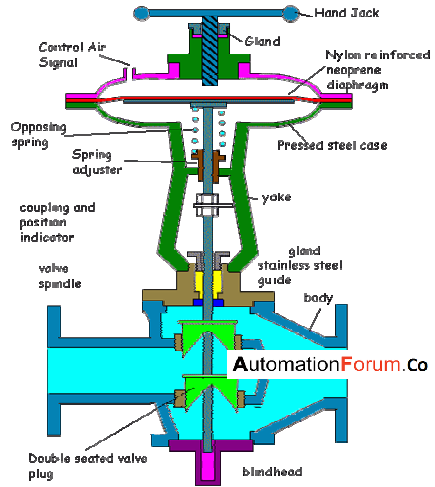
Most automatic valves are of double disc type, the double-disc design can be used to equalize the pressure across the disc and it can be varied to change the flow characteristics through the valve or to change the operation of the valve such as by decreasing the response time of the valve’s action. A piston balance valve allows the force exerted across the seating area to be as equal as possible while being directed in the opposite direction. The double-disc arrangement has the flow coming from the left. In the closed position, the fluid pressure would press against the bottom of the top disc and against the top of the bottom disc equalizing flow pressure. Even when the valve is open there is an equalizing force that gives the valve a smooth operation.
Piston Valve Symbol
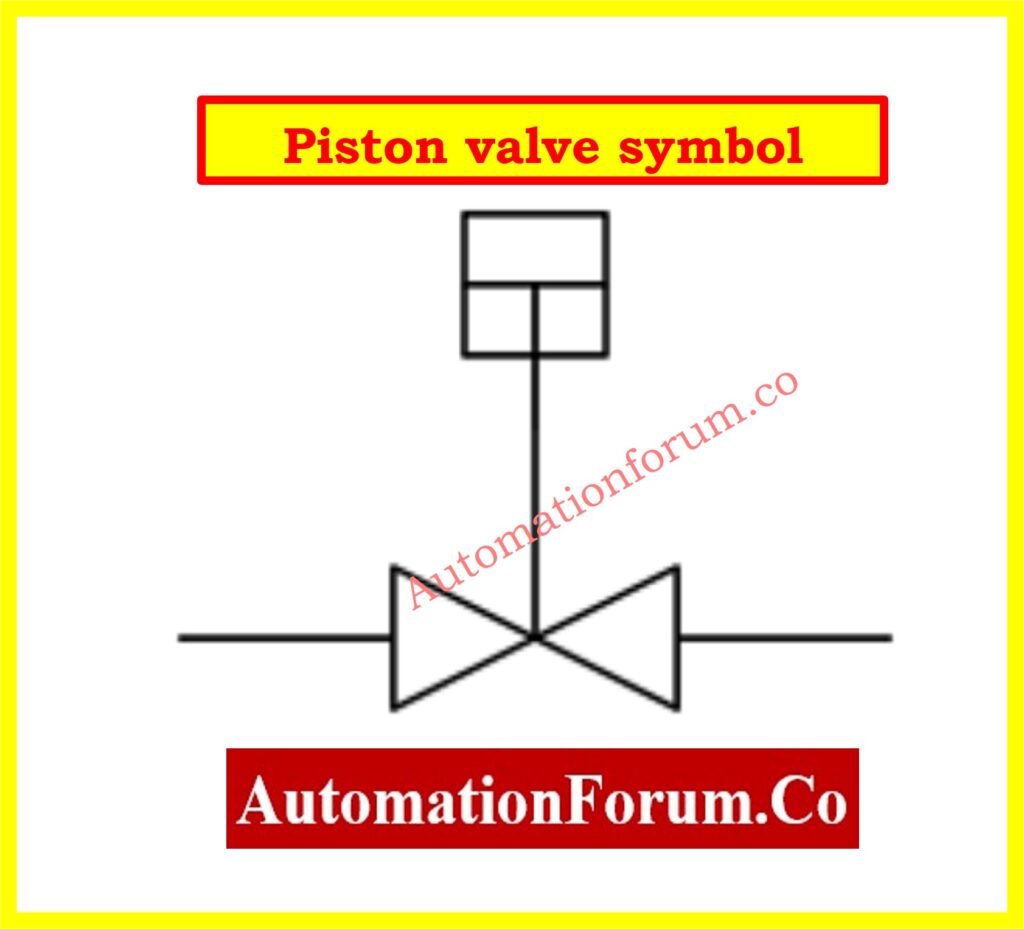
The standard schematic symbol for a piston valve resembles other linear motion valves, with additional detail representing the piston mechanism. The vertical movement of the line illustrates the opening and closing of the valve as the piston moves up and down. The symbol can vary slightly depending on the specific type of piston valve, but it typically emphasizes the movement of the piston rather than a rotating element like in globe or gate valves.
What are the types of piston valves?
Balanced and unbalanced are the two types of piston valves. Balanced valves are used in high-pressure service and unbalanced ones for low-pressure service.
There are two types of piston designs available regulating the type and the normal. In the regulating type, the bottom part of the piston is tapered to have a throttling effect. The sealing rings are the heart of piston valves
Other Types of Piston Valve
Two-Port Piston Valve
Commonly used for on/off isolation in systems handling steam, gas, or fluids. It is straightforward in design and provides a robust seal, making it ideal for systems requiring minimal leakage.
Three-Port Piston Valve
Often used in systems that need flow diversion or mixing, such as in condensate or steam control applications. It has three ports to direct the flow to multiple lines, offering greater flexibility in fluid management.
High-Pressure Piston Valve
Engineered for high-pressure applications, particularly in steam systems or other industrial applications where pressure can be extreme. It features reinforced seals and stronger materials to handle the pressure without losing performance.
Thermic Fluid Piston Valve
Designed specifically for heat transfer systems, these valves handle high-temperature thermal oils or other heating media used in industrial processes such as chemical plants or refineries.
What are the applications of piston valves
Typical Applications of Piston Valves:
- Thermic Fluid Supply, Return & Balancing Line Isolation: Piston valves isolate the flow of high-temperature thermic fluids in supply and return lines, ensuring controlled and efficient heating/cooling.
- Pressure Reducing Stations: In pressure control systems, piston valves isolate or regulate pressure levels, providing reliable shutoff in both steam and fluid circuits.
- Main Steam Isolation on Steam Header: These valves provide isolation in steam headers for maintenance or operational purposes. Their tight sealing ensures that no steam is lost, maintaining system efficiency.
- Steam Trap Isolation: Piston valves are frequently used to isolate steam traps during maintenance. Their ability to seal tightly prevents any unwanted steam leakage, reducing energy loss.
- Pressure Reducing & De-superheating Stations: Piston valves are employed in stations where both pressure reduction and temperature regulation are required. They isolate and control steam at precise pressure and temperature levels, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
- Steam and Condensate Manifolds: Piston valves are used in both steam and condensate manifolds to ensure reliable isolation and control of the fluid flow, minimizing leakage and ensuring system safety and efficiency.
Piston Valve Function
- A piston valve works by utilizing a cylindrical piston that moves vertically within the valve body.
- The piston is surrounded by durable sealing rings, typically made of graphite or another high-temperature material, which form a tight seal as the piston moves.
- This design allows for effective isolation and minimal leakage. The sealing rings ensure that when the valve is closed, there is no bypass of fluid or gas, making piston valves ideal for critical applications such as steam or high-temperature fluids.
- Their robust design makes them more durable compared to traditional valves in harsh conditions.
What is a Piston Valve used for?
- Piston valves are used primarily for on/off control and isolation in systems handling steam, gases, and various liquids.
- Their design is ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature environments, making them popular in industries such as power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
- They are often used where tight shut-off and minimal leakage are crucial, such as in steam lines, thermal fluid systems, and condensate recovery systems.
- The robust sealing mechanism in piston valves makes them an excellent choice for applications requiring reliable performance over long service intervals.
Why Is a Piston Valve Used in a Steam Line?
- Piston valves are favored in steam lines due to their ability to provide a tight shut-off, even in high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
- The piston design, with its dual sealing rings, ensures minimal leakage, which is critical in steam systems where energy efficiency and safety are paramount.
- Steam systems require robust valves that can handle the extreme conditions without frequent maintenance, making piston valves ideal for this application.
- They also reduce the risk of thermal expansion issues, as their seals can handle temperature fluctuations better than traditional valve types.
Purpose of Piston Valve Relief
- The piston valve relief is an important feature designed to protect the valve and system from overpressure conditions. In steam systems or other high-pressure applications, pressure can build up to dangerous levels if not properly controlled.
- The relief mechanism in piston valves ensures that excess pressure is safely vented, preventing damage to the valve components and the surrounding system.
- This relief function is essential in maintaining safe operation in systems where pressure surges are a concern, helping to avoid accidents or equipment failure.
Piston Valve vs. Globe Valve
This below table highlights the key differences between piston valves and globe valves, making it easier to choose the appropriate one based on specific application needs.
What is the difference between globe valve and piston valve?
| Feature | Piston Valve | Globe Valve |
| Mechanism | Uses a piston that moves up and down to block or regulate fluid flow. | Operates with a disc that moves in and out of a seat to control flow by throttling or isolation. |
| Sealing | Piston is sealed by two rings, providing a tight shut-off with minimal leakage. | Disc and seat contact provides a seal, but more prone to leakage over time due to wear. |
| Best Suited For | High-pressure, high-temperature systems, especially steam applications. | Systems requiring precise flow control and throttling, such as cooling water or fuel lines. |
| Leakage | Minimal leakage due to the dual sealing rings, offering a reliable shut-off. | More prone to leakage over time, especially in high-pressure applications. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to the durability of the sealing rings and piston mechanism. | Requires more frequent maintenance due to wear on the seating surfaces. |
| Applications | Commonly used in steam lines, thermal fluid systems, and high-pressure applications. | Used in applications requiring flow throttling, such as HVAC systems, fuel lines, and cooling water lines. |
| Temperature & Pressure Handling | Excellent for handling high temperatures and pressures, particularly in steam systems. | Suitable for moderate temperature and pressure but not as robust as piston valves in extreme conditions. |
| Throttling Capability | Less effective for throttling; mainly used for isolation and on/off control. | Better for throttling and fine flow control. |
| Service Life | Long service life due to robust design, especially in harsh environments. | Shorter service life compared to piston valves, especially in high-pressure or high-temperature conditions. |
| Cost | Typically more expensive due to durable design and specialized applications. | Generally less expensive than piston valves but requires more maintenance over time. |
Top Piston Valve Manufacturers
- Haitima Valve Corporation: Known for its high-quality industrial valves, including piston valves for steam and high-temperature applications.
- Crane Fluid Systems: Offers a wide range of valve solutions, including piston valves designed for steam systems, HVAC, and other critical industrial processes.
- Velan: A leading manufacturer of industrial valves, Velan provides piston valves designed for durability and performance in steam and thermal fluid systems.
- Armstrong International: Specializes in steam systems and manufactures piston valves specifically designed for high-efficiency steam management.
- Cair Euromatic Automation: Focuses on automation and valve solutions, including piston valves for specialized applications in fluid and steam systems.
Glandless Piston Valve:
A glandless piston valve eliminates the need for a conventional gland packing system. Instead, it uses durable sealing rings and a piston mechanism to ensure tight shut-off without leakage. This design is ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications like steam and thermal fluid systems. The glandless feature minimizes the risk of fluid leakage, reduces maintenance requirements, and enhances the valve’s lifespan. These valves are often preferred in industries where contamination from gland leaks is unacceptable, such as chemical processing, power generation, and steam control systems, offering efficient, low-maintenance operation.
3-Way Piston Valve:
A 3-way piston valve is designed for applications that require flow diversion, mixing, or distribution between multiple lines. It has three ports, allowing it to direct fluid to two different pathways or mix two fluid streams. Commonly used in steam, condensate, or thermal fluid systems, 3-way piston valves offer versatility in controlling complex flow systems. Their robust construction and piston-based sealing mechanism ensure minimal leakage and reliable operation, even in high-temperature, high-pressure environments. These valves are ideal for applications such as condensate recovery, steam distribution, and temperature regulation in industrial processes.
To get more info about the control valve check the following links





