- Types of PLC Hardware
- Compact PLC (Fixed PLC)
- Modular PLC
- Rack-Mounted PLC
- What are the different types of modules used in PLC?
- PLC Hardware Modules and Their Functions
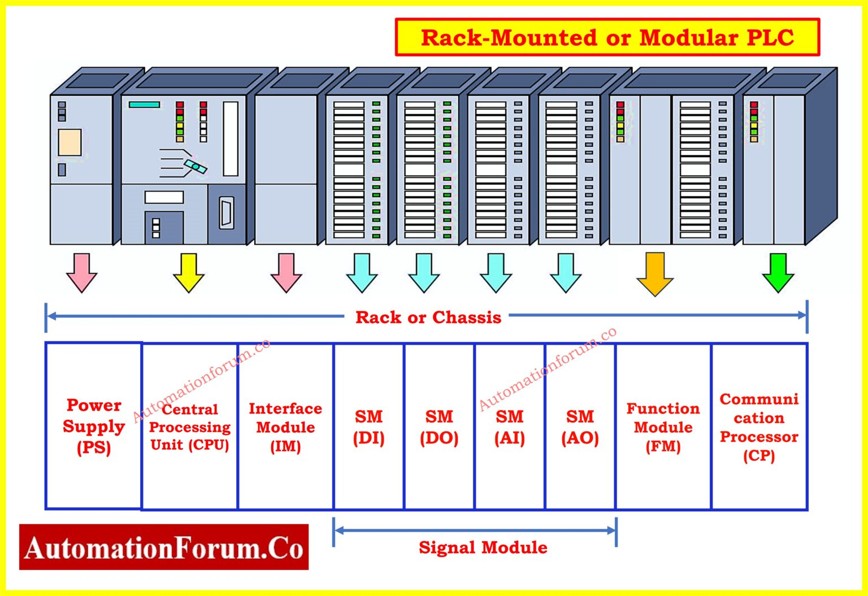
- Rack or Chassis
- Power Supply (PS) Module
- What is CPU module in PLC?
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Interface Module (IM)
- Signal Module (SM)
- Function Module (FM)
- What are PLC communication modules?
- Communication Processor (CP)
- Safety PLC Module
- Redundancy Module
- What are PLC modules?
- What are the hardware components of a PLC?
- What are modular PLCs?
- What does a PLC module do?
- What is CP in PLC?
Today’s industries depend heavily on Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) to accomplish efficient reliable automated control functions. A PLC system includes software programs combined with physical hardware devices. The programming and execution capabilities that software supports in PLCs use hardware elements that include input/output (I/O) modules along with power supplies and CPUs and communication processors to establish operational foundation.
This guide examines PLC hardware through an evaluation of different modules within PLC systems and their operating functions.
Types of PLC Hardware
Three main classes exist for PLC hardware systems.
- Compact PLCs (Fixed PLCs)
- Modular PLCs
- Rack-mounted PLCs
Compact PLC (Fixed PLC)
The fixed PLC design includes integrated hardware components which manufacturers build into a single compact device that cannot expand after manufacturing. These components typically include:
- Input and Output (I/O) modules
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Power Supply (PS)
- Communication modules
Advantages of Compact PLCs:
- Cost-effective for small automation applications.
- Requires minimal wiring and space.
- Easier to install and configure.
Limitations of Compact PLCs:
- The system contains a set limit of I/O points that cannot be expanded.
- Limited processing power and memory.
- Less flexible for large or complex automation systems.
Modular PLC
The modular structure of PLC systems enables programmers to extend their systems by adding more modules. The system consists of multiple components which can be installed onto chassis racks or buses containing stacked slots.
Advantages of Modular PLCs:
- The system offers expansion options depending on current and future operational needs..
- Higher processing power and larger memory capacity.
- Suitable for medium to large industrial applications.
Limitations of Modular PLCs:
- Modular PLCs cost significantly more than compact PLCs at their initial purchase.
- Requires more space and wiring.
Rack-Mounted PLC
A rack-mounted PLC functions as a subsection of modular PLCs by placing modules directly into standardized racks. The enhanced processing capabilities and expanded connectivity are features of this PLC type.
Advantages of Rack-Mounted PLCs:
- Suitable for large-scale industrial automation.
- The system includes redundant features which improve reliability performance.
- Supports multiple communication protocols for integration with other systems.
Limitations of Rack-Mounted PLCs:
- These systems have high initial costs and need skilled staff to perform setups.
- These PLCs occupy larger physical space because they exceed the size parameters of both compact and modular setups.
The following section introduces the main hardware components found in modular or rack-mounted PLC systems.
Refer the elbow link for Understanding PLC Racks and Chassis: Types, Differences, and Purposes
What are the different types of modules used in PLC?
PLC Hardware Modules and Their Functions
A modular PLC system incorporates numerous hardware modules which handle specialized operations within the system. A PLC system includes these primary modules for operation:
Rack or Chassis
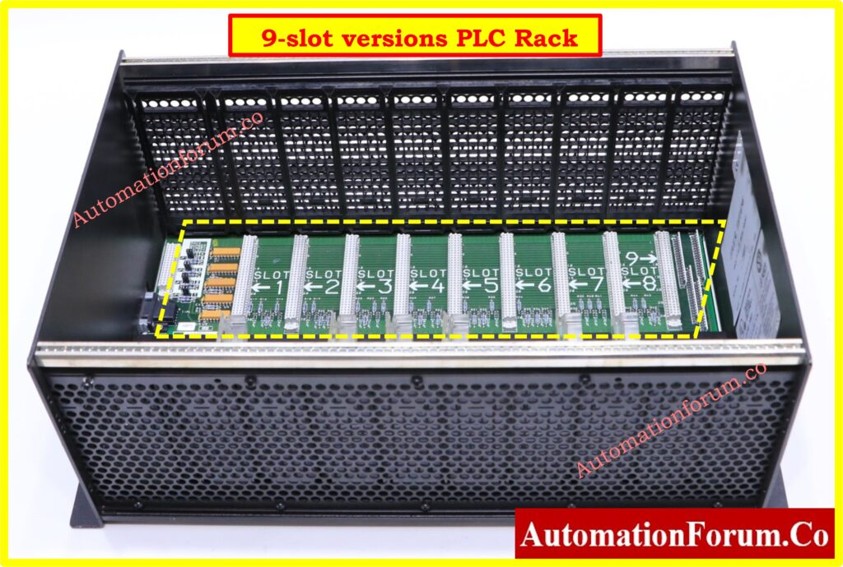

A modular PLC system requires the rack or chassis as its foundational structural block. The system links different modules by using a backplane communication system within the central rack.
Functions of Rack or Chassis:
- Power distribution takes place equally between all modules connected to the backplane.
- A rack system functions to support the mechanical stability of distinct PLC hardware components.
- Acts as a link between the CPU and other modules.
- The bus connection enables all controlled components to send messages to each other.
Power Supply (PS) Module

The power supply module generates the required electrical voltage and current which distributes to all PLC modules and CPU.
Key Features:
- Converts AC voltage (100-240V AC) into a regulated DC voltage (typically 24V DC).
- The device has different current rating options between 5A to 50A that depends on specific system needs.
- Provides overcurrent and short-circuit protection.
What is CPU module in PLC?
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
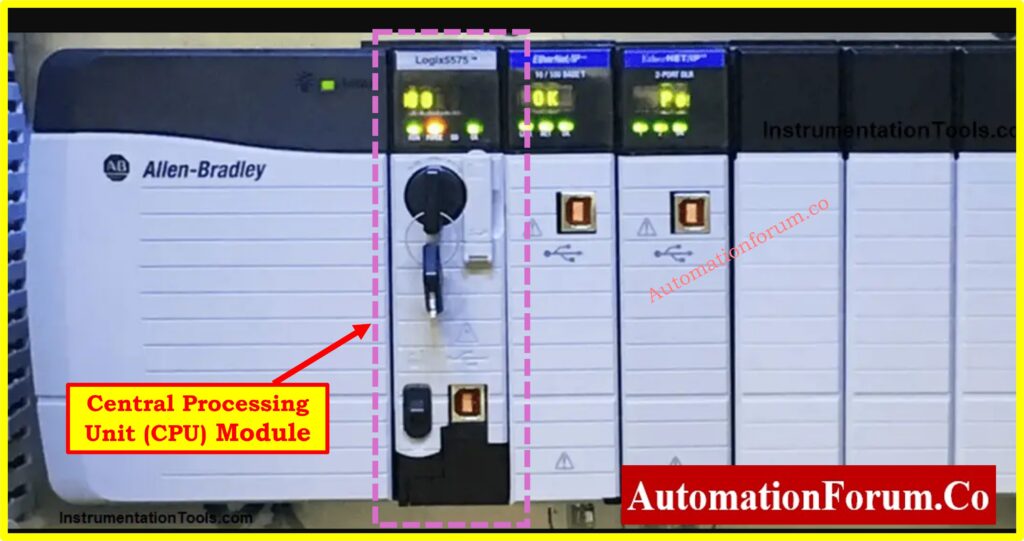

The PLC system relies on its CPU to function as its primary intelligent processing core. All system operations rely on the memory-stored logical instructions which the CPU both executes and processes to achieve necessary controls.
Functions of the CPU:
- Performs arithmetic and logical operations.
- Executes user-defined control logic.
- Plc monitors incoming signal states through monitoring systems and transforms these signals into output controls according to the programmed logic.
- Provides different operating modes:
- Programming Mode: The programming mode lets users download and edit debugging programs directly from their personal computer.
- Run Mode: During Run Mode the control program functions without interruption.
- Stores and manages system memory.
Interface Module (IM)

The interface module serves as an added option for connecting multiple racks within modular PLC systems where multiple racks exist in different levels.
Functions of the Interface Module:
- The PLC system can expand through the connection of additional racks.
- The module enables quick data exchange among different rack systems.
- The main rack can accommodate extra I/O modules through interface modules.
Must read: Understanding Remote I/O in PLC Control Systems
Signal Module (SM)
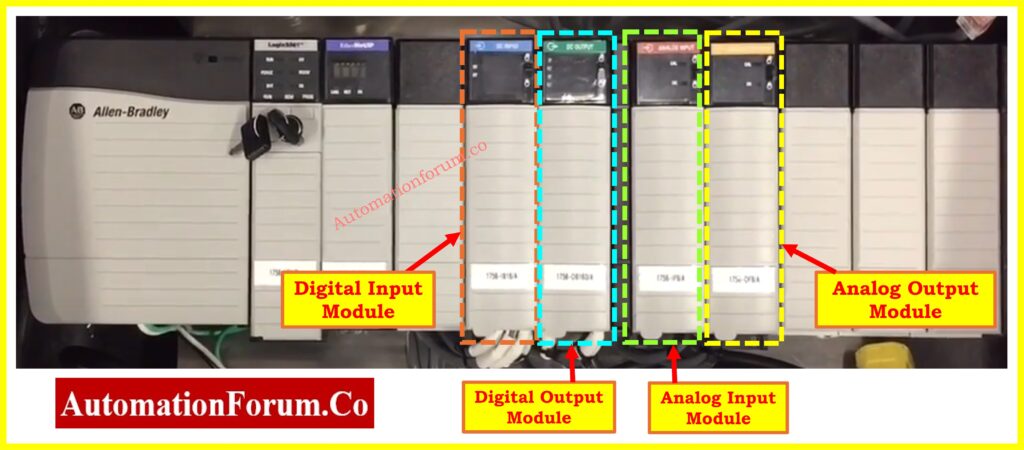
The signal modules operate as data connectors between PLC systems and field devices by utilizing both input and output functions.
Types of Signal Modules:
- Digital Output Module: Digital Output Module functions as a signaling device to operate solenoids and actuators and relays through control signals.
- Analog Input Module: The Analog Input Module functions as a sensor device which accepts ongoing measurements from temperature, pressure and flow sensors.
- Analog Output Module: The Analog Output Module serves to transmit continuous signals that drive control valves and variable speed drives.
- Combination Modules: Provide a mix of digital and analog inputs/outputs.
Function Module (FM)
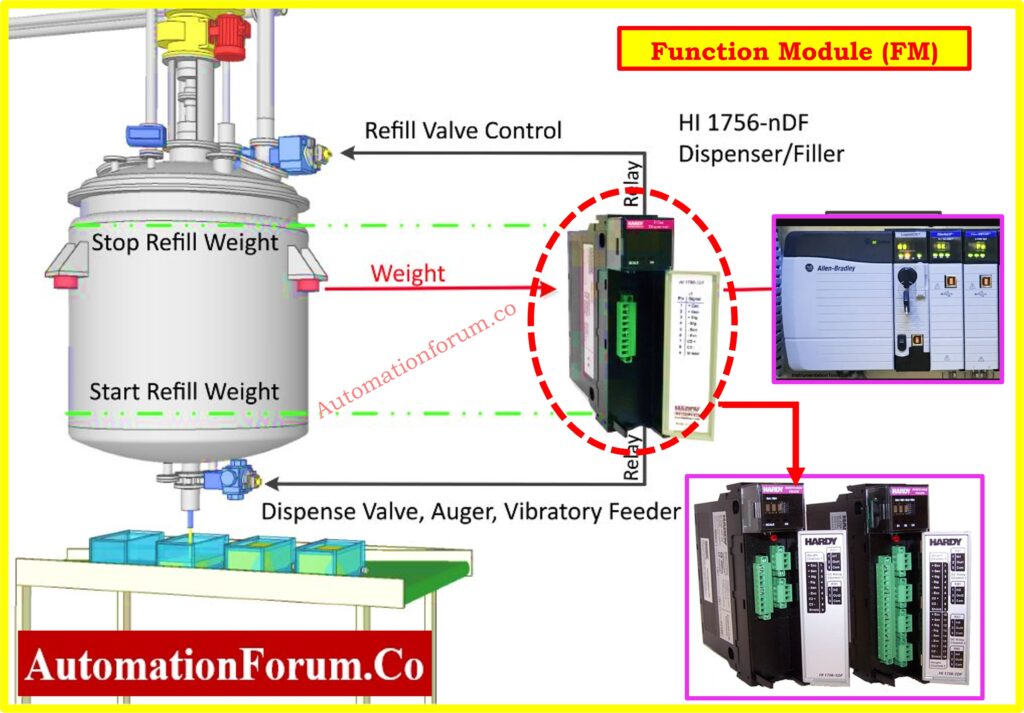
Function modules exist as optional elements that perform specialized functions which exceed basic input and output capabilities.
Common Function Modules:
- High-Speed Counter (HSC) Module: High-Speed Counter (HSC) Module functions for measuring high-speed rotations in devices that have rotary encoders.
- PID Module: The PID Module allows users to achieve process control accuracy through implementation of Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) algorithms.
- Weighing Module: The Weighing Module allows devices to communicate with load cells and weight sensors through its interface.
- Position Control Module: The Position Control Module supports motion control functions for servo motor positioning in various applications.
- CNC Module: Enables integration with CNC machines for advanced machining operations.
What are PLC communication modules?
Communication Processor (CP)
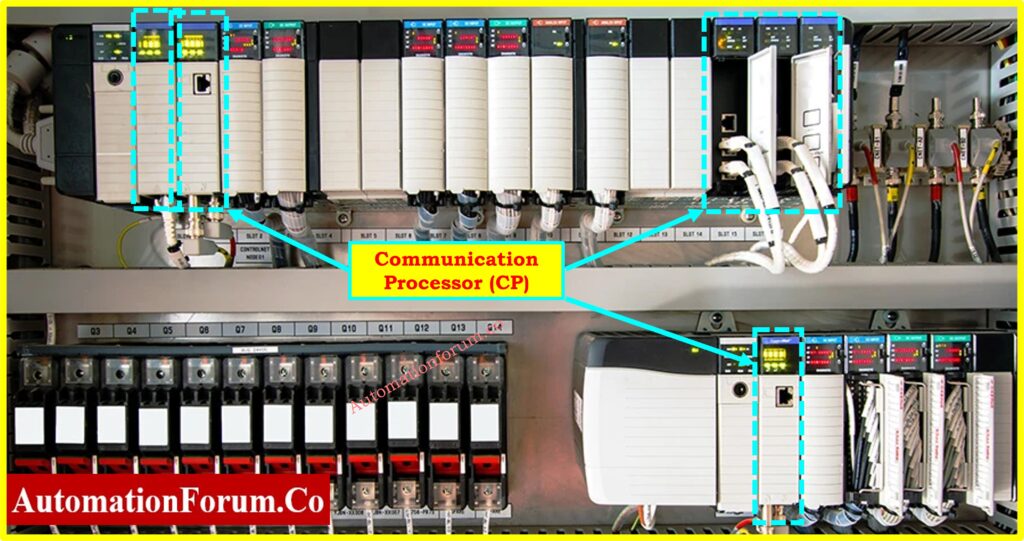
Communication processors represent optional expansion modules which enable more networking ports for system data exchange between devices.
Functions of Communication Processors:
- Facilitates communication between multiple PLCs.
- The feature enables communication between PLCs and SCADA systems along with HMI along with other industrial control systems.
- The machine control system supports multiple industrial communication protocols which include:
- Ethernet/IP
- Profibus
- Modbus
- DeviceNet
- Profinet
Safety PLC Module
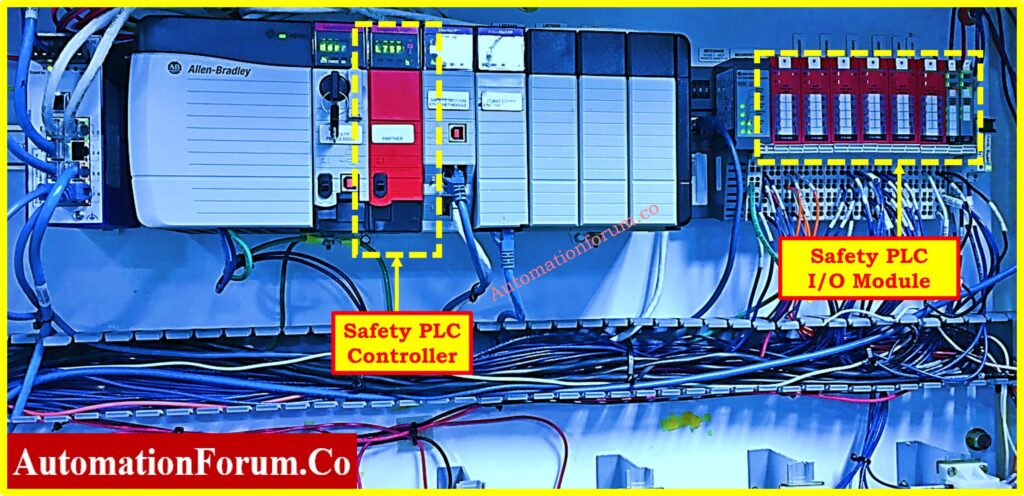
The safety PLC module ensures operational safety through its observation of emergency stop functions and safety relays and failsafe circuits.
- The system prevents unsafe process operation through emergency shutdown features which activate when failure conditions occur.
- Industrial safety standards are maintained by the safety module.
- The system serves applications in hazardous zones where stringent safety procedures must be followed.
Redundancy Module
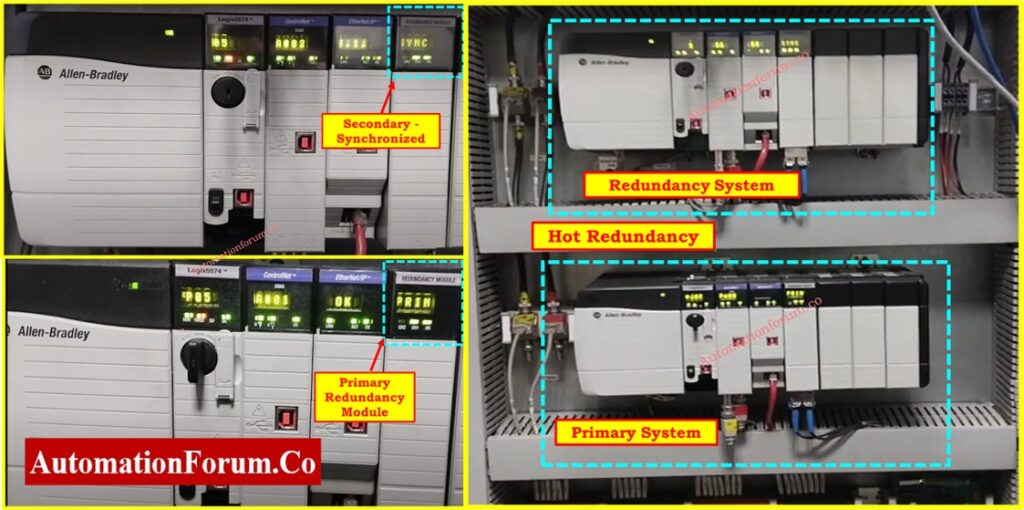
The redundancy module serves critical industrial applications because system reliability takes top priority.
- This system implements an additional CPU together with backup power components for maintaining continuous system functionality.
- Your system will operate uninterrupted when modules experience failure.
- High-availability systems that include power plants and oil refineries and manufacturing facilities implement these modules because system outages lead to substantial financial losses.
- Operators can switch components during operation since hardware modules perform a hot-swappable function.
Refer the link below for additional information on PLC programming and simulation approaches.
PLC Modules FAQ
What are PLC modules?
The programmable logic controller system depends heavily on Input/Output (I/O) modules which function as essential components. These devices serve to transmit signals between the CPU and external process control devices to make communication and operation possible.
What are the hardware components of a PLC?
The standard PLC hardware configuration includes several key elements which include:
- Power Supply: The power supply unit delivers the fundamental electrical power.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): A Central Processing Unit (CPU) serves as the main operational component within PLC systems by executing programmers and processing data.
- Mounting Rack: The Mounting Rack serves to hold different PLC modules in a reliable manner.
- Read-Only Memory (ROM): Stores the PLC’s firmware and system programs.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Stores temporary data and user programs.
- Input/Output (I/O) Modules: Interface with external devices such as sensors and actuators.
- Programming Device: The Programming Device functions as the tool for creating and testing application programming followed by distribution of programs to the PLC.
What are modular PLCs?
Programmable logic controllers that use modular design approaches operate as flexible controllers for industrial needs. PLC modules offer expandability through their modular design which lets users customize their system with additional or less modules to match their industrial requirements. The modular design enhances automation systems by giving them better capabilities to scale and adapt to changing needs.
What does a PLC module do?
A PLC module facilitates communication between the CPU and external devices. A PLC module obtains sensor data which transfers through its CPU for processing before sending output commands to actuators and control systems.
What is CP in PLC?
The Siemens S7-1500 PLC system among others implements specialized Communication Processor (CP) modules to boost network connectivity. Real-time data exchange operations become possible through CP modules while these modules also boost communication reliability and enable network and device integration.
Click on the PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Knowledge Quiz link below to test your knowledge.





