1. What is Ethernet Protocol?
Ethernet/IP is basically an application layer protocol and is a flexible best-in-class Ethernet network. It is a simple way of arranging data inside a TCP/IP packet.
On Ethernet/IP network, data is known as attributes and is represented by values. They are grouped altogether to create objects.
2. How Ethernet/IP protocol communicates?
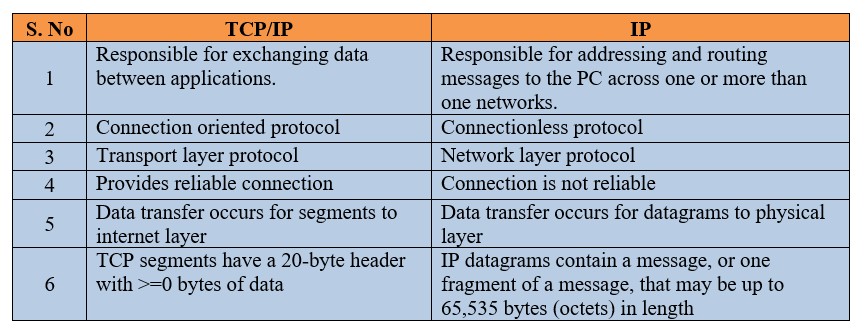
To know about the working of Ethernet/IP protocol, we have to discuss first about the Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model (OSI Model) where different layers of communication network are specified.
OSI Model consists of seven different layers. Here is the diagram.
- Application: This layer is specific to the end-user application like web browsers.
- Presentation: The function of this layer is to arrange application data into network format like encrypting or decrypting of data for making a secure transmission.
- Session: This layer establishes connection between the application to the network layer. It happens between two devices.
- Transport: The layer is also termed as TCP or Transmission Control Protocol and is on top of Network layer (IP).
- Network: This layer is where routing or forwarding of packet, setup and establishing connections occur.
- Data Link: The layer is responsible for transfer of data
- Physical: Physical layer is all about physical media or components required like cables, frequencies, sufficient voltages.
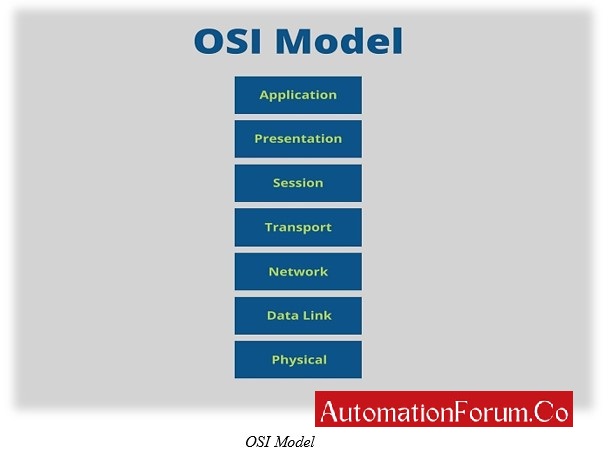
It is to note that Ethernet is functional at the data link layer and physical layer stage. It is actually the physical connection which transfers data from node-to-node.
The physical layer conducts connection in copper wire, fiber and wireless. Depending on the physical layer, data link layer establishes connection based on few standards like IEEE 802.3 or 802.1 for copper, IEEE 802.3 for fiber and IEEE 802.11 for WIFI.
To segment this further, data travels through our PC via a series of networks known as packets and to send and receive the packets, some rules should be set. Here the protocol comes into play. For different devices, protocols set the rules for sending and receiving data packets.
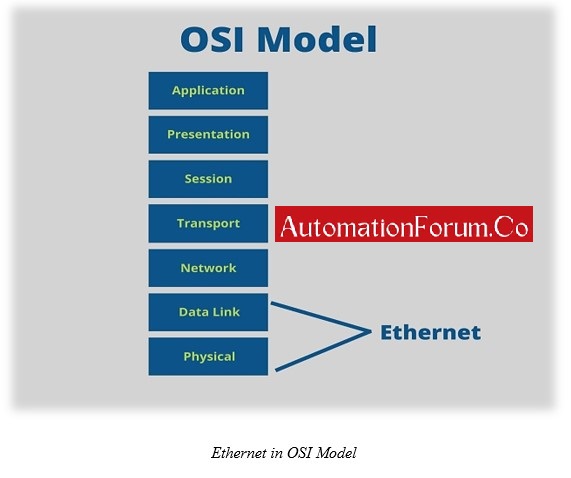
In case of Ethernet, there are three different layer protocols which are:
- CIP
- TCP/IP & UDP
- IP
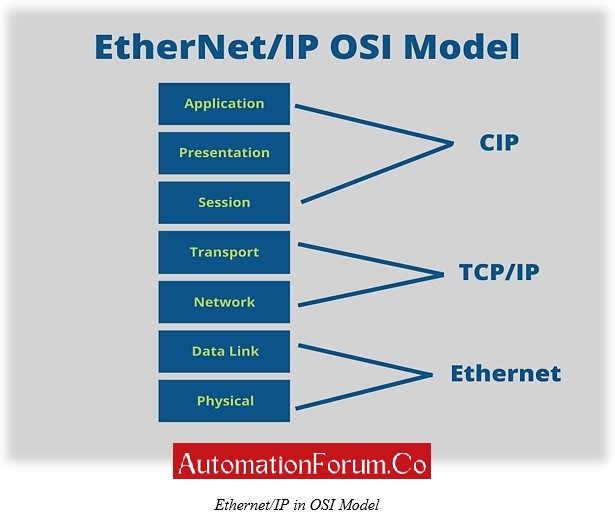
In Ethernet, Ethernet/IP will progress through CIP layers to the TCP/IP and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) layers, and finally to the IP layer.
3. What are the topologies of Ethernet/IP?
Ethernet/IP is an active technology solution with the network segments conducting point-to-point connections in a star topology. This topology links layer-2 and layer-3 switches.
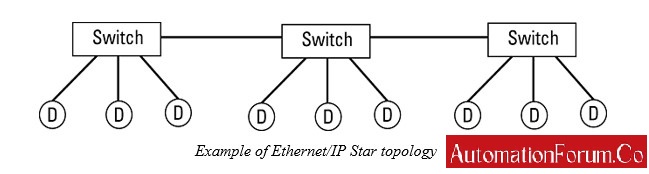
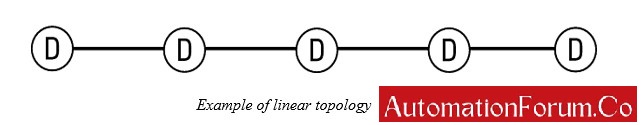
Ethernet/IP also supports linear topology which allows the networked devices directly chain together with no requirement of wiring back to a central Ethernet switch.
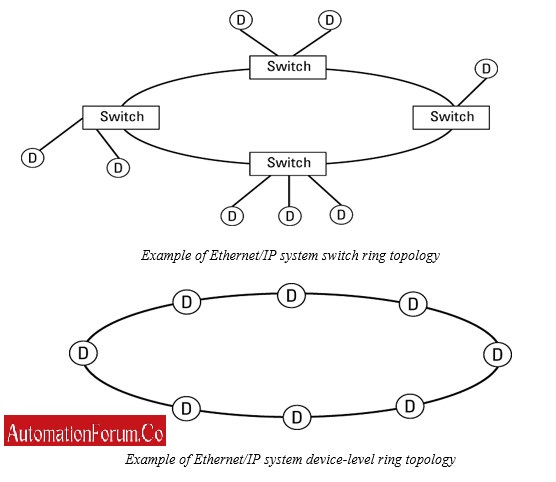
Ethernet/IP also provides a single fault-tolerant ring topology where no operation is interrupted if any link is broken within the ring. Two types of ring topologies are there. One is optimized for devices (device-level ring) and the other one is for switches.
4. Advantages of having Ethernet/IP based communication:
- Established: Ethernet/IP is carried by the mother organizations: ODVA – Open Device Net Vendor Association, IAONA – Industrial Automation Open Network Alliance, CI – ControlNet International and IEA – Industrial Ethernet Organization
- Standard: Ethernet/IP is a certifiable standard protocol. The organizations which are supporting Ethernet/IP ensure a consistent standard through certified labs for testing.
- Compatibility: Ethernet/IP is compatible with common protocols. Using traditional Ethernet, this can transport devices which make it easier to implement.
- Support: Since Ethernet/IP is being used for decades, it will proceed as a growing technology solution in future. There are also a lot of training, tools and vendors which are willing to support.
- Open: The access of Ethernet/IP is completely free for the vendors & developers.
- Universal Use: Now-a-days, most industries prefer to use Ethernet/IP. There are a large number of vendors who can help or support the CIP protocol.
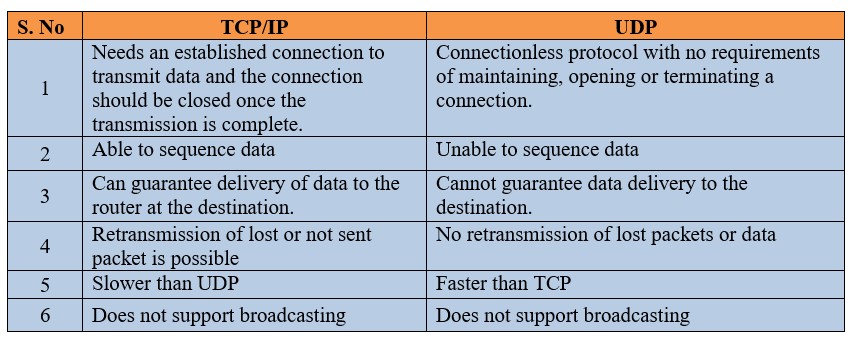
5. Comparison between TCP/IP and UDP:
6. Comparison between TCP/IP and IP: