- Essential Steps to Request a Quote for Automation System Integration
- Defining Standard Practices and Component Preferences for Your Factory
- Determining the Required Volume of Production
- Evaluating the Waiting Period and Urgency of Your Project
- Assessing Current Site Conditions
- Confirming Drop Site and Installation Area
- Assessing Nearby Environmental Conditions of your Site
- Providing Sample Tools or Drawings
- Assessing the Availability of a Qualified QA or QT Team
- Defining Your Budget for the Automation Project
- Understanding Your Current Network Architecture
- Defining Your Automation Goals
- Ideal Machine Footprint
- Automation Experience
- Downloadable Checklist: Key Requirements for a Successful Industrial Automation Project RFQ
In this post, we’ll explore the key factors required to obtain a quote for an industrial automation project.Starting a new automation project is exciting, especially when the benefits include time and cost savings, reduced personnel, increased efficiency, fewer errors, and improved overall output. However, before you can reap these benefits, you need to prepare a Request for Quotation (RFQ) for potential vendors. A well-prepared RFQ helps vendors clearly understand the scope of your requirements.
But before jumping into creating an RFQ, have you evaluated whether your company is ready for automation? Identifying and addressing these prerequisites is essential to ensure the project aligns with your organization’s needs. Neglecting this step can lead to incomplete RFQs and project delays. In this post, we’ll outline the crucial factors you must assess in your organization to effectively prepare an RFQ and secure accurate quotes for your automation project.
Essential Steps to Request a Quote for Automation System Integration
Defining Standard Practices and Component Preferences for Your Factory
- Understand the automation systems your team is familiar with; for example, if your staff is trained on Siemens PLCs or Allen Bradley systems, specifying these brands in your RFQ can reduce training time and simplify troubleshooting.
- Review the components and configurations used in previous automation systems, such as Mitsubishi, ABB, or Honeywell, to maintain consistency and utilize existing expertise.
- Assess your maintenance team’s preferences and experience; if they have a strong background in working with Schneider Electric or Rockwell Automation systems, include these as preferred options in your requirements.
- Specify detailed requirements in your RFQ, including preferred brands like Omron, Yokogawa, or Emerson, and ensure they align with your business needs and operational goals.
- Align your automation choices with your team members skills and familiarity to minimize disruptions, enhance efficiency, and simplify ongoing maintenance.
- Consider any company-wide standards or historical preferences when selecting components or systems to ensure compatibility and a streamlined integration process.
Click here for Top 15 PLC brands
Determining the Required Volume of Production
- Understand your production requirements and determine whether you need a high-speed system (e.g., servo or stepper motors) or a standard system with a regular PLC. The speed of the system directly affects the choice of components and project cost.
- Analyze your annual production volume goals to ensure the automation system can meet the desired output efficiently. For example, an operator assembling one part per minute may produce 480 parts during an 8-hour shift, whereas an automated system can significantly increase output depending on the cycle time.
- Assess the cycle time required for your automation system. For instance, does the system need to assemble a part in 20 seconds or two seconds to meet your production demands? This requirement will directly influence the selection of automation components and drive the cost of the project.
- Consider the return on investment (ROI) by aligning production speeds with business objectives. For example, systems designed for slow, steady production (e.g., VFD motors) may cost less, while high-speed systems (e.g., servo motors) may be necessary for faster outputs.
- Compare systems that suit your production needs; similar setups with different components (e.g., servo motors versus VFD motors) can offer varying efficiencies and cost implications.
Evaluating the Waiting Period and Urgency of Your Project
- Determine the timeline for your project execution and the urgency of having the automated system operational on your shop floor. This is a critical factor to include in your statement of work (SOW) or request for quotation (RFQ).
- If the project is urgent, prioritize vendors you’ve previously worked with and trust for quick and reliable execution, tailoring your RFQ to align with their capabilities.
- Factor in the time needed to evaluate new vendor proposals, as they may offer better solutions or improved output compared to your existing vendors.
- Assess whether you have the time and resources to accommodate a new vendor while ensuring timely project completion.
- Include clear deadlines and delivery expectations in your RFQ to help vendors provide realistic timelines and avoid delays.
- Consider the potential waiting period for installation, commissioning, and production start-up, ensuring your timeline accounts for unforeseen challenges.
Assessing Current Site Conditions
- Evaluate the availability and stability of the electrical power supply at your site. If power fluctuations are common, specify robust components like a PLC designed to handle unstable power conditions.
- Check the presence and reliability of utilities such as water, steam, and air, along with their backup systems, as these are crucial for the functioning of many automation systems.
- Assess network stability and the availability of network providers to ensure consistent communication between automated systems.
- Determine the scope and feasibility of laying communication cables, including considerations for cable length, routing, and environmental factors.
- Identify any specific environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, or exposure to dust and chemicals, that might influence the choice of components or system design.
Confirming Drop Site and Installation Area
- Verify that the drop site (the area where materials will be delivered and installed) is prepared and ready for installation.
- Assess whether the required space for the automation system is finalized or if there are pending civil works or layout changes.
- If the installation area is tentative or not yet finalized, include this information in your RFQ, specifying approximate dimensions or conditions.
- Request vendors to design the system with flexibility in mind or to provide spare parts for potential adjustments in the future.
- Ensure the RFQ clearly communicates any site-specific requirements or constraints to help vendors prepare accurate quotes and avoid delays.
Refer the below link for Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) of a PLC Panel: A Step-by-Step Basic Guide
Assessing Nearby Environmental Conditions of your Site
- Evaluate the surrounding environment of the installation site, including potential hazards such as extreme temperatures, dust, humidity, or chemicals.
- If the site is located in a hazardous or difficult environment, clearly specify these conditions in your RFQ. This includes factors like corrosive atmospheres, high vibration, or areas requiring specialized safety precautions.
- Inform vendors about any additional requirements for safety equipment, such as PPE, protective barriers, or environmental protection kits, which may impact the project’s cost and timeline.
- Consider the impact of local environmental factors on installation and commissioning, such as accessibility, working conditions, or any restrictions imposed by local regulations.
- Ensure that the RFQ communicates these conditions to help vendors provide accurate quotes for the necessary safety measures and adjust the commissioning time accordingly.
Providing Sample Tools or Drawings
- If you have existing electrical or mechanical drawings, tools, or sample parts from similar projects, include this information in the RFQ. This allows vendors to reference existing materials and avoid duplicating design work, ultimately reducing project costs.
- Specify whether the parts or systems are pre-assembled or need assembly, as this will help vendors understand the complexity and scope of the project.
- If tooling or special equipment is required, provide details on these items to ensure vendors can accurately assess the requirements and factor them into their proposal.
- Sharing drawings and sample parts allows engineers to understand the inner workings of the system, identify potential design modifications, and determine how machinery can manipulate parts rather than relying on manual labor.
- Ensure the RFQ clearly mentions the availability of these references and tools to help vendors prepare more accurate and cost-effective solutions.
Refer the link for the Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) Activities for SCADA System: Step-by-Step Checklist
Assessing the Availability of a Qualified QA or QT Team
- Evaluate whether your company has a qualified quality assurance (QA) or quality testing (QT) team in place to oversee the installation and performance of the automation system.
- If you have an in-house QA or QT team, you can include severe quality requirements in the RFQ so that they can validate and confirm that the system fulfills your standards.
- If you lack a qualified team, you may need to hire third-party auditors or quality checkers, which will increase the overall cost of the project.
- Clearly communicate the capabilities of your QA or QT team in the RFQ to help vendors understand the level of quality assurance expected.
- Consider the integration of automated inspection and testing systems, such as machine vision, measurement gauges, or air testing systems, to ensure that parts meet the required specifications and that the system performs as intended.
Defining Your Budget for the Automation Project
- Your budget is the foundation of your request for proposal and has a direct impact on the project’s scope and specifications. Before preparing the RFQ, make it clear how much funds you are willing to invest in the automation system.
- Consider the estimated return on investment (ROI) after installing the system. A well-structured ROI assessment will help you decide whether to increase your budget to include advanced features or higher-quality components.
- Consider the cost-benefit analysis for automation. For example, substituting manual work with automated technologies can result in significant labor cost savings. According to studies conducted by the Boston Consulting Group, increased automation has the potential to lower labor expenses by up to 22 percent.
- Based on your expected ROI, determine whether you can devote extra dollars to expand the system’s capabilities, perhaps improving long-term efficiency and production.
- Ensure that your RFQ represents the financial limits, as well as the potential cost savings and performance gains that automation will offer.
Understanding Your Current Network Architecture
- In modern industrial automation, excellent communication is critical for data exchange, increasing production efficiency, decreasing errors, and improving system reliability.
- Evaluate your current network infrastructure and plan any necessary expansions to meet the connectivity requirements of the automation system. Ensure that your network is capable of handling the new system’s data flow and communications protocols.
- The communication parameters in the RFQ should be defined based on your current network configuration. This includes establishing network protocols, bandwidth requirements, and any required modifications or additions to support the automation system.
- Avoid demanding network functionalities that your existing system cannot handle. Be realistic about your present network’s capabilities, and mention any limits in the RFQ.
- Indicate in the RFQ whether any network upgrades or new installations will be required to enable good communication between the automation system and other plant systems.
Refer the below link for the Site Acceptance Test (SAT) Procedure for PLC Systems
Defining Your Automation Goals
- Make sure your automation goals are clear, such as increased production efficiency, improved output, and reduced errors.
- Assess your employees’ readiness and prospective training requirements for the new system.
- Determine your company’s strengths, limitations, and any potential challenges that may develop during or after commissioning.
- Consider whether you’re prepared for smart manufacturing technologies such as IoT or robotics, and whether they should be integrated.
- Specify the intended output and performance standards for the automation system.
Ideal Machine Footprint
- The machine footprint is a critical consideration when constructing an automated system. Though not typically included in the SOW or RFQ, both the vendor and the client must be aware of the available shop floor space.
- The customer must also know how much room to set aside in their facility for the new automated machine.
Automation Experience
- While not often included in the SOW or RFQ, it is important to determine the customer’s level of automation experience.
- This allows vendors to determine the level of technical depth required in machine, control system, and robotics descriptions.
- It also indicates the company’s knowledge with specific brands, such as Mitsubishi versus Allen Bradley PLCs.
Click here for Common Causes of Programmable Logic Controller(PLC) Failure and Mitigation Strategies
Downloadable Checklist: Key Requirements for a Successful Industrial Automation Project RFQ
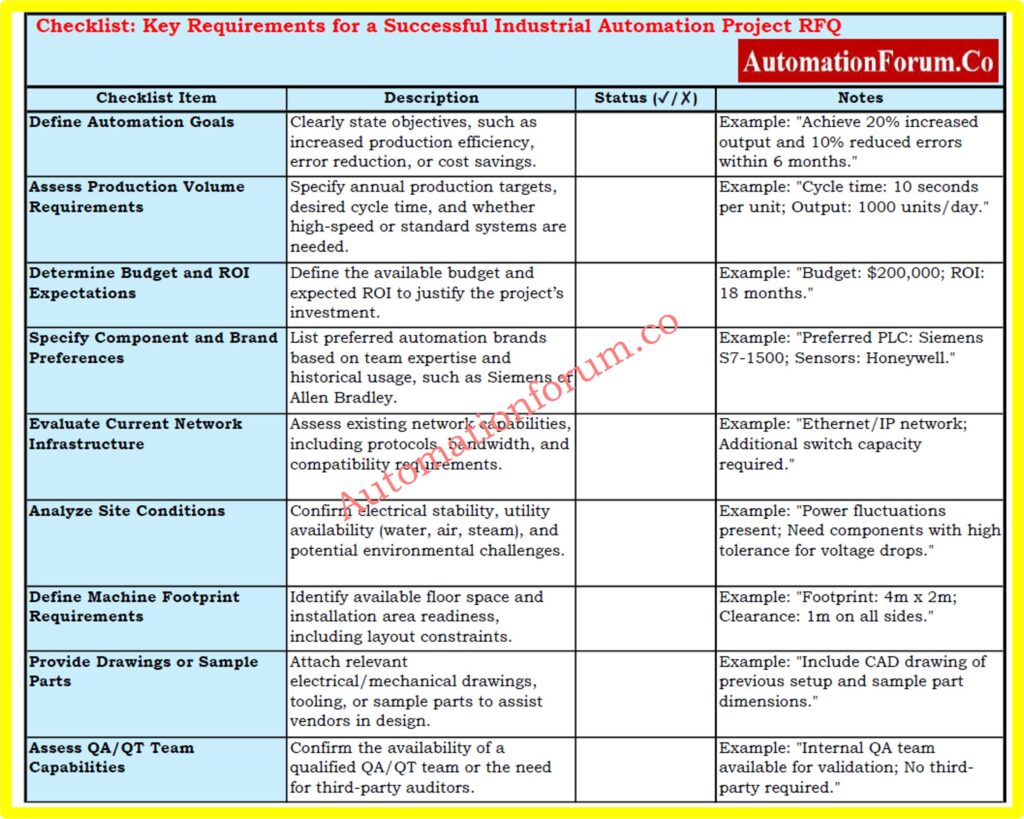
Simplify your industrial automation RFQ process with this detailed checklist covering technical, operational, and budgetary requirements. Download now to ensure project clarity and vendor alignment!
Click here for 50+Collection of Essential Instrumentation and Automation Control System Checklists





