- Section 1. Safety Measures
- Section 2. Required Documentation
- Section 3. Gland Specification Check
- Section 4. Required Tools and Equipment
- Section 5. Procedure for Cable Glanding
- Section 6. Additional Checks for Cable Glanding
- Section 7. Cable Termination and Identification
- Section 8. Bending Radius of the Cable
- Section 9. QC Inspection
- Section 10. Testing and Pre-Commissioning of Cable
- Section 11. Final Documentation
- Section 12. Required Spares for cable glanding
- Section 13. Safety Monitoring and Final Housekeeping
- Cable Glanding & Termination Excel Checklist for Download
- Frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to cable glanding and termination
- What are the steps for cable glanding?
- What are the steps for cable termination?
- What is the difference between cable glanding and termination?
- What are cable termination standards?
- What is the minimum distance between cable glands?
- Which tool is used for cable termination?
Section 1. Safety Measures
When it comes to cable glanding and termination procedures, safety is essential. Important safety considerations include the following:
- Make sure that all safety regulations are met and that all work is done in compliance with an approved permit system.
- Employees are required to wear the proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety goggles, insulated gloves, hard hats, and safety shoes.
- Only individuals with the necessary training and certification should handle cable glanding and termination tasks.
- Hazard Identification: Recognize and reduce risks such electrical shock, height-related tasks, and confined spaces.
- All personnel should complete site-specific induction training covering project safety requirements.
- Plans for emergencies, first aid kits, and fire extinguishers must to be easily accessible at the location where the work is being done.
Section 2. Required Documentation
Before beginning the task, check that the following documentation is obtained and has been approved:
- Up-to-date single-line diagrams and construction related drawing.
- Detailed cable schedule with specifications and routing.
- Junction box (JB) schedule with relevant details.
- Guidelines from cable and gland manufacturers manual.
- Detailed inspection and test plans (ITP).
- Job safety analysis (JSA) describes risk assessments and safety precautions.
- Ensure all modifications are recorded on as-built drawings during and after installation.
Refer the below link for the Types of Engineering Drawings and Documents used in Instrumentation

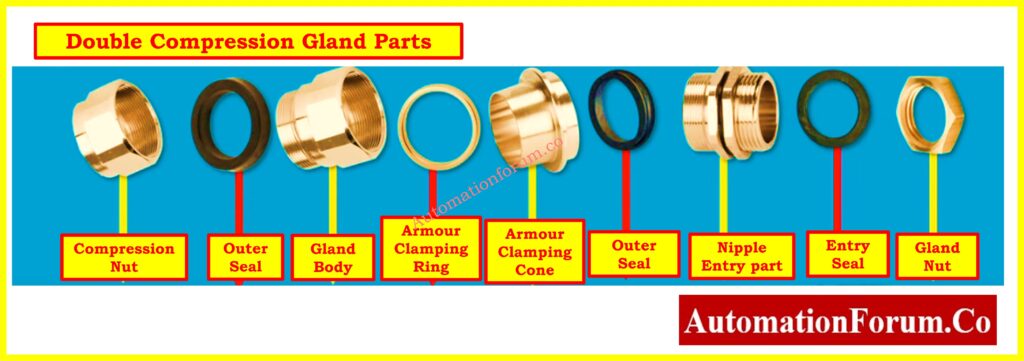
Section 3. Gland Specification Check
Examine and confirm that all manufacturer and project specifications are in compliance.
- Verify that cable glands are the right size, kind, and material compatibility and that they are installed according to the guidelines.
- All cable glands and lugs must have the qualities and colors specified in the project documents.
- Check to make sure termination kits are complete and fulfill all project specifications, including correct installation techniques.
- To avoid electrical problems and ensure safety, make sure insulation and creepage distances meet applicable criteria.
- Verify that every cable has the correct labeling and identification, with accurate and permanent marks for simple identification and troubleshooting.
Section 4. Required Tools and Equipment
Make sure you have all of the necessary tools and equipment ready for the cable glanding and termination process:
- Standard electrician tool kit
- Hacksaw and cable cutters
- Crimping tools and soldering irons
- Insulation resistance tester and multimeter
- Non-conductive cleaning materials
- PPE (insulated gloves, safety glasses, etc.)
Section 5. Procedure for Cable Glanding
The process for correct cable glanding is described in the following steps:
5.1 Preparation
- Make sure all temporary marks are accurate and check cable test records.
- Get the equipment ready for cable entrance by removing the gland plates.
- Mark and cut gland plate holes precisely according to the size and arrangement of the cables.
- Make sure that cable glands are properly sealed and grounded when you install them.
- To ensure the safety and integrity of the enclosure, cover any unused gland plate holes.

5.2 Gland Installation
- Examine cable test results and confirm temporary marks.
- Remove the gland plates from the equipment and prepare for cable insertion.
- Mark and cut holes in gland plates based on cable size and configuration.
- Install cable glands securely to ensure a good seal and grounding.
- Cover unused gland plate holes to keep the enclosure functional.
5.3 Stripping and Cutting of Cable Jackets
- Strip cable jackets to the required length according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Clean the stripped cable surface to ensure proper bonding of seals.
- Maintain proper creepage and clearance distances as per project specifications
5.4 Termination Kit Installation
Follow manufacturer’s instructions carefully for the installation of the termination kit.
- Strip the insulation from the cable cores, clean thoroughly, and crimp the cable lugs securely.
- To ensure reliable protection, use the prescribed insulating and taping methods.
- Install pre-molded modules and check that drain wires are properly secured.
5.5 Splicing Activities
- Prepare cables by cutting and stripping them according to the project schemes.
- Clean the cable ends and insert sleeves as needed.
- Crimping, taping, and insulating should all be done according to normal technique.
- Install protective housing and heat-shrink tubing to ensure outside protection and durability.
Click here to know more about cable schedule
Section 6. Additional Checks for Cable Glanding
- To avoid problems, double-check that the threading on the fittings precisely matches the holes.
- Make sure the cable gland seals are the right size for the cables you’re working with.
- Ensure the cable glands grip the cables securely, so they stay firmly in place without any slipping.
- Verify that the cable armour is properly earthed to prevent any electrical hazards.
- For general safety, remember to make sure the gland is properly earthed.

Section 7. Cable Termination and Identification
- To make sure everything is wired correctly, carefully complete all cable terminations in accordance with the cable schedule or internal wiring diagrams.
- To facilitate identification and troubleshooting in the future, make sure each conductor has a distinct identification tag at the termination points.
Section 8. Bending Radius of the Cable
- Keep a close eye on the cables’ bending radius. To prevent damage or problems with performance, make sure they are well within the designated limits and are not bending too tightly.
Refer the below link for the Instrumentation Cable and Wiring Inspection Procedure: Essential checklist for Project Engineers
Section 9. QC Inspection
In order to guarantee adherence to project standards, quality control is crucial. The requirements for a QC inspection are outlined in the steps below:
- Examine cables physically for any flaws or damage.
- Check that glanding, splicing, and termination are done correctly in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Verify the color coding, phasing, and identification of the cables.
- Verify that the right clamping and termination accessories are being used.
- Prior to the final client inspection, work with QA/QC staff to arrange internal inspections.
Section 10. Testing and Pre-Commissioning of Cable
To confirm the reliability and practicality of cable installations, testing is essential:
- Continuity Check: To ensure correct connections, confirm that the cables are continuous.
- Insulation Resistance: To ensure adherence to project standards, measure insulating resistance with calibrated equipment.
- Hi-Pot Testing: When necessary, do high-voltage testing to guarantee worker safety and accurate equipment calibration.
- Keep track of every test result and confirm that it satisfies the project acceptance requirements.
Section 11. Final Documentation
Keep thorough records of every action and examination:
- Send inspection records and test results to the QA/QC division.
- Verify that the client and contractor representatives have approved all paperwork.
- As-built drawings should be updated and maintained to reflect current installation conditions.
- For project handover, compile a complete dossier of records.

Section 12. Required Spares for cable glanding
Make sure the following components are available for cable termination and glanding:
- Shrouds and cable glands
- Termination kits (pre-molded modules, heat shrink, etc.)
- Ferrules and cable lugs
- Sealing compounds and insulation tapes
- Accessories for earthing
Section 13. Safety Monitoring and Final Housekeeping
- Organize frequent safety briefings and toolbox talks.
- Check that safety regulations are being followed in the work zones.
- Make sure that tools and electrical equipment are stored properly.
- Keep your workspace tidy and secure by practicing housekeeping.
Cable Glanding & Termination Excel Checklist for Download
For electrical and instrumentation projects, our thorough checklist provides cable glanding and termination that is safe, effective, and of high quality. It includes sections for quality control, documentation, and safety.

Refer the below link to Download Checklist
Click here for 50+Collection of Essential Instrumentation and Automation Control System Checklists
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to cable glanding and termination
What are the steps for cable glanding?
- Choose a gland that is appropriate for the size and type of cable.
- To get the desired length, remove the cable jacket.
- Make sure the sealing components are positioned correctly before inserting the cable into the gland body.
- For a good seal, adjust the sealing elements.
- Tighten the locknut to secure the gland.
- To make sure the gland is securely fastened and sealed, tighten it one last time.
- Make sure the cable is held in place and the gland is firmly fastened.
- Make sure the gland is functioning properly by conducting the required tests.
What are the steps for cable termination?
- Prepare the Cable End: Make a straight cut at the cable termination.
- Place the Connector Ferrule: Slide the connector ferrule onto the cable end.
- Strip the Cable: Use a stripping tool to remove insulation and expose the conductors.
- Insert the Cable into the Stripper: Rotate the stripper 3 to 5 full turns to strip the desired amount.
- Crimp the Connector: Use a crimping tool to secure the connector to the conductor.
- Inspect the Termination: Ensure the connection is solid and the insulation is intact.
- Test the Connection: Perform tests to verify the termination is correct and secure.

What is the difference between cable glanding and termination?
Cable glanding is the technique of using a cable gland to secure the cable entry point in order to ground, seal, and relieve tension.
Cable Termination: To ensure correct electrical connectivity, termination entails attaching the cable conductors to devices or connectors.
What are cable termination standards?
Cable termination standards specify how the wires in a cable should be connected at both ends. Especially in networking and telecommunications infrastructure, these standards ensure consistency and compatibility in cabling systems. T568A and T568B are common standards for copper cables.
What is the minimum distance between cable glands?
Cable glands should generally be spaced at least 5 mm apart, or half the size of the bigger gland, whichever is larger. This provides enough space for appropriate setup and maintenance.
Which tool is used for cable termination?
For terminating cables, the UR/UY/UG connection crimper is frequently utilized. By crimping the connectors to the conductors, this instrument ensures secure connections.





