Table of Contents
- What is Multimeter?
- What do these Counts & Digits mean?
- Multimeter Digits
- A 6 ½ Digit Multimeter Display
- A 7 ½ Digit Multimeter Display
- An 8 ½ Digit Multimeter Display
- Multimeter Counts
- What is the Accuracy of a Digital Multimeter?
- How do Digital Multi Meters provide consistent readings?
- What is meant by Resolution in measurement?
- What is the Range of a multimeter?
- What is the difference between Counts & Digits?
- People also ask
What is Multimeter?

- A multimeter is a digital device that measures voltage, amps, and resistance across circuits by joining two contacts to various parts of an electrical system.
- A multimeter is more than one thing. A multi-range DC voltmeter, multi-range AC voltmeter, multi-range ammeter, and multi-range ohmmeter are all combined in one instrument. It is completely filled with all the components required for this arrangement.
- Multi-meters can be used by technicians to identify levels of voltage and resistance, as well as changes in electrical currents.
- Since these Digital multimeter used for measurement comes in various makes and models.
- A multimeter is 3 & ½, 4 & ½, 6 & ½, 7& ½ digits or 2k, 4k, or 6k counts.
- Generally, the accuracy of the Multimeter is ‘0.15% + 2 digits
- But, the two main factors Multimeter Digits and Counts make more noise in selecting a multimeter for our application.
What do these Counts & Digits mean?
- Counts and digits are two distinct methods of expressing the same thing.
- Counts and digits are synonyms for describing the resolution of a digital multimeter.
- Today, total counts are more commonly used to categorize digital multi meters than digits.
- The resolution of a digital multimeter is also specified in counts.
Multimeter Digits
- Consider 3 ½ digit Multimeter.
- This format is expressed as a whole number followed by a fraction of ½ or a ¾.
- The whole number defines actual digits displayed from 0 to 9.
- The fraction is ½ or ¾.
- Fraction ½ defines MSD for each range maybe 0 or 1.
- A ¾ means the MSD for each range is greater than 1.
- A 3 ½ Digital Multimeter displays three full digits and one-half digits.
- Three full digits include any numbers from 0 to 9, and one ½ digit can have only 0 or 1.
- In the 3 ½ Digital Multimeter, the three-digit position displays 0 to 9 numbers, and the leftmost position can only display 0 or 1.
- Similarly for other types of Digital Multimeter like 4 ½, 6 ½, 7 ½, & 8 ½, the Four, Six, Seven, & Eight positions display complete 0 to 9 numbers, & the leftmost position or ½ position displays only 0 or 1 number.
- The schematic of various DMM is shown below.
A 6 ½ Digit Multimeter Display

A 7 ½ Digit Multimeter Display

An 8 ½ Digit Multimeter Display

Multimeter Counts
3 ½ Digit Multimeter
Here, this 3 ½ Digital multi-meter display has 2000 counts, It indicates a digital value from 0000 to 1999 counts.
4 ½ Digit Multimeter
- Here, this 4 ½ Digital multi-meter display has 20000 counts. It indicates a digital value from 00000 to 19999 counts.
- Therefore, advanced Multi-meters do not have a restriction of 0 or 1 at the left most digits
Example: Practically it is easy to define or specify a Multimeter by its counts rather than digits.
- If the Multimeter display has 4000 counts. It indicates a digital value from 0000 to 3999 counts.
- A count informs us what the instrument will display before it changes to the next range.
- A multimeter can read 19.999 V instead of 20.0V having a count value of 20000.
- But, this multimeter displays 020.00 V instead or simply 20.00 V.
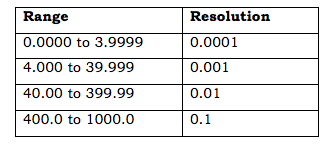
- The range and resolution values for DMM are intended to measure 1000V with a count of 40k
What is the Accuracy of a Digital Multimeter?
- The accuracy of DMM is characterized as the highest acceptable error occurring under particular circumstances of operation.
- It’s represented by a percentage and informs us how comparable the displayed measurement is to the exact (standard) value of the measured signal.
- Accuracy necessitates a comparison to an industry standard.
- Depending on the application, the accuracy of a digital multimeter is essential.
- Most AC power cable voltages may vary around 5% or more.
- A voltage measurement considered at a standard 115 V AC receptacle is an example of this model.
- A digital multimeter with measurement accuracy of 3% is appropriate if a digital multimeter is only used to check if a receptacle is energized.
- Higher accuracy may be required for some applications, such as the calibration of automotive, medical aerospace, or specific industrial equipment.
- A digital multimeter reading of 100.0 V with a 2% accuracy can vary from 98.0 V to 102.0 V.
- This holds good only for some applications, but these are not good for sensitive electronic equipment.
- Accuracy can also involve the inclusion of a specified amount of digits (counts) in the basic accuracy rating.
- For example, a (2%+2) accuracy means that a reading of 100.0 V on a multimeter can range between 97.8 V and 102.2 V.
- The use of a higher-accuracy digital multimeter opens up a wide range of possibilities.
- Fluke handheld digital multimeter have basic dc accuracy ranging from 0.5% to 0.025%.
How do Digital Multi Meters provide consistent readings?
- Precision is an ability of a digital multimeter to deliver an identical measurement again and again.
- The arrangement of holes on a shooting range target is a typical method used to describe precision.
- This example defines that a rifle is directed towards the target’s bulls-eye and fired from the same position every time.
- If the holes are close together yet separate from the bulls-eye, the rifle is said to be precise but not accurate.
- The rifle is said to be more accurate and precise if the holes are tightly packed within the bulls-eye.
- It is neither accurate nor precise if the holes are distributed randomly across the target).
- Precision, or repeatability, is much more significant than accuracy in some situations.
- When measurements can be replicated, an error pattern could be recognized and rectified.
What is meant by Resolution in measurement?
- Resolution is the minimum increment that can detect and display.
- Consider two rulers as an example of a nonelectrical case.
- One with 1/16-inch hatch marks has better resolution compared to the one with quarter-inch hatch marks.
- Consider testing simple 1.5 V household batteries.
- If the resolution of DMM is 1 mV in the 3 V range, it is easy to see a change of 1 mV at the time of voltage reading.
- The user visualizes small changes like 0.001 at the 3 V range.
- Reducing the digital multimeter range setting improves resolution as long as the measurement is within the set range.
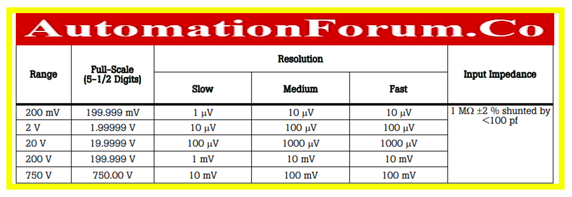
What is the Range of a multimeter?
- Digital multimeter range and resolution are linked to each other and specified in their specifications.
- The majority of DMM available in the market come with an auto-range function to select the appropriate range that depends on the magnitude of the measurement.
- This provides the most accurate measurement resolution as well as meaningful reading.
- The multimeter will display OL if the measurement exceeds the specified range (overload).
- Without burdening the multimeter, the most accurate measurement is obtained at the lowest possible range setting.
What is the difference between Counts & Digits?
- Counts and digits are terms used to describe the resolution of a digital multimeter.
- Digital multimeters are classified based on total counts rather than digits.
Counts
- The resolution of a digital multimeter is also specified in counts.
- For some measurements, higher counts provide better resolution.
Digits
- The Fluke product line includes digital multimeter with 3 ½ and 4 ½ digits.
- A 3 ½ digit digital multimeter displays three full digits and half digits for a number ranging from 0 to 9.
- The half digit is regarded as the MSB.
People also ask
What do a number of counts mean on a multimeter?
Count on DMM represents the highest displayed value
What does 4000 count display mean?40
- 4000 counts:
- Counts represent the resolution of DMM.
- 4000 counts mean DMM can display 4000 different values within a range, like 0 to 3999
What is a 50000 count multimeter?
- If DMM is having 50000 counts, it means the range varies when it reaches a value of 50000 on display
- Like a 50000 count DMM displays 49.999 V instead of 50 V or 50.00 V





