- Various types of Treatment Plants for Water used across industries
- What is Water Treatment Plant (WTP)?
- Role of RO in WTPs
- Operations linked to WTPs
- What are three types of Water Treatment?
- What is an Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)?
- Operations linked to Effluent Treatment Plant
- What is Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)?
- Operations linked to Sewage Treatment Plant
- What is Sewage?
- What is Effluent?
- What is TDS in Water?
- What are the four types of Sewage Water Treatment?
- How Does Effluent Treatment Plant Work?
- How Does Sewage Treatment Plant Work?
- Difference between WTP STP and ETP
- Difference between Sewage and Effluent
Various types of Treatment Plants for Water used across industries
Basically, in every power plant and process industry we come across terms WTP, ETP and STP.
There are three types of treatment plants
- Water Treatment Plants (WTP),
- Effluent Treatment plants (ETP), and
- Sewage Treatment Plants (STP).
In this post, we will study what are WTP, ETP, and STP plants. And difference between these plants.
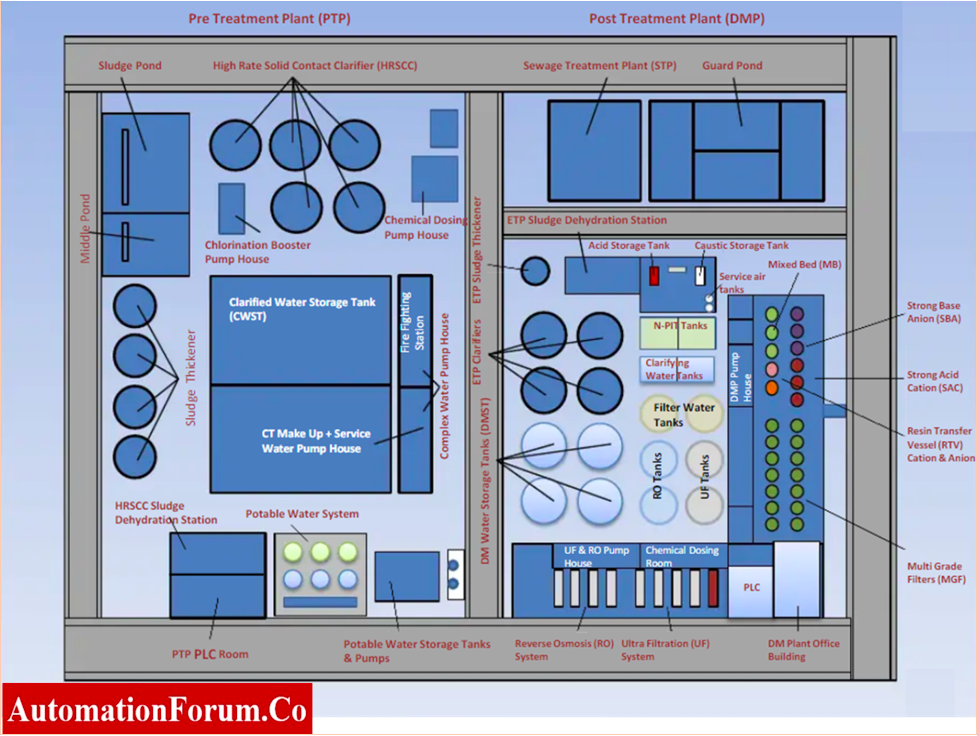
What is Water Treatment Plant (WTP)?
- In WTP bad water or hard water is purified into usable soft water for various purpose.
- This treated water is called de-mineralized water and can be used as raw water in power plants for preparing steam.
- The final product of WTP is De-mineralized filtered water that can be used for domestic or industrial purposes as boiler feed water.
- These WTP plants are commonly used in almost every industry to obtain pure water with quality.
- When contaminants or some substances are mixed then the physical and chemical properties of the water change and become harmful to use. so treatment of this water is very essential before consumption.
- Generally, a water filter installed in the home is also a type of water treatment plant.
- This filter unit purifies the water from a bore well, or river water to usable water in small quantities.
- But, the same principle is used in Water Treatment Plants (WTP) installed in a power plant or in process industries
- Here the quality of filtration is the same as in a home unit with a huge quantity of de-mineralized water.
- The main task of these WTP is to produce 100% usable water for drinking and other purposes.
- These plants consist of various processes like ultra-filtration, with the use of multiple filters such as softener, activated carbon, multi-graded, RO, ultraviolet lamp usage, electro deionization to treat wastewater coming from various sources to produce pure water for domestic and industrial use.
- Compared to ETP & STP, WTP doesn’t have much rough or hard water at the input side for the filtration process.
- But the main task of WTP is to provide clean water with 100 % purity potable for domestic and industrial use.
Role of RO in WTPs
- RO (Reverse Osmosis) unit is the main component in the treatment
- WTP plant becomes effective with these filtration processes.
- This provides purity of about 95% to 99% through its membranes and discharges the remaining dissolved salt in the reject line for drainage.
Operations linked to WTPs
- WTP treats incoming rough water and produces pure and clean water
- Ultra-filtration method uses various filters such as softener, activated carbon, multi-graded,
- RO and UV method uses an electro-deionization technique.
What are three types of Water Treatment?
Generally, in all power plants and in process industries we come across three types of treatment plants.
- Water Treatment Plant (WTP),
- Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) and
- Sewage Treatment Plant (STP).
But, all three treatment plants have worked for the purpose of treating waste or raw water into reusable water.
What is an Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)?
- Effluent is processed wastewater coming from industries and factories.
- It contains harmful chemicals and toxic and non-toxic materials in it.
- Before draining wastewater into sewers, every industry must have an effluent treatment plant.
- It is against the safety norms of the pollution board for discharging wastewater into the drain without filtering it.
- The chemicals mixed through coagulation, and precipitation breaks solid and chemical waste.
- This Effluent Treatment Plant saves industries and the environment from being polluted by using final filtered water.
Operations linked to Effluent Treatment Plant
This Effluent Treatment Plant treats wastewater includes various operations such as screening, sedimentation, clarification, centrifuging, and evaporation with drying methods, and so on.
What is Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)?
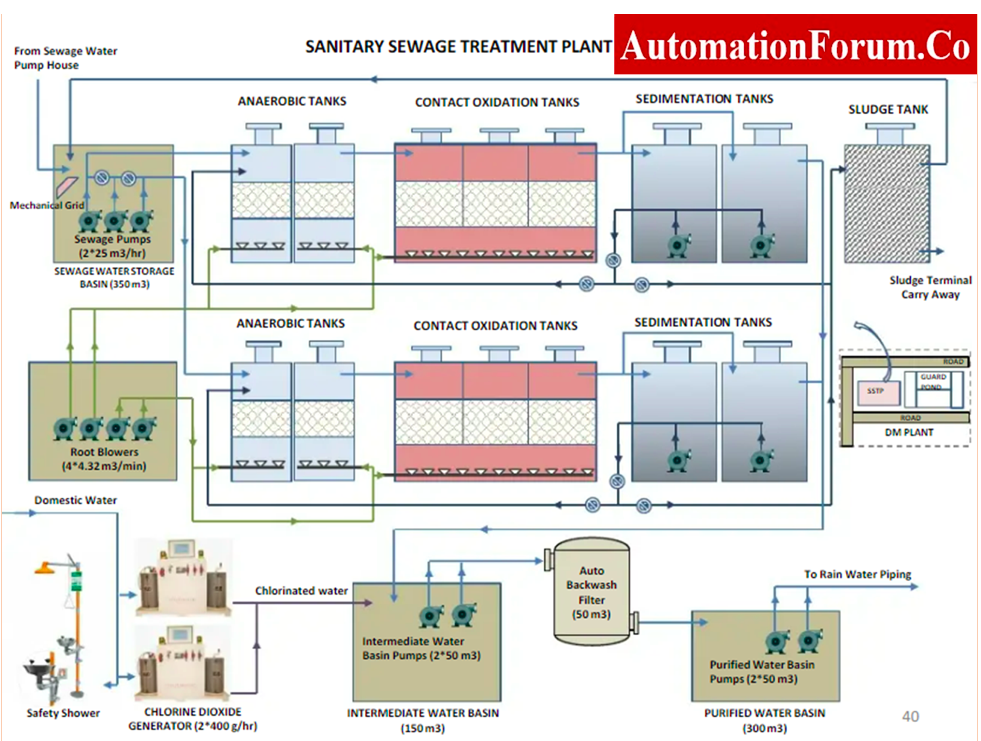
- Sewage is the household, domestic and commercial wastewater outlet.
- Sewage contains excreta of humans, animals, rainwater, and debris from sewers in them.
- It consists of a maximum number of solid waste materials in it and is more harmful to human use.
- The final output may not be 100% usable, but it is enough to drain it into disposal waste and also, use it for some content for other processes.
Operations linked to Sewage Treatment Plant
This Sewage Treatment Plant treats wastewater and includes various operations such as screening, sedimentation, scrapping, aerobic biology, fixed-film or suspended growth treatment, air blowers, etc. to treat wastewater.
What is Sewage?
- Sewage is defined as liquid or solid waste products suspended within the water.
- Sewage contains excreta from humans, and animals, a mixture of both toxic and chemical materials, and so on.
What is Effluent?
- Effluent is defined as industrial discharge
- The effluent contains waste outlets from various factories and process industries.
- Industrial effluents are some things that flow out like rivers or lakes.
- Effluent consists of harmful, non-toxic, and poisonous materials that are very dangerous to living beings.
- Generally, this effluent is totally different from Sewage because the effluent is industrial or process waste discharge, Sewage is daily household waste products such as toilet outlets, baths, other waste discharge, and so on.
What is TDS in Water?
- In water, the term TDS is a short form of Total Dissolved Solids commonly known.
- The term TDS in water describes the small number of inorganic salts & organic matter present in it.
- The main ingredients of water are magnesium, calcium, chloride, sulfate, sodium, carbonate, hydrogen-carbonate potassium cations (positively charged ions), & nitrate anions (negatively charged ions).
What are the four types of Sewage Water Treatment?
Four types of Sewage Water Treatments
1.Physical Treatment: In physical treatment the separation or removal of particulate solid matter and external particulate in industrial and sanitary wastewater effluents.
2.Chemical Treatment: In chemical wastewater treatment the dissolved contaminants are forced to separate easily by the addition of specific substances by precipitation. The chemical treatment method uses four main types of chemicals such as
- Anti-foaming agents
- pH neutralizers,
- Coagulants.
- Flocculants.
3.Biological Treatment: These systems are a minute part of a large process to treat wastes by using bacteria to break them into sludge.
4.Sludge Treatment: This defines the treatment processes to manage, & dispose of sewage sludge generated. The main intention of this treatment is to reduce sludge weight and volume to minimize transportation and disposal costs.
How Does Effluent Treatment Plant Work?
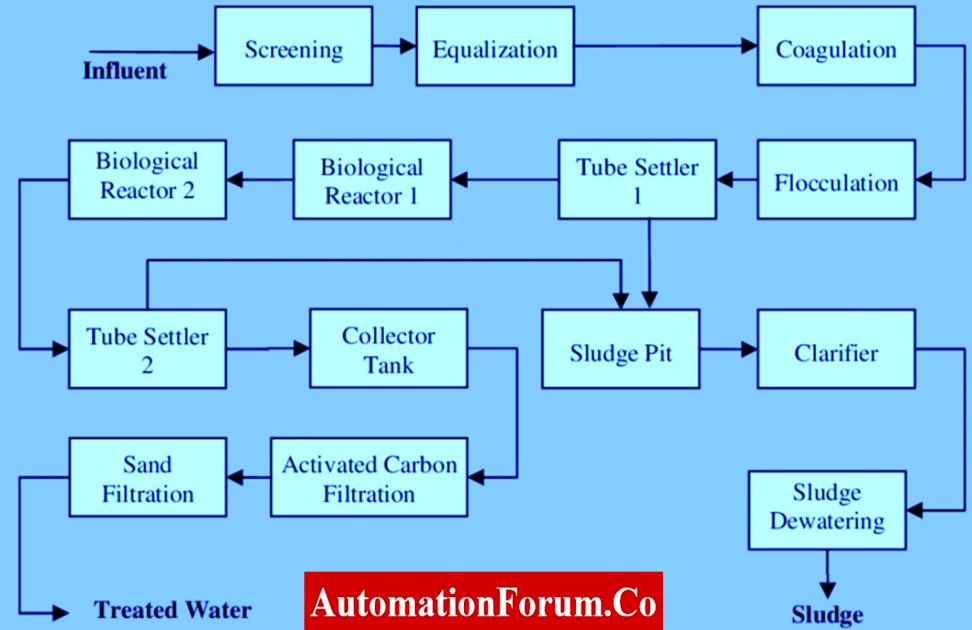
- Effluent treatment plant works in several phases to eliminate impurities from industrial wastewater.
- They screen out solid waste and dust particles and sterilize and purify the water on a molecular level.
- This treated water can be released to water bodies without disturbing the ecological balance.
- The working of an Effluent treatment plant is categorized into two stages.
1. Primary Stage:
- Here maximum amount of solid and visible waste is removed.
- The dust and debris are also removed in this stage only.
- Solid waste from the effluent is removed by screening.
- Some coagulants are used for contaminants to get clumped and sink to the bottom of the tank so that water is easily separated.
- Waste water is added to a tank to increase the growth of bacteria so that a bacterium breaks the contaminants easily.
2.Secondary Stage
- Here water is finely cleaned. Some activated carbons are added to capture harmful chemicals and heavy metals.
- Chlorine and UV rays are frequently used to sterilize wastewater.
- Most plants prefer only ultraviolet rays to reduce the cost of chlorine.
- In case chlorine is used, the wastewater is required to pass through carbon filters to pull out excess amounts from the water.
- RO- filters might also be used to get free from molecules larger than water molecule to make the water pure.
- After this stage, the water is considered safe to be released into the environment.
- In effluent treatment plants machinery equipment must be maintained and kept clean to achieve higher purity of treated water.
How Does Sewage Treatment Plant Work?
- A sewage treatment plant separates waste from the sewage and turns it into safe water.
- Sewage treatment plants break the organic waste contents present in the sewage to make clean water.
- This water is treated to a level safe to release into the environment.
- This treatment plant deals with a huge amount of sewage.
- The sewage treatment process works in three different stages.
1.First Stage
- Here sewage is kept in a tank for an extended period.
- Here, the solid presence in the sewage sinks at the bottom of the tank and the wastewater liquid gets separated.
2. Second Stage
- Here separated water is stored in the tank to allow ample airflow.
- This ample airflow allows for the growth of bacteria that is capable of the quick breakdown of the waste in the water.
- At this stage, water is almost nearly safe to release into the environment since water is separated fully by the bacteria.
3. Third Stage
- It is the last stage of a sewage treatment plant here the waste water is screened to separate the remaining solids present in the waste water.
- After this third stage, the water is safe to release into the water body.
- The sewage will not burden the environment and bodies if treatment is perfectly done at all stages.
Difference between WTP STP and ETP
| WTTP | ETP | STP |
|---|---|---|
| Acronym Stands for water Treatment Plant | Acronym Stands for Effluent Treatment Plant | Acronym Stands for Sewage Treatment Plant |
| Treats raw water from various water sources such as rivers, ponds, bore wells suitable for use in boiler | Treats effluent from industrial waste water such as chemical or organic waste. | Treats sewage produced by process industries, large extension Areas, Hotels, Hospitals & Commercial Buildings. |
| Includes Ultra-filtration, Activated Carbon Filter, & Reverse Osmosis (RO) to remove hard mineral content present in water. | It consists of physical, chemical, and biological processes to eliminate contamination present in it. | Includes membrane bioreactor technology for micro and Nano-filtration with biological wastewater treatment process. |
| Typically used in all power plants | Typically used in industries such as pharmaceutical, automobile, food processing industry, and so on. | Used by Hotelier, Industrialist, Large Apartment and so on. |
Difference between Sewage and Effluent
| SEWAGE | EFFLUENT |
|---|---|
| Sewage is the domestic waste produced by people community | Effluent is the industrial or business processes waste material discharged to a river body. |
| Sewage is carried by drains & pipes. | Effluent is totally different from daily household waste products. |
| Sewage is a mixture of chemical and toxic materials. | Effluent is defined as something different from our daily waste like toilets, baths, and so on. |
| Sewage is water and excrement. The piping system used to convey the sewage is called sewerage | Effluent is a word applied to industrial waste or sewage. Sewage becomes influential when it enters the local treatment system. Once treated it is again an effluent. |





