What is a Pump?
A pump is a device that is used to transfer liquids, gases, or slurries. It enhances the fluid’s mechanical energy. The excess energy can be put to good use by increasing:
- Pressure
- Elevation
- Velocity
To know more about Pump CLICK HERE
Classification of Pumps:
Pumps are classified into two major categories, they are:
- Positive Displacement Pump and
- Dynamic Pump
Positive Displacement Pump:
Against the system’s resistance, the positive displacement pump forces particular volumes of liquid to be displaced. The pump delivery pressure is directly affected by the system resistance, which will continue to rise until the delivery pressure equals the system or the driver or pump is overloaded. As a result, relief valves must be installed in the pump or immediately after the pump in the delivery line to offer the necessary protection.
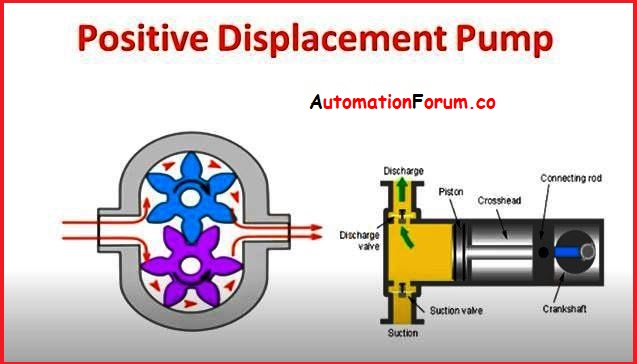
The flow rate is theoretically dependent on the pump speed and shape due to the forcible displacement of certain volumes. In actuality, there is always leakage between the moving and stationary wetted components due to the necessary clearances. When a result, the head capacity curve is a nearly flat line with a minor capacity drop as differential pressure or head rise increases.

Uses of Positive Displacement Pump:
1.It is capable of handling shear sensitive liquids.
2.Use for applications requiring a lot of pressure.
3.Use for applications requiring varying viscosity.
Positive displacement pumps come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Depending on their construction, they fall into one of two types:
1. Rotary Pump
2. Reciprocating Pump
Rotary Pump:
Rotary pumps transfer liquid by a rotating mechanism (gear, lobe, or vane) inside a rigid container. Pumping rates vary depending on the rotor’s rotational speed.When compared to reciprocating pumps of the same weight, the rotary pump can pump more fluid. Regardless of the resistance the pump is pushing against, a fixed volume of fluid is moved. However, any blockage in the system might rapidly harm the pump or cause the system to fail. A relief valve is required for rotary pumps to safeguard the pump and piping system. At a preset pressure, the relief valve raises and returns the system liquid to the suction side of the pump, the supply tank, or the sump. They are, in essence, self-priming.The chamber in rotary pumps moves from inlet to discharge and back to inlet.
- Gear pumps,
- Lobe pumps,
- Screw pumps,
- Sludge pumps, and
- Vane pumps
are among the many types of rotary pumps available.
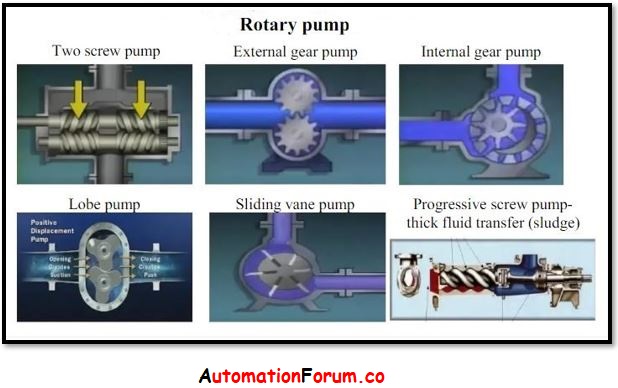
Rotary pump is further classified into two different types based on the rotor as:
- Single rotor rotary pump and
- Multiple rotor rotary pump
Uses of Rotary Pump:
- The automotive industry is the most common user of rotary vane pumps. This sort of pump is used in a variety of sections of the car, including braking, power steering, automatic transmission, and supercharging.
- Rotary vane pumps are also used in the systems of various other types of vehicles, such as aeroplanes.
- Espresso and soft drink distribution equipment, as well as some air conditioning units, employ this sort of pump.
- As it is a form of vacuum pump, the rotary vane pump can be used in both industrial and laboratory environments.
- The most typically pumped fluids are gas, oil, and water.
Reciprocating Pump:
The Reciprocating Pump is a Positive Displacement pump that operates on the principle of the piston moving forward and backward. It’s a device that transforms mechanical to hydraulic energy. When a specified amount of fluid ex: sump needs to be transferred from the lowest to the highest location by applying pressure, reciprocating pumps are used. Reciprocating pumps transfer liquids by altering the pump’s internal volume. On both the suction and discharge sides, valves are required. Pumping rates were changed by altering the number of strokes per minute or the duration of each stroke.
The Reciprocating Pump are further classified into 3 types, they are:
- Diaphragm pump,
- Piston pump and
- Plunger pump
Diaphragm Pump:
A diaphragm pump is a positive displacement pump that employs a combination of reciprocating action and either a flapper valve or a ball valve to transfer liquids. It can be hydraulically or mechanically activated.Self-priming diaphragm pumps are good for thick liquids. Diaphragm pumps generate liquid flow by moving a cupped, elastic surface up and down. The pump surface is usually constructed of polytetrafluoroethylene, Teflon, synthetic rubber, or some comparable material.
- Membrane pump,
- Air operated double diaphragm pump,
- Pneumatic diaphragm pump
are the type of diaphragm pump.
Uses of Diaphragm Pump:
- Diaphragm pumps are used to transport abrasive fluids like concrete, as well as acids and chemicals.
- They’re also used in cars and aeroplanes.

Piston Pump:
A piston pump is a pump that uses a piston to move fluid from one location to another. It is a well-known reciprocating pump. The piston of this pump travels up and down in the compression cylinder. This piston is attached to a crankshaft, which is driven by an electric motor and receives power from it.
Inlet and output check valves, connecting rods, a crankshaft, and a piston are all part of the piston pump.
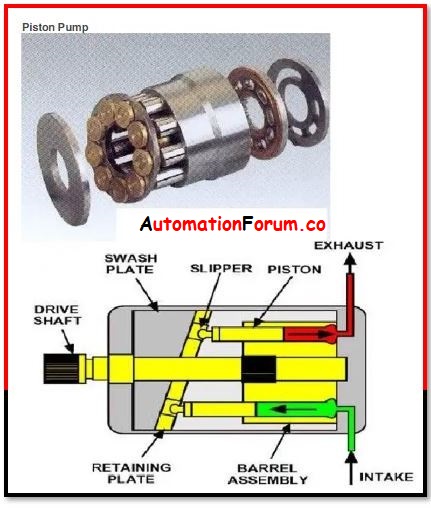
Uses of Piston Pump:
- Piston pumps are used to manage extremely low flow rates at high pressure.
- These pumps are used to convey fluids with a high viscosity.
- They used to be in charge of pumping hydraulic oil.
- High-pressure cleaning is also done using the piston pump.
- Pumps like these are used in industrial processing equipment.
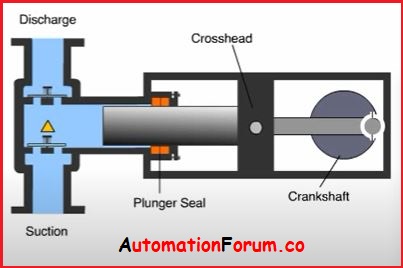
Plunger Pump:
A plunger pump is a positive displacement pump with a stationary high-pressure seal and a smooth cylindrical plunger that moves through it. This distinguishes them from piston pumps and enables them to operate at higher pressures.
The plunger pump does not move with the piston, but the stuffing box has a fixed seal. The suction valve is opened by a retracting plunger that provides a suction effect in the liquid end. The liquid end receives the medium. After that, the plunger travels forward. The plunger increases the pressure of the fluid to be pumped by displacing the available volume through its own volume. The suction valve closes and the pressure valve opens, allowing the pressured fluid to enter the process area.
Dynamic Pump:
The dynamic pump is a form of velocity pump that uses increased flow velocity to impart kinetic energy to the fluid. When the velocity of the flow is lowered prior to or as it exits the pump into the discharge pipe, this increase in energy is transformed to a gain in potential energy (pressure).The First Law of Thermodynamics, or more precisely Bernoulli’s principle, explains this conversion of kinetic energy to pressure. It is classified into two types. They are:
- Centrifugal Pump and
- Axial Pump
Centrifugal Pump:
Centrifugal pumps are the most prevalent type of pump now in use. Centrifugal pumps are widely utilised due to their design simplicity, high efficiency, wide range of capacity and head, smooth flow rate, and ease of operation and maintenance, and come in a variety of configurations.
One or more impellers are attached to and revolve with the pump shaft in centrifugal pumps. This gives the liquid the energy to flow through the pump and pressurise it so it can move through the piping system. As a result, the pump transforms mechanical energy from a motor into fluid energy. Some of the energy is converted to kinetic energy, which is represented by fluid pressure, and some is converted to potential energy, which is represented by raising the fluid against gravity to a greater height.
The energy transfer from the impeller’s mechanical rotation to the fluid’s velocity and pressure is commonly defined in terms of centrifugal force. The centripetal force is applied by a pressure that is reflected in the outlet pressure.

Uses of Centrifugal Pump:
- When large flow rates and moderate head increases are required, centrifugal pumps are typically used.
- Fluids with suspended particles can be handled by centrifugal pumps.
Axial Pump:
Axial pumps use a motor-driven rotor to guide flow in a direction parallel to the pump’s axis. As a result, the fluid travels in a reasonably straight path from the entrance pipe to the output pipe. In turbo-jet engines, axial pumps are commonly utilised as blowers. Axial pumps are more efficient than centrifugal pumps for this application. Axial pumps have alternating rows of rotors and blades that are stationary. As air passes through the axial pump, pressure rises due to the blades and rotors. The compressed air then exits the pump at a high pressure.

Uses of Axial Pump:
For large volume flows and small delivery heads, axial pumps are used. The following are some examples of typical application areas:
- Irrigation
- Plants for Sewage Treatment
- Pumps for Cooling Water
- Drainage Methodologies





