- What is a MODBUS?
- How does a MODBUS work?
- What are the major types of MODBUS which is used for industrial communication?
- What is the major difference between the MODBUS TCP and MODBUS RTU?
- What are the advantages of MODBUS?
- How should we connect MODBUS devices together in a network?
- What is RS 232, RS 422, and RS 485 and what is their difference?
- Explain MODBUS Map?
- What are the Advantages of Modbus TCP/IP over RTU?
- Why Modbus is combined with Ethernet?
- What are the advantages of RTU?
- What are the MODBUS TCP/IP devices and MODBUS RTU devices?
What is a MODBUS?
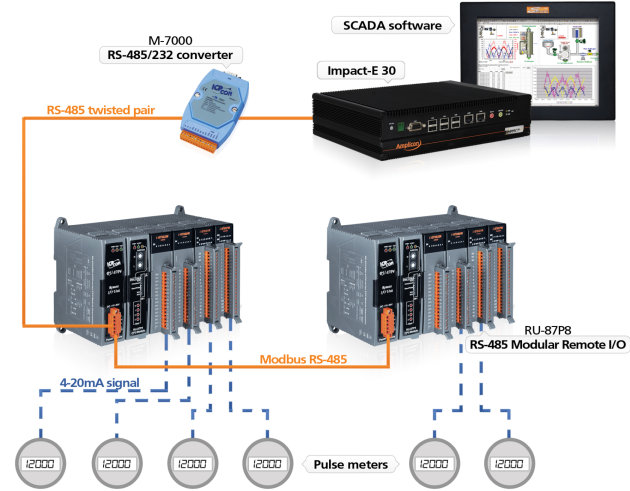
MODBUS is a communication protocol that is used for many industrial applications. This communication protocol can be used to do the data transfer between the process control equipment and the HMI. MODBUS was developed by MODICON to communicate with industrial electronic devices such as PLC, PAC, or DCS over a twisted pair of wires. MODBUS is an application layer protocol that is based on master/slave or request/reply architecture. MODBUS was openly published so there is no need to pay a royalty fee to use it.
How does a MODBUS work?
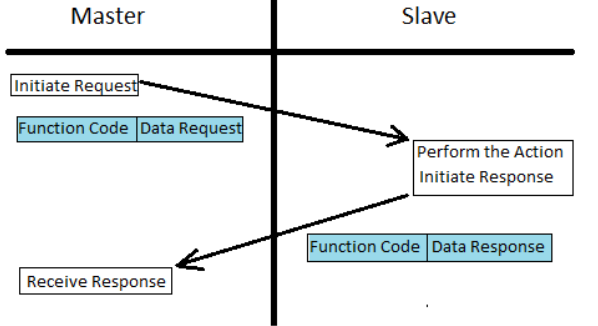
The devices which use MODBUS would communicate in a master/slave arrangement. In this type of communication, the master would communicate with one or multiple slaves. Mostly the master would be a PLC, PC, DCS, PAC, or RTU. The slaves are mostly the field devices, so in this configuration, the master would request to read or write a value. These values could be analog or digital, the slaves would respond to this request by giving the data to the master or by taking the action which is required. In case the slaves or Fieldbus wasn’t able to perform the requested action then the slave would create an error message and it would be transmitted to the master.
What are the major types of MODBUS which is used for industrial communication?
MODBUS ASCII
This is a type of MODBUS communication protocol that uses ASCII characters to do serial communication. This type of communication protocol is the slowest but it can be used when telephone modem or radio links are used. The major advantage of this protocol is that it utilizes characters to delimit the message. So due to this if there is any delay in the transmitting medium then there won’t be any misconceiving of the message by the receiving device.
MODBUS RTU (serial RS232, or RS485 networks)
This type is for serial communication, in this type the data would be coded in binary and it would only require one communication byte per data byte. This is the most widely used industrial protocol.
MODBUS TCP

This is simply the MODBUS over Ethernet, in this type of communication it won’t use device address for communication instead of that it would use IP addresses. In this communication, the Modbus data would be encapsulated inside the TCP/IP packet. So if any Ethernet network with TCP/IP would support the MODBUS TCP.
What is the major difference between the MODBUS TCP and MODBUS RTU?
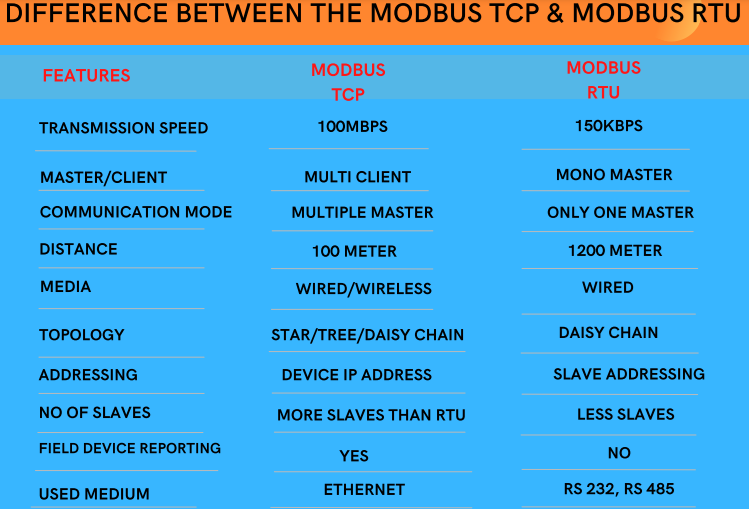
Modbus RTU + TCP/IP layer = Modbus TCP
What are the advantages of MODBUS?
- It can run on all of the communication media such as twisted paired wires, wireless, fiber optics, Ethernet, telephone modems, etc. So due to this feature of MODBUS, it can be used for industrial communications.
- Simple and rugged protocol
- It would allow the communication between several devices which is connected to the same network
- We can use the MODBUS to connect a supervisory computer to the RTU
How should we connect MODBUS devices together in a network?
In order to create a network the devices must use a multidrop network and each slave must have a unique address. Certain instruments use electrically isolated 2 wire RS485 interface while we can also use older instruments in 4-wire (RS422/ RS 485) mode.
What is RS 232, RS 422, and RS 485 and what is their difference?
These are the standards that are used to do serial communications. All these standards would define the wiring, signal levels, transmission baud rates, and parity checking.
RS 232 – It can be only used for one master and one slave communication and its wiring distance would be 15m they are also sensitive to the error which is created by the electrical noise
RS 422 – In this type the master can be connected up to 10 slaves using 4 wires (full-duplex) to a maximum wiring distance capacity of 1200m.
RS485 – In this type, the master can be communicated up to 32 slaves and it can be done in a two-wire system (half-duplex) or in a four-wire system (full-duplex) to a maximum distance of 1200m.
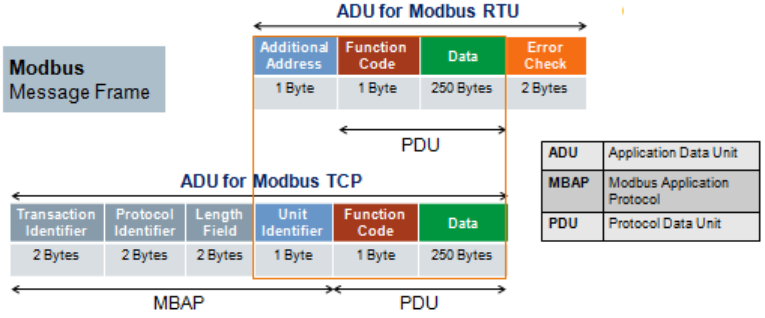
Explain MODBUS Map?
A Modbus Map contains the details of the individual slave device. Such as their data and where the data is stored and how the data is stored.
What are the Advantages of Modbus TCP/IP over RTU?
The major advantage is that in the TCP/IP more than one master can be used while in the RTU it is not possible. The RTU would exchange data in the binary format while the TCP/IP is a MODBUS RTU protocol with the TCP interface that runs on Ethernet. The TCP/IP refers to the transmission control protocol and internet protocol and this would provide the transmission medium for Modbus TCP/IP messaging. This would allow the Modbus TCP to communicate over existing fiber and ethernet networks. The communication speed of the Modbus TCP would be in the gigabit range. The Modbus TCP can have more slaves than the RTU, and it would also allow multiple masters to poll the same slave device simultaneously.
Why Modbus is combined with Ethernet?
Ethernet is a widely used network protocol that has universal worldwide acceptance. It is also an open standard that is supported by many manufacturers and its infrastructure is widely available and also widely installed. The TCP/IP suite of the Ethernet act as a foundation for accessing the world wide web. So many devices support ethernet and it provides fast communication and because of this, it is used in many industrial applications.
What are the advantages of RTU?
- The messages in the RTU is smaller in size and due to this it can exchange more data
- It does a cycle redundancy check to determine if there is an error
- It can achieve higher throughput when compared to ASCII mode
- Reliability
What are the MODBUS TCP/IP devices and MODBUS RTU devices?
Supported Modbus TCP/IP devices
- Modicon 184/384
- Modicon 484
- VersaMaxENiu
- Quantum
- STAT_PLC
Modbus RTU
It is designed to be used with a serial device that supports the RS 232, RS 485, and RS 422 protocols. It is used with the PLC and SCADA





