Basics of Pressure Regulator (Pressure Reducing Valve – PRV)
Self-Operated devices which work off the medium alone
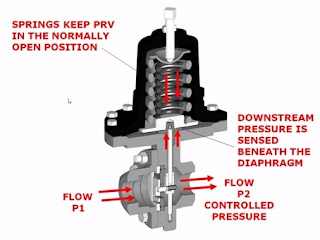
Pressure reducing valve – PRV : Lowers inlet pressure to desired point
How PRV works?
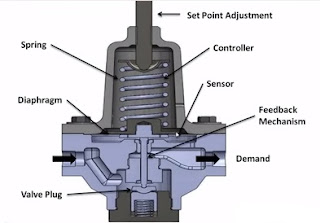
Internal architecture of a Pressure regulator
Basic Characteristics of a pressure regulator is standalone self actuating controllers.
What to expect from a regulator?
1.Accurate regulation
2.Tight shutoff
3.Fast response
4.Minimum maintenance
5.Low noise
6.Low initial cost
Advantages of regulator
No external power is needed to position the valve
No need for separate measuring elements or feedback controllers
Design tend to be simple,providing low cost,high reliability and easy maintainability
Absence of stem packing eliminates external leakage and source of high friction
Regulators are in direct contact with the controlled variable and offer very fast response
Disadvantages of Regulators
The controlled media must be relatively clean and benign as material of constructions are limited
Regulators lose controllability when the pressure drop across the valve becomes small because the media cannot supply enough operating power
Operating points are not constant due to drops
Regulators cannot accommodate anti-noise /cavitation trims
Failure modes fixed
Do not use a regulator when following conditions are there
1.The desired pressure or temperature set point is beyond the range of regulator
2.Process offset cannot be tolerated
3.The pressure drop is extremely small or extremely great
4.A “fail safe” feature is required
5.The system requires control of a multi-variable process
6.Feedback is required
Understand what is Piloted regulator,Advantages and Disadvantages