Table of Contents
What is Diaphragm seal?
Diaphragm seals, also known as chemical seals, are used to measure pressure when the process medium should not come into contact with the measuring instrument’s pressurized components.
Function of Diaphragm seal
A diaphragm seal has two primary tasks:
- Separation of the measuring instrument from the process medium
- Transfer of the pressure to the measuring instrument
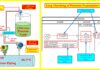
Working principle of Diaphragm seal
- Diaphragm seals, also known as chemical seals or remote seals, are used to measure pressure when the process medium should not come into contact with the measuring instrument’s pressurized components.
- The pressure is transferred by the elastic diaphragm to the fluid from the measured medium and from there to the measuring component, i.e. the measuring instrument or the transmitter.
- In between the diaphragm seal and pressure measuring instrument, a capillary is connected in order (for example) to eliminate or to
minimize temperature effects from the hot fluid to the measuring instrument.

- A closed system is formed by diaphragm seal, capillary and measuring instrument. Therefore, the sealed filling screws on the diaphragm seal and the measuring device must never be opened because the system function is impacted after any filling liquid escape.
- If the diaphragm is leaking, the system fill fluid can enter the medium.
Applications of Diaphragm gauges in liquid conditions
- If the medium is corrosive and the pressure measuring element itself cannot be sufficiently protected against it.
- If the medium is extremely viscous and fibrous, it causes issues in the stress measuring tool owing to dead spaces and constrictions.
- The medium has a tendency towards
crystallisation or polymerisation - If the medium has a very high temperature. As a result, the pressure measuring instrument is strongly heated. The heating leads to a high temperature error in the pressure measurement.