What is meant by Instrumentation?
- Instrumentation is the monitoring and management of various industrial processes through the use of various measuring tools, sensors, and control systems. The type of industry, the process involved, and the degree of control necessary all influence the instrumentation used at various levels of industries.
- The instrumentations are used at various levels of industries is essential for keeping processes under control and ensuring effective and safe operations
- In general, these tools enable businesses to streamline operations, cut expenses, and boost productivity.
How Instrumentation plays a main role in Process Industries?
- Instrumentation is used in the majority of industrial processes to track production line performance as well as chemical, physical, and environmental aspects.
- The pH sensor, chromatograph, infrared analyzer, and refractometer are instruments used to monitor chemical qualities.
- In the industrial world, controlled processes are used to transform, modify, or refine raw materials to produce finished goods.
- During the process, the raw materials will be in liquid, gaseous, or slurry (a mixture of solids and liquids) condition.
List some objectives of Instrumentation in Industries
- Instrumentation is used by industries to produce process.
- To safeguard the safety of the workforce
- To provide a high-quality product
- To increase Profitability
Give some examples of Process Industries
- Various Industries are
- Chemical industry
- Oil and gas industry
- Food and beverage industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Water treatment industry
- Paper & pulp industry
- Power generation industry
What is need of Process Control in Industries?
- All industrial and manufacturing activities revolve around instrumentation and process control. Every process in a manufacturing facility needs to be closely watched and managed in order to move forward in a way that is both safe and optimized.
- Process control aims to automate product production without the involvement of a human operator.
- Process control helps minimize product variability and guarantee a consistent high level of quality.
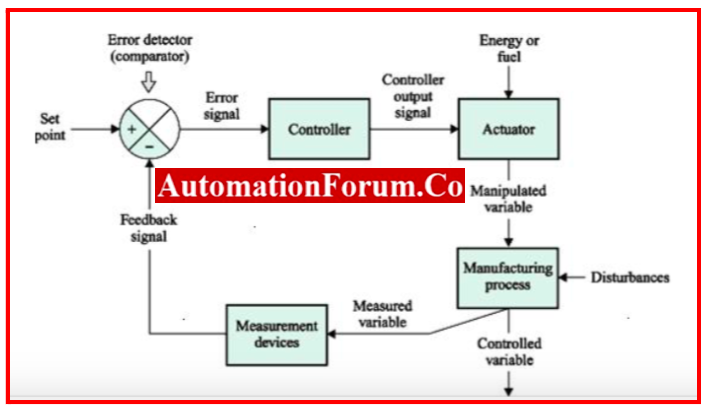
Measurement Device/ Sensor:
- This is the sensor, detector, or transducer that is installed to sense the measured variable and to generate an output signal that indicates the condition of the controlled variable.
Transducer:
- Sensor is also called as transducer. A transducer is device that converts energy from one form into another. Typically, a transducer transforms the measured variable into a measurable electrical signal.
Process Variable:
- The Process variable is the variable that is eventually maintained at a specific set point.As an illustration, consider temperature, pressure, flow rate, level, pH, and humidity.
Energy:
- The manipulated energy is frequently electrical current, steam, water, oil, or gas.
Transmitter:
- “Conditions” the signal from a transducer so that it can be transferred to a receiver or controller from a distance.
- Many sensors have outputs that are too small to send over long distances, thus a transmitter amplifies the signal and outputs it as a standardized signal, like 0-10 V dc or 4-20 mA dc.
Ex: A thermocouple’s microvolt output is amplified to a signal that is standardized at 0- 10 volts or 4-20 milliamps.
Explain how instruments are used at different levels in the various industries?
Measuring Instrument
At this level, measurements of parameters including temperature, pressure, flow, and level are made using simple sensors and switches. Thermocouples, pressure gauges, flow meters, and level sensors are a few examples of instruments employed at this level.
Considering example Thermocouples: These temperature sensors are utilized in instrumentation to gauge a process’s internal temperature. The voltage generated by the temperature difference between two different metals is what they use to measure. Temperature readings can be made from the voltage produced, which is proportional to the temperature differential. Industries including chemical processing, oil and gas production, and power generation frequently use thermocouples

Controlling instrumentation
It is used to control the flow of materials and energy through a process. It consists of more sophisticated sensors and controllers. At this level, PID controllers, mass flow controllers, and smart sensors are a few examples of instruments that are employed.
PID Controllers: PID (proportional-integral-derivative) controllers are utilised to regulate the movement of materials and energy. Using feedback, PID controllers modify the process according to the discrepancy between the desired setpoint and the actual process variable. In fields including manufacturing, food processing, and HVAC systems, they are frequently employed.
Advanced Control in Industries
This level consists of more sophisticated control systems that are used to track and manage several operations inside a building or other structure. Distributed control systems (DCS) and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems are two examples of instruments used at this level.
Distributed Control Systems (DCS): An instrumentation system for controlling a plant or facility, DCS combines numerous controllers, sensors, and other devices into a single system. Advanced communication protocols are used by DCS systems to provide real-time monitoring and control of numerous operations from a single location. They are frequently employed in sectors including petrochemicals, energy production, and oil and gas.
Software in instrumentation:
This level consists of sophisticated software tools and analytics that are used to enhance overall efficiency and optimize processes. Advanced process control (APC) systems, predictive maintenance software, and machine learning algorithms are some examples of instruments utilized at this level.
Machine Learning Algorithms: Machine learning algorithms are used to analyze vast volumes of data from sensors and other devices in order to increase efficiency and optimise processes. These algorithms can make predictions based on the current situation and learn from prior performance. They’re frequently employed in sectors including manufacturing, healthcare, and finance.
Predictive Maintenance Software: Predictive maintenance software is utilized to track the condition of the machinery and forecast when maintenance is required. This lowers maintenance expenses and helps to avoid unscheduled downtime. In order to identify anomalies and foretell when maintenance is required, predictive maintenance software analyses data from sensors and other equipment. It is frequently employed in sectors of the economy like manufacturing, energy, and transportation.





