Instrumentation Engineering
Instrumentation engineering is a branch of engineering that deals with the design, development, installation, and maintenance of instruments and control systems used in industrial and manufacturing processes. It involves the use of sensors, transducers, and other electronic devices to measure and control various physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and level.
Instrumentation engineers are responsible for selecting and configuring the appropriate instruments and control systems to ensure that processes operate safely, efficiently, and within regulatory compliance. They also design and implement automation systems, which can help improve productivity and reduce operating costs.
Classification of Instrumentation Engineering

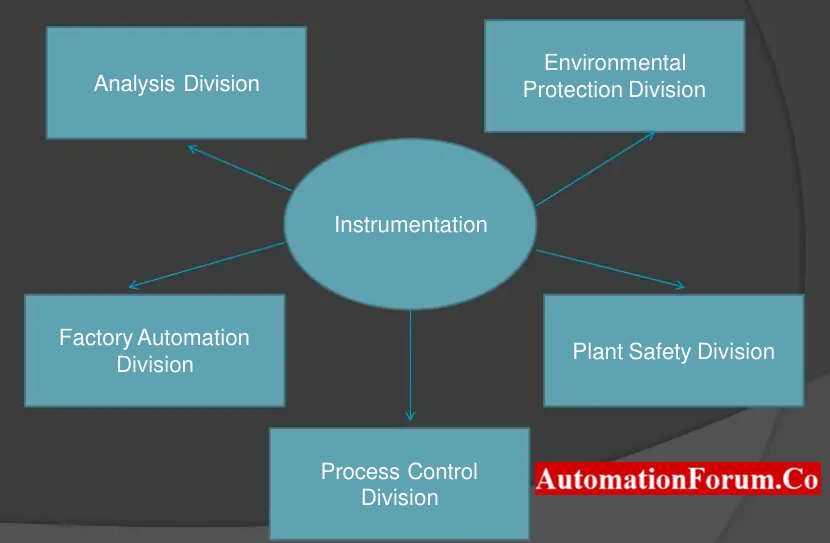
Instrumentation engineering can be broadly categorized into the following subfields:
- Process Control Instrumentation: This subfield involves the design and implementation of instruments and systems for measuring and controlling parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow, and level in industrial processes.
- Analytical Instrumentation: This subfield focuses on the design and development of instruments and systems for analyzing chemical and physical properties of materials, such as gas chromatographs, mass spectrometers, and spectrophotometers.
- Biomedical Instrumentation: This subfield involves the design and development of instruments and systems for medical applications, such as electrocardiographs, blood glucose meters, and ultrasound machines.
- Environmental Instrumentation: This subfield focuses on the design and development of instruments and systems for monitoring and analyzing environmental parameters, such as air and water quality.
- Control System Engineering: This subfield involves the design and development of control systems for various applications, such as automotive, aerospace, and robotics.
- Mechatronics: This subfield involves the integration of mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering to develop advanced systems such as robotics, automated manufacturing systems, and automotive systems.
- Industrial Automation: This subfield involves the design and development of automated systems and control strategies to improve productivity, quality, and efficiency in industrial processes.
What is an Instrumentation Engineer do?
An instrumentation engineer designs, develops, installs, and maintains instruments and control systems used in various industries and applications. Their responsibilities may include:
- Designing and selecting appropriate instruments and control systems for measuring and controlling physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow, and level in industrial processes.
- Developing control algorithms and strategies to optimize process performance and efficiency.
- Integrating and testing instruments and control systems to ensure proper functioning.
- Developing and maintaining documentation, such as technical manuals and operating procedures.
- Troubleshooting and resolving technical problems in instruments and control systems.
- Implementing safety measures to ensure the safety of workers and the environment.
- Collaborating with other engineers and technical professionals to develop integrated systems and projects.
- Staying up-to-date with advancements in instrumentation technology and industry regulations.
Instrumentation engineers work in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and aerospace. They may work in teams or independently, depending on the project and organization.
What is the importance of Instrumentation engineering?
Instrumentation engineering is important for many reasons, including:
- Improved Process Control: Instrumentation engineers design and implement systems that improve the accuracy and precision of process control. This leads to improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and higher quality products.
- Enhanced Safety: Proper instrumentation and control systems can help reduce the risk of accidents and injuries in industrial processes, thereby enhancing workplace safety.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements, such as environmental regulations or safety standards. Instrumentation engineers help ensure compliance with these regulations by designing and implementing systems that meet regulatory requirements.
- Increased Automation: Automation can reduce labor costs and increase productivity. Instrumentation engineers design and implement systems that automate processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs.
- Advancements in Technology: Instrumentation engineering plays a crucial role in advancing technology in fields such as aerospace, automotive, and biomedical engineering.
- Environmental Protection: Instrumentation engineers design and implement systems that monitor and control environmental parameters, such as air and water quality. This helps protect the environment and ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
- Improved Quality of Life: Instrumentation engineering contributes to the development of medical equipment, such as MRI machines and pacemakers, which improve the quality of life for individuals with medical conditions.
Overall, instrumentation engineering is essential for the safe, efficient, and effective operation of many industrial processes, and for the advancement of technology in various fields.
Instrumentation engineers need to have certain skills to do well in their jobs.





