What is industrial automation?
Automation is the use of machines, control systems, and information technologies to optimize productivity in the manufacturing processes with little human involvement.
Industrial automation helps us to process the plant operation in more optimized conditions by using various control systems such as Programmable Logic Circuit (PLC), Human-machine Interface (HMIs), and robotics.
Automation employs logic and programming to provide information to machines on how to accomplish a function; these machines provide great control, which enhances manufacturing performance.
In a manufacturing environment, industrial automation may consist of various types of equipment. In industrial automation control, multiple process variables such as temperature, flow, pressure, distance, and liquid levels can be recorded at the same time. All these variables are recorded, processed, and controlled by complex microprocessor systems or PC-based data processing controllers.
Advantages of Industrial Automation
The main advantages of industrial automation are
- High reliability
- Increased productivity
- Quality enhancement and
- Reduced labor expenses
Block diagram of Industrial Automation

What are the types of Industrial Automation?
There are different types of industrial automation available in the market based on their use. They are:
- Fixed (Hard) Automation
- Programmable Automation
- Flexible (Soft) Automation
- Totally Integrated Automation (TIA)
Fixed (Hard) Automation
This type of automation is used in high-volume production settings with dedicated equipment. To perform well there is a pre-installed operating set are available with the equipment
Fixed (Hard) Automation Advantages:
- High production rates
- Low unit cost
Fixed (Hard) Automation Disadvantages:
- The initial investment is high
- High chance for failure
Programmable Automation
The production equipment in this method is built to be able to modify the operation sequence to meet different product configurations.
It is mainly used when manufacturing products in batches because we can customize and make adequate changes throughout the manufacturing process.
A program of instruction always controls the manufacturing process in programmable automation. In this case, we can just load the program into the hardware system and begin producing new products at any moment.
Advantages of Programmable Automation :
- Very flexible
- Able to deal with design variations
- Appropriate for batch production
Disadvantages of Programmable Automation:
- High investment.
- Production rate is low than fixed automation.
Flexible (Soft) Automation
The material-handling system connects several machine tools in flexible automation, and all components of the system are controlled or controlled by a central computer.
Flexible (Soft) Automation Advantages:
- Continuous production of variable mixtures of products
- Flexible to deal with product design variation
- The production rate is medium
Flexible (Soft) Automation Disadvantages:
- High investment
- Cost is high compared to fixed automation
Totally Integrated Automation (TIA)
Integrated industrial automation refers to the comprehensive automation of production operations, in which all processes are coordinated digitally and controlled by computers. It includes technology such as:
- Computer-aided process design
- Machine systems that are adaptable
- Machine tools for computer numerical control
- Material-handling robots are examples of automated material-handling systems.
- Systems for automatic storage and retrieval
- Control of production and scheduling by computer
- Conveyors and cranes that are automated
Main Components ofIndustrial Automation
- PLC – Programmable Logic Controller
- DCS- Distributed control system
- SCADA
- Advance Solutions
- Cyber Security
- OT
PLC
A PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLER (PLC) is an industrial control system that continuously analyses the status of input devices and makes choices to control the state of output devices based on a custom program. To automate a process or machine, a PLC monitors inputs, makes choices based on its program, and controls outputs.
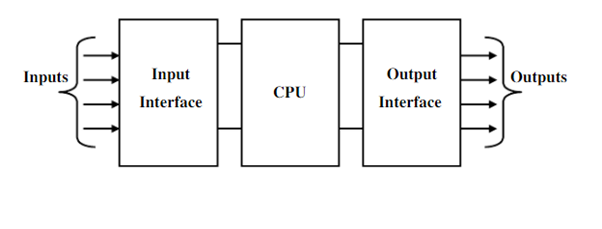
PLC has composed of three main parts:
- Input,
- CPU and
- Output.
Architecture of PLC
Basic PLC Operation :
A PLC consists of Input modules, a central processing unit (CPU), and output modules. An input device collects digital or analog signals from various field devices known as sensors and converts them into a logic signal that the CPU may use. Depending on the program instructions stored in the system memory, the CPU makes decisions and executes control instructions. A programming tool provides the appropriate instructions, which specify what the PLC will do in response to the presented input. An operator interface allows the device to show process information and add new control settings.
What are the advantages of PLCs?
The advantages of PLCs are
- Smaller in size compared to Relay logic solutions.
- Easy to handle
- Faster response
- Less maintenance
- Easier to troubleshoot.
- Better reliability
- Remote control and communication capability.
Major PLC manufacturers list
- Siemens.
- Rockwell Automation / Allen Bradley.
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Schneider Electric.
- ABB.
- Honeywell Process.
- Omron.
- Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems.
Distributed Control System (DCS)
A distributed control system, or DCS for short, is a manufacturing plant control system with autonomous controllers scattered throughout the system.
The distribution of control system architecture throughout the plant has resulted in more efficient methods of improving control stability, process quality, and plant efficiency.
DCS are commonly used in the following processes,
- Oil and Gas
- Petrochemicals
- Chemical plants
- Nuclear power plants
- Water treatment plants
- Sewage treatment plants
- Food processing
- Automobile manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
A DCS is made up of both software and hardware. The simplicity of local installation with most controllers reduces installation expenses. On-site, low-latency automated control improves reliability, while central control functions and remote control alternatives allow for human oversight. Unlike a central controller system, individual processes have their own controllers with separate CPUs, allowing other processes to continue in the event of a breakdown.
What is the Function of a DCS?
While DCS are used in a variety of industries to manage complicated production processes, they are most commonly seen in large, continuous manufacturing plants like Oil and Gas, petrochemical industry. Individual controllers receive instructions from the DCS, which are then distributed throughout the plant. When properly set, the DCS can increase safety while simultaneously increasing production efficiency.
Major DCS manufacturers list
- Honeywell
- Yokogawa
- Emerson Electric
- Invensys Limited
- Siemens
- Metso
- ABB
- General Electric
- Mitsubishi
- Rockwell
SCADA
Supervisory control and data acquisition is a control system architecture that consists of computers, networked data transfers, and graphical user interfaces for high-level monitoring of equipment and processes. This process can be industrial, infrastructure, or facility-based: Manufacturing, power generation, manufacturing processes, and refining are all examples of industrial processes that can run in continuous, batch, repetitive, or discrete modes. Water treatment and distribution, wastewater collection and treatment, oil and gas pipelines, electricity transmission and distribution, and other infrastructure activities are examples of public or private infrastructure activities.
Subsystems of SCADA
The SCADA System is made up of subsystems. They are as follows:
a) A human-machine interface, or HMI, is a device that displays process data to a human operator and allows the human operator to monitor and control the process.
b) A supervisory (computer) system that collects (acquires) process data and sends commands (controls) to the process.
C) Remote terminal units (RTUs) link to process sensors, transform sensor signals to digital data, and transmit the digital data to the supervisory system.
Major SCADA manufacturers list
- Honeywell
- Schneider Electric
- ABB
- Siemens Energy
- General Electric
Cyber ??Security in Industrial Automation
Organizations are more interconnected in digital networks. Access to industrial automation and process control systems is possible through the company’s internal and external networks.
The transfer of data between different systems and networks makes them more vulnerable to attacks and subsequent system failures. Ensuring the availability and integrity of these systems requires precautions against unauthorized internal and external access to industrial control systems.
Importance of Cyber Security:
First, we have to know there are many reasons why digital or cyberattacks occur, in some cases, it is just for the fun to the hackers and in some cases, people use it as a money-making way.
The significance of cybersecurity is highlighted here.
In any of the above circumstances, the impact of these attacks can be devastating, causing immense financial and reputational harm to the people or industry. For these reasons, IT and OT security are more important than ever before, even if most companies are unprepared or unaware from even the basic security perspective. Unless an effort is made to safeguard this next phase of IT/OT fusion, many existing frameworks will be vulnerable to these assaults. IT/OT combo not only lets businesses build future-proof enhancements, but it also allows them to do it safely.
Solutions available in Cyber ??Security for Industrial Automation
Various methods to Prevent Cyber Attacks
The Various types of Cyber security solutions are
Cyber & Malware attack
Anti-malware software is recommended to prevent malware attacks. Installing this software on a computer help us to find and remove the malware’s if there is any on our machine and it also prevents malware attack in future.
What is DOS and how to prevent it?
DoS or Denial of Service attacks is one of the best offensive attacks since they take down a target’s servers, making it difficult to access their locations or use their online services. Having more bandwidth capacity is the simplest approach for countering DoS attacks. If you’re concerned that your company might be a target for DoS attacks, simply having enough server capacity to handle the increased traffic activity can keep the attacks at bay. There are also third-party administrations that can help your firm stay online during a DoS attack.
Phishing and the prevention for Phishing assaults
In a phishing attack, a cybercriminal tries to get personal information from you by tricking you into giving it to them. Scammers who are more adventurous may attempt to steal a victim’s government-managed ledger data. A recent phishing scheme used Google Docs to trick users into entering their Google login credentials.
The easiest and efficient way to prevent phishing attacks is to make sure the workers are aware of both how normal and harmful an attack can be; remind them to keep extra care while checking emails and to report any email they find suspicious. Apart from this, make sure workers are using security features like two-factor authentication for their email accounts.
Cyber security in Industrial Automation and Industrial Control Systems :
Cybersecurity is a word that describes how industrial automation and control systems (IACS) protect themselves from unforeseen events, actions, opportunities, or attacks. Accidents can happen anywhere, including the Internet, company systems, program evaluations, and unauthorized access, and they can have a major impact on health, safety, and the environment.
OT Networks
Operational technology (OT) is a combination of hardware and software that detects and/or modifies industrial equipment, resources, processes, and events through direct monitoring and/or control. The term was coined to describe the technical and functional differences between standard IT systems and industrial control system environments. Here are some examples of technologies that work:
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
- Supervision and Data Acquisition Systems (SCADA)
- Distribution Control Systems (DCS)
- Computer Numerical Control Systems (CNC)
- Scientific Instruments (eg digital oscilloscopes)
- Building Management and Building Automation Systems (BMS) / (BAS)
- Controlling lighting for indoor and outdoor applications
- Integrated energy, safety, and security monitoring systems
- Transportation systems for the built environment
Advance Solutions
Historian
It is a time base data system or tool designed to collect the data from an automation system. The saved data can subsequently be utilized to illustrate process data trends on charts, generate reports, or perform data analysis.
Standard Elements of a Historian System
A Historian system is made up of three basic components:
Data collectors collect data from various sources such as PLC, OPC servers, files, and network devices.
Server Software: It processes the data which was collected by the data collector and serves it to the client applications.
It also provides some other services like alarm management, calculation, and data context subsystems.
Client applications for data reporting, charting, and analysis.
Alarm Management
The main role of the alarm management system is to alert the operator if any abnormal operating situations occur in the industry. The alarm occurs due to the following reasons:
- A manmade or natural issue
- Equipment problem,
- Product Quality Control.
Emergency Shut Down (ESD) systems are also used to halt the process when if the alarm occurred due to danger of serious safety, environmental, or financial issues.
Advance Process control
Advanced Process Control, or APC, is model-based software used to control the operation of a process and is commonly called multivariate predictive control (MPC).
Improved operational economics or production improvements are common inspirations for implementing these applications. The advanced process control software may offer the following features:
- Tools for offline and online model creation, model verification, and data analysis that ensure model accuracy
- Driver program for obtaining historical data from control systems or online process historian systems.
- Operator direction to inform the operator of where the APC is taking the process.
- Controlled variable prediction based on future projected motions of managed variables
- APC adjustment at runtime to account for changes in process dynamics without the need to recompile the model
- Not the PID or process controller tuning and related performance, but the APC controller monitoring and performance analysis software
Asset Management System (AMS)
An Asset Management Solution focused on reducing the downtime of an Automation System.
Industrial automation has a large number of smart machines like PLCs, HMIs, VFDs, etc, and these devices are either configured or programmed based on the industry. Smart machines are usually connected to an Ethernet network. Sometimes, some disruptions will occur in the industry, and quick recovery from these disruptions is very important to reduce downtime and product loss. These disruptions occur due to man-made or natural issues and an Asset Management System can solve these problems.
Capabilities of AMS
The capabilities of AMS software are listed below:
- Archive critical files and documents
- Automatic disaster recovery
- Track or audit all changes to operating settings:
Archive critical files and documents: When changes are made to any of the resources, a version history records the user name and the date of the change. The most recent revision is stored, and the number of backup versions kept is determined by the user. So if any error happens, the user can revert back to previous versions and can run the industry without much delay or downtime.
Automatic disaster recovery: By using AMS software, we can schedule the backups of files. If any differences that are detected are assembled into a report that can be automatically emailed to a list of users.
Track or audit all changes to operating settings: For example, When a user modifies a parameter value or a setpoint in a controller, the event is automatically recorded in a centralized audit log, which includes the device, user, time, and action executed.
Other benefits of AMS. You may automatically scan the running network and add new assets to AMS. Workstation software packages may be tracked and readily uploaded. Security scans can be performed on several devices at the same time. Assets can also be tracked using a mobile device.
Data Collection Software and Change Management System
A data collection is a computerized system for collecting and storing data from various input and output devices in an electronic format. The advantages of employing data collection technologies include the elimination of paper surveys and the ability to instantly export data for data analysis and reporting.





