- What are Flanged Pipe Fittings?
- What materials are used to make Flanged Pipes?
- What are the different types of flanges?
- List out the benefits of a flange pipe fitting
- What are the types of Flange Faces?
- Some Useful Questions related to flanges
- What is the purpose of pipe flanges?
- Why do we use flanges instead of welding?
- What tools are used for pipe fitting?
What are Flanged Pipe Fittings?

- A flange is a metallic ring welded at end of the pipeline with a maximum number of holes drilled in it for inserting bolts and nuts of appropriate sizes.
- The flange joint is made pressure-tight by sandwiching a rubber gasket between pair of ?anges.
- The gasket is crushed between pair of metallic flanges to seal all potential leak paths to ensure no leakage of working fluid.
- The material used to make the gasket is softer than the flange material, generally, rubber is used to make the gasket.
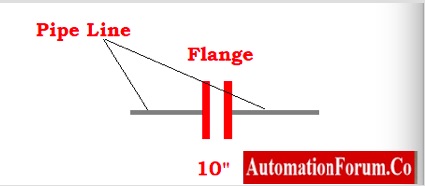
- In P&ID diagrams ?anges are represented by two short parallel lines perpendicular to the pipeline as shown below.

- A flange varies in concern to their sealing design and gasket type. But the most common flange design is raised face flange which is designed to seal by means of concentric grooves machined on the flange face.
- This concentric groove forms a sealing surface for high leakage path length compared to smooth faces to damp process ?uid leakage under operating pressure.
- The figure below shows the symbolic representation of a flange pipe size of 10 inches.
- Ring Type Joint (RTJ) is another ?ange face design, here a unique metal ring lies inside a concentric groove between mating flanges.
- Generally, these Ring Type Joint flanges are found on high-pressure applications.
- In Ring Type Joint flanges the grooves are completely free of foreign material to achieve proper sealing.
- Flange rating is defined by American National Standards Institute (ANSI) based on pressure class with standard 16.5.
- These pressure classes are appointed by numerical values followed by pounds or “#”.
- Some common ANSI ratings include the pressure classes 150#, 300#, 400#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, and 2500#.
- Pressure ratings depend on ?ange class and operating temperature
What materials are used to make Flanged Pipes?
- Different materials are used to make flanged pipes such as stainless steel, cast iron, aluminium, brass, bronze, and plastic.
- But, forged carbon steel is a widely used material within the oil and gas industry since it has a machined surface.
- For this specific purpose, these flanges are furnished with different layers of materials of varying quality.
- Normally, the flange material is selected during the selection of pipe material and in most cases, both flange and pipe are of the same material.
- All flange types come under the ASME en ASTM standards,
- ASME B16.5 describes dimensions, dimensional tolerances, etc.
- ASTM describes different material qualities.
What are the different types of flanges?
- In industrial applications, these flanges are used to connect valves and other equipment to pipelines
- Flanges are forged rings that come in various shapes and sizes for use in a wide range of industrial applications.
- Selection of flange type might be difficult for our required application with so many varieties and specifications.
- The most common and popular types of the flange and their uses are shown below.
1. Weld Neck Flanges

- These types of flanges are also called tapered hub flanges or high hub flanges.
- In these flanges, the environmental stress is vacated into the pipe confirming the reduction in high-stress concentration at the bottom of the flange.
- This flange consists of a round fitting that extends above the circumference of the rim.
- These flanges are made by forging welded to the pipe.
- These flanges are used in extreme temperature or pressure situations
2. Slip-on Flanges

- These flanges are most popularly used
- These flanges slip onto the pipe so-called name slip-on flanges.
- These flanges are welded on both the inside and outside.
- These are best suited in low-pressure and low-temperature applications.
- They can be offered at a minimum cost.
3. Threaded Pipe Flanges

- These pipe flanges are similar to slip-on
- But, treaded pipe flange design has a tapered thread.
- These flanges can be fixed easily to the pipe without welding.
- Like slip-on flanges, these are also best suited in low-pressure and low-temperature applications.
4. Blind Flanges

- These blind flanges are suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Gas or liquid flow through a pipe can be easily tested through this pipe.
- Blind flanges are used to shut off sections of the pipeline since these flanges do not have holes in them.
5. Socket Weld Flanges

- These socket welded flanges cab accept pipe into the socket to make fitting.
- These flanges are used on high-pressure hydraulic pipes.
- These flanges are used in smaller diameter pipe.
- Provides easy installation compared to other welded flange types
- Pipe lie inside the flange to safeguard the connection a single or multi-pass fillet weld.
6. Orifice Flanges
These orifice flanges are used in combination with orifice plates to measure the pressure or flow of working fluid in pipelines.
These orifice flanges have the ability to restrict pressure or flow in pipelines
These are available with plate and jack screws
List out the benefits of a flange pipe fitting
- In industrial applications, pipelines are used to convey various process fluids from one point to another point.
- These pipelines can be kept fully functional and connected at all times as a piping system is done through pipe flanges.
1. Flanges provide better flexibility
- In some cases, it is essential to make pipelines in hard areas, to achieve good pipeline connection in such a hard area more flexibility is required.
- Flanges keep you away from using adapters in pipes.
2. Accurate fitting in tight spaces
- Many pipeline deals with tight spaces.
- Assembling traditional flange fittings is easy where a wrench does not have clearance.
- Fitting is done easily in tight spaces with moderate torque.
3. Provides easy maintenance
- Flange connections make maintenance very easy in the case of rigid lines in continuous pipes and metal tubes
- Flanges make easy disconnecting, reconnecting, and zero-clearance assembly for better maintenance of manifold, tube, and hose connections.
4. Flange connections and fittings provide a tight-fitting
- These flange connections are less prone to loosening compared to standard hydraulic fittings.
- They reduce the likelihood that other components become loose during demanding hydraulic applications.
- Gives better load distribution by effective clamping around a flange head.
5. Flange connections are more robust compared to traditional hydraulic fittings.
- Flange connections are best at pipe ends and bend because these bends are subjected to high lateral forces and may experience loosening without flanges.
- Pipe connections get easily damaged with vibrations, high pressure, or shock pressures using traditional hydraulic fittings.
What are the types of Flange Faces?
Flange face type is an important characteristic and has a major impact on the final performance
1. Flat Face (FF):

These have a flat and even surface combined with full face gasket
2.Ring joint face:
It has a groove for resting a metal gasket to maintain the seal. These are used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
3. Raised Face (RF):

These faces have a small raised section near the bore.
4. Male & Female (M&F):

These use a matching pair of grooves and raised sections to protect the gasket.
5. Tongue and Groove (T&G):
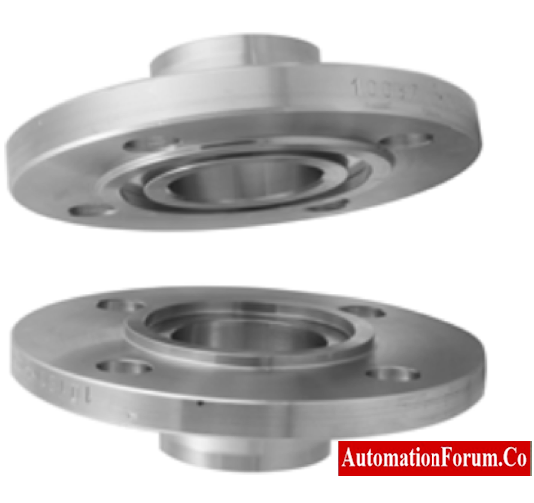

These flanges generate matching grooves and raised sections. This helps in installing and to align and provides a reservoir for the gasket adhesive. Standardized tongue-and-groove facings come in both large and small sizes. They are different from male-and-female in that the inside diameters of the tongue-and-groove don’t go into the flange base. This keeps the gasket on the inner and outer diameters.
Some Useful Questions related to flanges
What is the purpose of pipe flanges?
Pipe Flanges are used to connect pipes with each other, pipes to valves, and special types of equipment such as strainers and pressure vessels.
Why do we use flanges instead of welding?
Alternative to weld connections, these flange connections are used in piping because flanges provide maintenance operations because dismantling and refitting is easy, it can be done quickly and conveniently
What tools are used for pipe fitting?
- Welder’s gauge
- Pipefitter’s square
- Fitter grips
- Centering head
- Flange aligners
- Pipe wraps.
Pipe Flange: A pipe flange in a piping system links the piping and required components by using bolts and gaskets.
Pipe Fittings: A pipe fitting in a pipe system links straight sections of pipe or tube, adaptable for different sizes or shapes.
Pipe Joint: A pipe joint is a connection at the pipe end ensuring that two pipe sections can be joined to each other to install a pipeline of any length.





