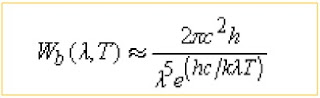What is Infrared ?
Infrared (IR) portion of the spectrum spans Wavelengths between 0. 7 t 1000 microns. Based on the principle that all objects warmer than absolute zero ( 0 ° K) emit energy some where in that range. Infrared thermometers are able to determine an object’s temperature without touching it by measuring the amount of infrared energy being emitted from the object. Modern IR instruments can on y measure between 0. 7 and 20 microns because they are not sensitive enough to measure the small amounts of energy available outside this range.
Basic Components
1. Lens to collect Energy emitted from an object.
2.Detector to convert the thermal energy to an electrical signal with signal conditioning ( filters
and amplifiers).
3. Emissivity adjustment to correct for various surface finish s and materials.
4. Temperature TB ( internal temperature ) must be known or determined through prior
calibration.
5. Ambient temperature compensation.
6. TA , the unknown temperature , is determined from the detector temperature.
Radiation Pyrometer – Fundamentals
Pyrometry literally means “fire” (pyros) “measuring” (metron). Pyrometers manipulate the fact that all objects above absolute zero temperature 0 K (-273.15 °C; -459.67 °F) radiate and absorb thermal energy. If the relationship between the radiation intensity and wavelength and the temperature can be established, the temperature can be found from the radiation.
Two principal theories are employed by pyrometry: Planck’s law and the Stefan-Boltzmann law. Planck’s law is used in narrow-band pyrometers, where only one or a few specific wavelengths are targeted. The Stefan-Boltzmann law is used in broad-band pyrometers, where a wide range of wavelengths are measured.
Planck’s Law
This is a derived formula,from the german physicist Max Planck,that portrays the amount of radiation emitted by a blackbody as theoretically determined by its temperature. It is an equation that produces a curve,termed Planck’s blackbody radiation curve,which illustrate that the warmer a body is,the greater is its blackbody emission at each wavelength and the shorter is the wavelength at which emission peak.
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
Stefan-Boltzmann law that relates the energy,E,radiated away from a perfect emitter,to the temperature,T,of that body.It has the form E,T,where E is the energy radiated per unit area per second.T is the temperature and is the Stefan Boltzmann constant. Its value is 5.6697 10 Wm K.The law was derived by the Austrian physicists Josef Stefan and Ludwig Boltzmann.