The cast or forged materials are used to make ANSI B16.5 flanges and flanged fittings.
According to the American National Standard ANSI B16.5, the maximum allowable shockproof pressure ratings for steel pipe flanges and flanged fittings are in psig and temperature ratings are in Degree Celsius.
| Maximum Allowable Non-Shock Pressure (Psig) | |||||||
| Temperature (°F) | Pressure Class (lb) | ||||||
| 150 | 300 | 400 | 600 | 900 | 1500 | 2500 | |
| Hydrostatic Test Pressure (Psig) | |||||||
| 450 | 1125 | 1500 | 2225 | 3350 | 5575 | 9275 | |
| -20 to 100 | 285 | 740 | 990 | 1480 | 2220 | 3705 | 6170 |
| 200 | 260 | 675 | 900 | 1350 | 2025 | 3375 | 5625 |
| 300 | 230 | 655 | 875 | 1315 | 1970 | 3280 | 5470 |
| 400 | 200 | 635 | 845 | 1270 | 1900 | 3170 | 5280 |
| 500 | 170 | 600 | 800 | 1200 | 1795 | 2995 | 4990 |
| 600 | 140 | 550 | 730 | 1095 | 1640 | 2735 | 4560 |
| 650 | 125 | 535 | 715 | 1075 | 1610 | 2685 | 4475 |
| 700 | 110 | 535 | 710 | 1065 | 1600 | 2665 | 4440 |
| 750 | 95 | 505 | 670 | 1010 | 1510 | 2520 | 4200 |
| 800 | 80 | 410 | 550 | 825 | 1235 | 2060 | 3430 |
| 850 | 65 | 270 | 355 | 535 | 805 | 1340 | 2230 |
| 900 | 50 | 170 | 230 | 345 | 515 | 860 | 1430 |
| 950 | 35 | 105 | 140 | 205 | 310 | 515 | 860 |
| 1000 | 20 | 50 | 70 | 105 | 155 | 260 | 430 |
In all process industries, flanges and flange fittings uses common features. The need for flanges is to accurately determine their pressure rating and corresponding temperature ratings.
The flanges fittings are important for personnel and plant safety and overall plant performance and reliability.
What is ANSI/ASME B16 Standard?
- ASME – American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
- ANSI – American National Standards Institute.
The ANSI and ASME B16 standards include pipes and fittings in cast iron, cast bronze, wrought copper and steel. Both ANSI and ASME flanges are identical.
Explain the difference between ANSI and ASME Flanges?
- When discussing the term measurements both the ANSI and ASME measurements are identical and are interchangeable in a few rare instances.
- Though both ANSI and ASME focus on different aspects of establishing the engineering standards.
- They both work towards the same goal of assuring that all engineers follow these same universal standards to assure quality and consistency for all mechanical devices and products.
The difference between ANSI and ASME:
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
- It is a non-profit organization.
- It has members from academia, government agencies, and businesses organizations.
- It mainly focuses on establishing engineering standards for the U.S.
- To ensure that products, services, and processes are consistent and predictable.
- To provide accreditation to companies and individuals.
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
- It is a group of mechanical engineers and representatives from engineering companies.
- It is also a non-profit organization.
- It establishes standards and codes for mechanical devices.
- It focuses on educating and evaluating mechanical engineers to obtain the Professional Engineer (PE) license.
- Its aim is to focus on finding the solutions to mechanical engineering problems.
What are Valve Pressure Ratings?
The valve pressure rating is defined as the selection and sizing of the valve beyond the capacity (Cv).
And the valve pressure rating is categorized into
Body Pressure Rating
- It is a static rating,
- It is defined as the amount of total pressure that the body and stem can contain without leaking.
Close-Off
- It has the maximum differential pressure across the ball or disc that the valve can hold against the rated seat leakage.
- Its pressure must be higher than the maximum differential pressure (DP) after the installation of the valve.
What is meant by thicker?
According to ASME B31.3 Piping Guide:
The steel pipe shall be seamless and must have a thickness of at least to schedule 80 of ASME B36.10. Where it is used for steam service of above 18 bars or water service above 7 bars with water temperatures above 105 °C.
What is a flanged pipe fitting?
A flanged pipe is used to connect the piping and its components in a piping system by the use of suitable gaskets and connection bolts.
The welded neck flange, slip-on flange, blind flange, socket weld flange, threaded flange, and lap joint flange (RTJ Flange) is the most commonly used flange in all industrial applications.
What is a steel pipe flange?
A steel pipe flange is used to connect two pipes together using bolts or welding.
These flanges are used to connect a pipe to tee, valve, choke, or any other piece of equipment.
There are a variety of flanges shapes available they are round, square, and rectangular shapes.
Pipe Flanges are considered a popular category of pipe fittings. These flanges are used to connect mechanically.
What are the different forms of ANSI flanges available?
There are five different types of ANSI flanges
1. Welded Neck flange:
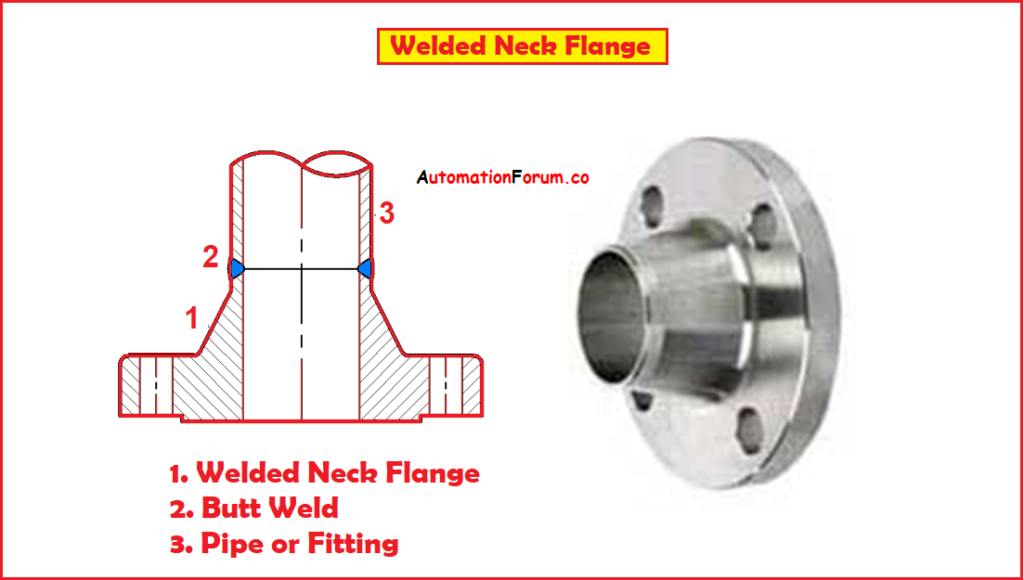
- Welded neck flanges can be easily identified at the long tapered hub that goes gradually over to the wall thickness from a pipe or fitting.
- The benefit of a long tapered hub gives strength in high pressure, sub-zero, and/or elevated temperatures.
- To reduce or eliminate the restriction on the fluid flow these neck flanges are bored to match the ID of the mating pipe.
- This reduces erosion and prevents turbulence at the joint.
- These flanges provide an excellent stress distribution through the tapered hub.
- This flange type is butt welded to a pipe.
2. Threaded Flange:
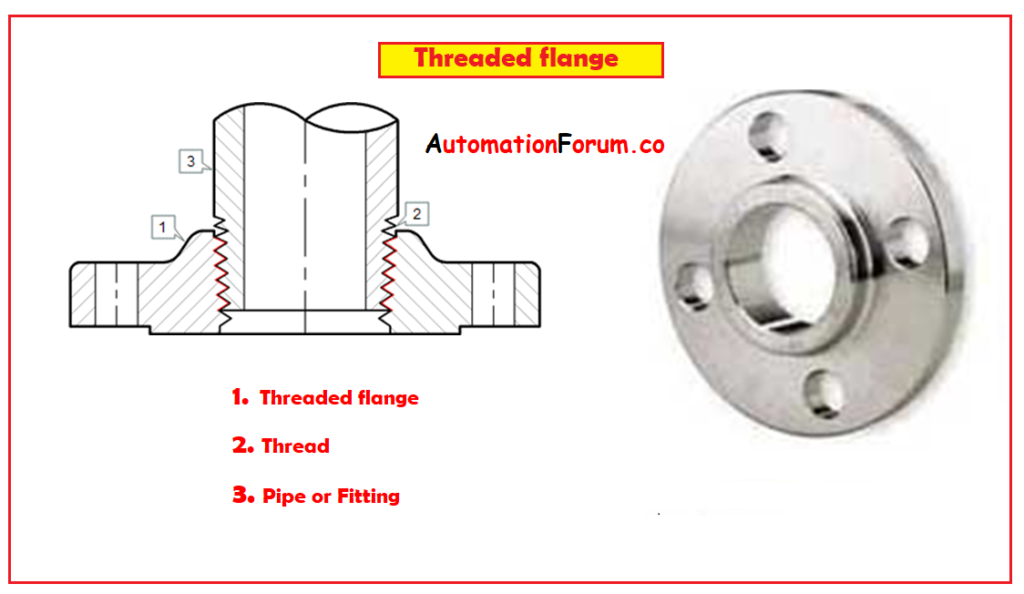
- Threaded flanges are a very popular type of flange they can be easily fitted into the fluid line or any assembly that does not require any welding.
- In some situations, the threaded connection and seal weld are also used.
- These threaded flanges are available in most sizes and for most pressure ratings.
- The pipe with thick wall must be selected because the threaded flange is not applicable for a lower thickness pipe, and the cutting thread on a pipe is not possible.
- Their threaded design allows reusing when an assembly is dismantled.
3. Slip-On Flange:

- These flanges are considered to be one of the easier types of flanges for proper fitting and alignment. These are selected for particular applications where dis-assembling is not required.
- The internal pressure of slip-on flange is about 65 % of that of welded neck flange.
- Their durability under fatigue is about 33% of that of the latter.
- The connection with the pipe is done with 2 fillet welds, as well at the outside and also at the inside of the flange.
- During welding, the space is necessary to avoid the flange face damage.
The disadvantage of the slip-on flange is
- That the pipe must be welded instead of just fitting.
- A combination of flange and elbow or flange and tee is not possible because fittings do have not a straight end that completely slid in the Slip-On flange.
4. Blind Flange:

- The bore is not available in blind flanges
- It is used to blank off the pipe endings, valves, and pressure vessel openings.
- These blind flanges are larger.
- These are the most highly stressed flange types.
- These flanges are applicable for higher pressure temperature ranges.
- These are the type of ANSI flanges that do not feature an outlet.
- These blind flanges are widely used in most industrial applications.
- These flanges require the stopping up of the valve, pressure vessel, or end of a flanged pipe.
5. Lap Joint Flange:
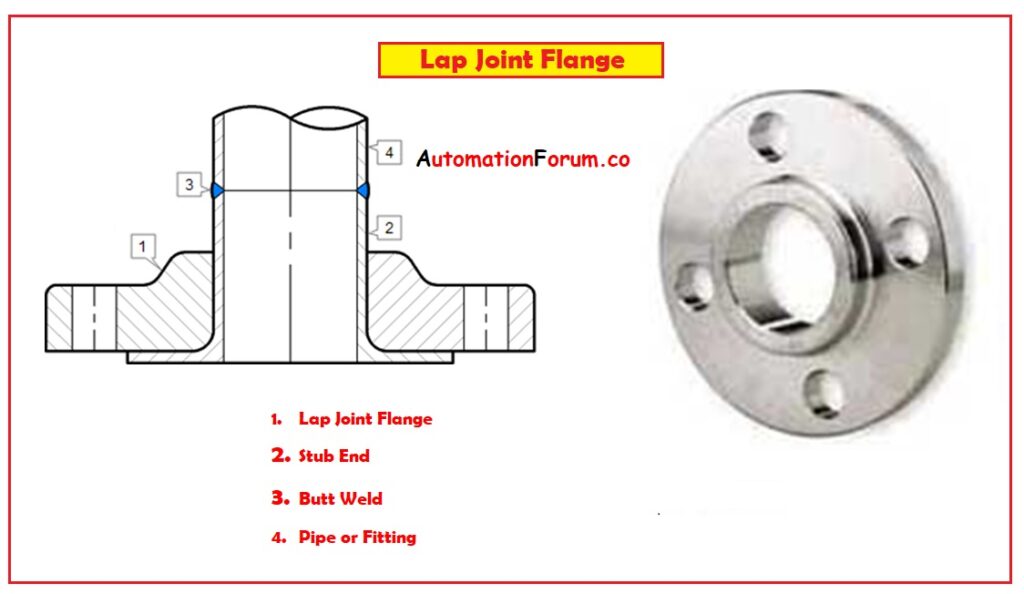
- These lap joint flanges are identical to slip-on flanges
- These flanges have a little pressure holding capacity.
- These flanges can be used at all pressure ranges and are available in a full-size range.
- These lap joint flanges vary from another type of flange, that requires an end connector, the pipe, valve, or other product to be connected with the flange does not come into physical contact with it.
- However, this lap joint flange assembly allows for the rotation of the flange and makes it well suited for applications where the assembly may need to be dismantled relatively frequently for cleaning and maintenance.
6. Stub End:

- A Stub end type of flange must be used with a lap joint flange, as a backing flange.
- These flange connections are applied in low-pressure and non-critical applications.
- The carbon steel flange can be used in the stainless steel pipe system because these flanges will not come in contact with the fluid flowing in the pipe.
- The Stub end flanges are available in almost all diameters of the pipe.
- The ASME B.16.9 standard defines the dimensions and their tolerances.
- The MSS SP43 defines the lightweight corrosion-resistant Stub end fittings.





