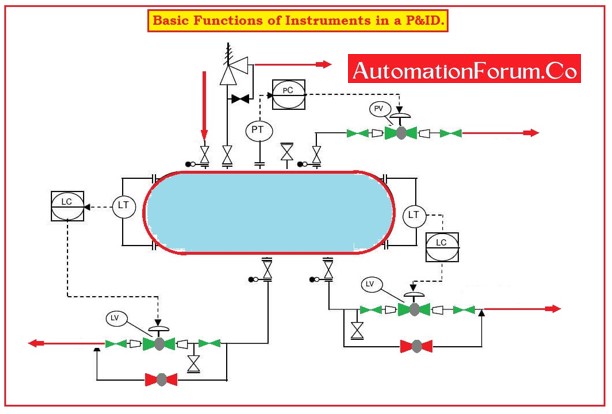
What are the primary functions of Instruments in P&ID?
The primary functions of Instruments in P&ID are to display, record, monitor, and control various process parameters such as flow, level, pressure, and temperature within the control loop.
What are instrument and control symbols?
An instrumentation symbol includes a variety of characters used to record and display measurements such as meters, transmitters, sensors, and indicators.
Instrument and control symbols consist of an instrument bubble called a circle with the instrument abbreviation lettered inside the bubble.
This abbreviation completely describes the type and function of the instrument and control component.
What is an instrument in P&ID?
Instruments in P&ID – Gauges, transmitters, local indicators, DCS indicators, interlocks, and other functions have to be shown in detail on the P&ID.
Interconnection between these instruments is indicated by different types of instrument signals such as hardwired signal, pneumatic signal, or hydraulic signal.
What are the differences between instrumentation and control engineering?
Instrumentation Engineering:
It is the science of the measurement and control of process parameters within a production or manufacturing area.
Control Engineering:
It is the engineering discipline that applies control theory to design systems with desired behaviors. It is also known as control systems engineering.
How do you classify instruments and control elements?
The instruments and control elements can be classified based on
- Process parameters
- Function they perform
- Classification based on Process Parameters: The common process parameters are
- Flow (F).
- Level (G)
- Pressure (P)
- Temperature (T)
- Classification of an instrument is based on the functions they perform: The functions performed by instruments such as display, monitoring, recording, and control of process variables.
Indication of Instrument:

An instrument can be indicated by a group of letters and numbers. Refer to the above diagram
- The process variable represents the first letter F in the instrument abbreviation.
- The second letter I and third letter C in the instrument abbreviation indicate the instrument function.
- The numerical 301 in the instrument abbreviation indicates the specified instrument number.
What are the functions of instruments in P&ID?
The common functions performed by instruments and control components are:
Alarms (A):
- These are commonly known as alerting devices.
- These devices consist of sound or siren and light outputs.
- These alarm systems inform plant operators about the existing condition of the process variables to attract the attention of the plant.
- In P&ID the alarm function makes us adjust or change the process variables such as flow, level, pressure, and temperature.
- The alarm is denoted by the letter (A).
Controllers (C):
- Controllers are responsible for controlling the process variable.
- A controller is a device that receives input data and information on the process variable from a sensor or measuring device such as RTD, T/C, Flow meters, and level indicators.
- The typical controller compares the received signal from sensors with a set point and takes corrective action by signaling to the control element.
- The control actions are performed by actuators and control valves.
- Letter (C) represents the controller function.
Indicators (I):
- An indicator is a human-readable device that displays only the essential information about the process variable.
- Indicators may be as simple as a pressure gauge or temperature gauge.
- But some indicators are built with control keys to enable operators to change the setting as required in the field.
- Gauges are a type of indicator mounted at the process station fixed to equipment to sense and display the variable.
- A level gauge (LG) is another type of indicator used to measure the level of liquid in a process vessel such as a tank, drums, and container.
- And in P&IDs, the indicator function modifies basic instrumentation variables such as flow level, pressure, and temperature.
- Most control systems use a multi-channel type indicator that displays various process variables within a single unit.
- The advantage of using a multi-channel indicator is it reduces the physical installation space required and makes it easy to control.
- Typically, on a P&ID the various Indicators are short-formed as PI, TI, FI, and LI.
Sensors:
- Sensors are the primary element in a process control loop and are installed on the equipment at a process station.
- They are often called the measuring element that actually measures the value of the process variable.
- These elements provide the inputs to digital controllers as a measured variable.
- Examples of sensors are RTD, T/C, and orifice meters used to measure temperature and flow respectively.
- The measured analog variables are now converted to digital through transducers.
- Sensors on P&IDs are represented by various combinations of letters like FE and TE represent a flow sensor (Flow Element) and a temperature Sensor (Temperature Element) respectively.
Recorders (R):
- A recorder is a device that stores the output of a process variable.
- A recorder stores a set of readings along with an actual time when the readings were collected.
- Different recorders display the data collected by them differently.
- Chart recorders are another type of recorder, these make a chart or graph of collected readings.
- These recorders make it easy to read or analyze past process information and are very useful in monitoring plant performance and in quality control of the products.
- The recorder unit is denoted by the letter (R) on P&IDs, It signifies an instrument with a recording function.
- Typically, on a P&ID the various Recorders are short-formed as PR, TR, FR, and LR.
Transmitters (T):
- Transmitters are popular and common in instrumentation and control systems.
- A transmitter is a field-mounted device that receives a signal from sensors.
- This transmitter converts the received signal to a standard signal and transmits this standard signal to monitor or controllers in the central control room for the purpose of monitoring or controlling.
- Typically, on a P&ID the various transmitters are short-formed as PT, TT, FT, and LT.
- On P&IDs, the transmitter function (T) modifies basic process variables such as flow, level, pressure, and temperature.
- Transmitter types include:
- Flow transmitters FT
- Level transmitters LT
- Pressure transmitters, PT
- Temperature transmitters TT and
- Analytic transmitters such as O2 [oxygen], CO [carbon monoxide], and pH transmitters.





