Voting logic can be described as the tolerance level of the reduction of the risk in the industrial process. The components in the industrial process should have a certain Safety integrity level (SIL). This level shows the risk handling properties of an industrial system or process. Voting logic would handle the faults in an industrial process and thus shutdown can be prevented.
There are different types of safety integrity level and if this level is high then the safety would be high too. So if we need to attain a higher SIL level then the complexity and cost of the system would increase too.
What is SIF?
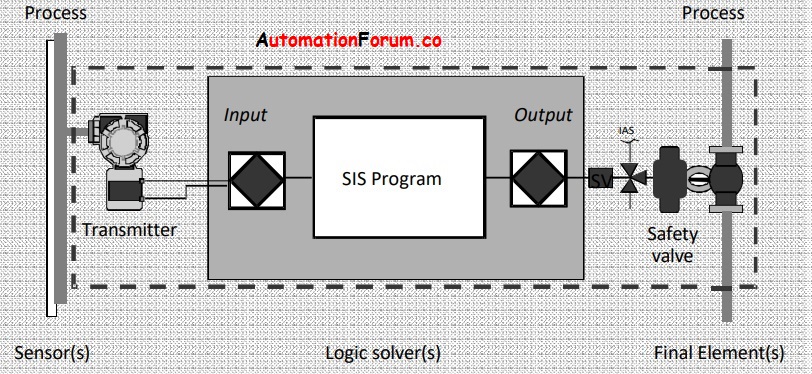
SIF means safety instrumented function, SIF is designed to reduce the chances of failure in an industrial process. So it would keep the process in a safe manner by reducing the chances of failure. It would also reduce the risk to a tolerable level. SIF can be described as the combination of the Sensors, final control element, and logic solvers. SIL level is a part of SIF the required level of SIL would be depended on the amount of risk which is required to be handled. A safety instrumented system is formed by one or more SIF.
So in this, the sensors would check the data or information to determine if there is an emergency situation. The logic solver would determine the actions that must be carried out based on the received data
Where should we require the safety integrated System?
• Emergency shutdown system
• Fire and gas system
• Burner management system
• Machinery control system
• High integrity pressure protection system
What are the different types of voting logic used in an industrial system?
1oo1
This type of voting logic is used to provide a small amount of safety, so it would be used in a system in which there would be less complexity. If you need to get a good amount of diagnostic coverage then this voting configuration can be described as 1oo1D. The D is to denote the automatic failure diagnostic features. The fault tolerance level of this voting system is really low, so if there is any fault then we can’t avoid a shutdown of the process.
1oo2
This type of voting logic is created as an up-gradation of 1oo1, so in this, there would be an improvement in the safety level. This is a two-channel voting system and if one of them fails then the other one would be there to handle the faulty condition. But in this, the trip rate would be really high and it is a disadvantage of this voting logic.

2oo2
This voting logic can be considered as the updated version of the above two voting logic. The chances of trip rate would be high in the single safety system, this can be prevented by using the 2oo2 voting logic. This type of voting logic has a channel duplication feature and this would be really useful to prevent the process trip. This type of voting logic configuration is used in a more complex system so due to this, the chances of failure are really low.
2oo3
This voting logic is also known as the triple modular redundant voting logic and this is used in a process system where a shutdown must be prevented. This is a three-channel system and the hardware system of this voting logic would be complex. But in this voting logic configuration, the chances of failure are low.

1oo2D
In this type of voting logic, the performance is improved when compared to 1oo2 and it doesn’t have any hardware complexity like the 2oo3 voting logic. This voting logic, it has the automatic self-testing feature. So during any fault in any of the channels, the faulty section would be isolated and the process would be carried out by the other channel. So this voting logic is really useful and this system is better than the 2oo3 voting logic due to less hardware complexity and also because of the self-testing feature.
2oo2D
In this voting logic configuration, the probability of failure is reduced due to the two-channel. This voting logic has a high level of diagnostic features. So the self-testing would be carried out really easily.
Voting at the I/O level to improve the safety and reliability:
Voting logic is a fail-safe design and it would make the process to safe conditions in case of component failure, system, or instrument.
1oo1 – Safety and reliability are low
1oo2 – High on safety and low on reliability
2oo2 – Safety and reliability are high
2oo3 – Safety and reliability are really high
1oo2D- Safety and reliability are really high than the 2oo3
2oo2D – Better safety and reliability features
| SIL Level | Voting configuration |
|---|---|
| SIL 1 | 1oo1 |
| SIL 2 | 1oo2 or 2oo3 |
| Sil 3 | 1oo3 |
| SIL 4 | It is used for special purpose |
How to choose the voting logic configuration for the System integrity?
The voting configuration is chosen based on several factors such as a number of system components, chances of failure, the complexity of the system, and the architecture of the system all of these play a major role. Hence voting configuration must be chosen based on these factors.