- What is an OT network?
- What is OT Security?
- What is an IT network?
- What are Industrial Control Systems (ICS)?
- Difference between IT and OT network
- What is IT/OT convergence?
- Benefits of IT/OT convergence
- What is Cyber Security?
- Cyber Security in Industrial Automation
- Importance of Cyber Security:
- The significance of Cyber Security is highlighted here.
- What are Cyber Security Standards?
- What are the benefits of cyber security standards?
- Why cyber security standards are needed?
- Threat to the ICS industry
- Various Cyber Security Standards ICS
- What is the Purdue Model for ICS Security?
- Major Cyber-attacks on Industrial Control Systems
- Solutions available for OT network
- Solutions available in Cyber ??Security for Industrial Automation
What is an OT network?
Operational technology (OT) is a combination of both software and hardware to direct monitoring and control various devices, physical structures, and infrastructure. Operational technology is used for monitoring various processes in a company ranging from critical infrastructure to managing robots.
OT is widely used in industrial control systems, such as SCADA systems. The demand for OT security develops tremendously as this technology advances and converges with networked technology.
OT technology is widely used in manufacturing plants, oil, and gas industries, aviation, railways, etc.
What is OT Security?
OT systems were free from cyber-attack in the past because OT systems were not connected to the internet. Due to the innovation of various digital technologies, OT systems are also connected to the internet.
The separation of IT and OT networks is common, resulting in duplication of security measures and a lack of transparency. These IT/OT networks can’t keep up with what’s going on throughout the attack surface.
What is an IT network?
IT, or information technology, is involved with the use of systems, mostly computers, and telecommunications, to accomplish various tasks such as receiving input, storing, retrieving, transmitting, modifying, and safeguarding data or information so that it can be shared among diverse organizations.
Hardware (computers, physical servers, and network equipment), software (operating systems, applications), and auxiliary equipment all make up an IT network. IT can be updated and reprogrammed in a variety of ways to meet the evolving and changing applications, business requirements, and user needs, rather than executing a fixed set of functions. In every sector, an IT network is utilized to manage computer systems and company data in a more secure manner.
What are Industrial Control Systems (ICS)?
Industrial Control System (ICS) is a type of operational technology (OT) and it is used to monitor or control various processes in the industries. This might be the conveyor belt in the mining site or an alarm that lets the employee if any fault occurs in any of the factory equipment.
Usually, ICS is managed by SCADA, which helps to see the users in a graphical interface. It also allows the user to monitor the current status of equipment.
Difference between IT and OT network
| S.No | OT Network | IT Network |
| 1 | It is a combination of both hardware and software. | Networking, information processing, enterprise data centers, and cloud systems are all part of IT. |
| 2 | OT is the livelihood of all institutions. | IT is extremely important at the corporate (or “Enterprise”) level |
| 3 | OT is focused on their back-end production activities | IT-focused on front-end informational activities |
| 4 | OT is an industrial-oriented | IT network is business-oriented |
| 5 | Mainly interacts with machines | Mainly interacts with information |
| 6 | Works on real-time data processing | Works on transactional data processing |
| 7 | Any disruption in the OT network will have a direct impact on the overall business. | IT network failure can have a negative influence on a company’s bottom line, depending on the industry. |
| 8 | It controls physical access to any device | IT networks to ensure security by authenticating devices and users on the network. |
| 9 | Safety is a priority for OT. | Confidentiality is a top priority for IT |
| 10 | Need special precaution for updating OT networks. Sometimes, need to shut down or redundancy method has to use the plant for updating | IT security updates are so frequent and no need to shut down for updates |
| 11 | The typical lifetime of OT equipment is about 12-18 months | More robust and work longer |
What is IT/OT convergence?
The integration of data from systems that handle manufacturing information (such as production plans and raw material shipments) with data from systems that directly monitor and control manufacturing is known as information technology/operational technology convergence (such as records of oil refinery temperatures and pressure).
Benefits of IT/OT convergence
The benefits of IT/OT convergence are
- Helps to enable decision making based on the real-time data
- Can reduce unplanned downtime
- Efficient use of equipment
- Eliminate unwanted hardware and software
- Reducing capital as well as operational expenses.
What is Cyber Security?
It is a security standard used by organizations to increase the safety standards of industries to reduce the number of cyber security attacks. Cyber security is a technology used to protect devices such as computers, networks from cybercriminals.
Cyber Security in Industrial Automation
Industries are more interconnected in the era of digital technologies and hackers or cybercriminals always try to find possible ways to access industrial automation devices such as PLC, DCS via internal or external networks of the company. In this digital world, transferring data between various systems and networks make them more vulnerable to attacks on the network system of the company. Due to this, the company has to take more precautions against unauthorized external or internal access to industrial control systems (ICS).
Importance of Cyber Security:
First, we need to be aware of what are the reasons behind the digital attacks. In some cases, hackers do it just for pleasure for themselves and some cybercriminals do it in a money-making way. Other than the above-mentioned reasons, even some companies do cyber-attacks to wreck their opponents or to gain the secrets of the company.
The significance of Cyber Security is highlighted here.
In any of the above cases, the impact created by the cybercriminals can be ridiculous, devastating, causing immense financial as well as reputational harm to the company. Sometimes this can affect the existence of the company. For this reason, IT, as well as OT security, is more important than in the previous era. Some companies are not much aware or prepared even the basic security measures. Businesses may not only construct future-proof upgrades with the IT/OT combination, but they can also do so securely.
What are Cyber Security Standards?
Standards of cyber security are proliferating day by day. Businesses, as well as governments, have to more mandate the implementation of cyber security standards. Due to the cyber security standards are more useful, a large number of organizations are involved in the development of cyber security standards. They give concrete benefits that justify the effort and money spent developing and implementing them.
Systems, data, and users are exposed to both traditional and innovative security threats because security technology has not kept up with the rapid expansion of IT. Threats to systems and technology include politically & financially motivated criminals or attackers, and malicious or careless permitted users, all of whom have the potential to endanger cyber security. While it is impossible to eradicate all threats, advances in cyber security can aid in the management of security risks by making it more difficult for attackers to succeed and reducing the impact of cyber-attacks.
What are the benefits of cyber security standards?
Cyber security standards improve security and manage to risk in various ways. Standards also help to establish various common requirements for security and the skill sets required for security solutions.
Other advantages of cyber security standards can be found here.
- They often result in quality improvements
- They reduce the number of technical variances
- Make replaceable technologies readily available to consumers.
- Provide a framework for comparing items and services by allowing them to be measured against objective criteria.
Another advantage of cyber security standards is that the process of developing them, which typically involves a wide range of subject-matter experts, prototyping, and incorporating conformity assessment criteria and methodologies, ensures that they are implementable and reflect recommended practices.
Why cyber security standards are needed?
When a technology’s security requirements aren’t available, it might lead to many security issues. Organizations who embrace the technology may be unaware of the technology’s inherent security flaws and the consequences of using the technology on the security posture of the company. Organizations may also lack trustworthy knowledge on how to optimize the technology’s security capabilities or what additional security measures are required to compensate for those capabilities’ flaws. This frequently leads to unsafe implementations and inadequate security maintenance, increasing the probability of systems being exploited and the organization’s vulnerability to harm.
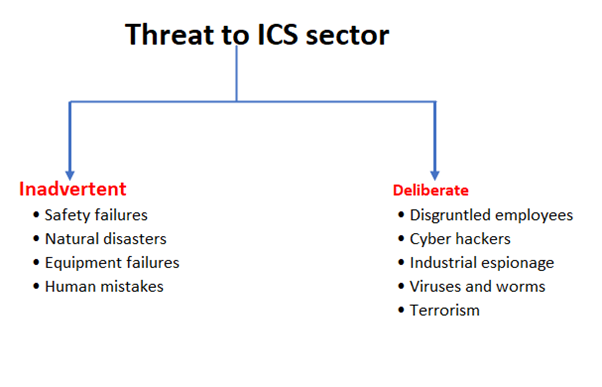
Threat to the ICS industry
The ICS industry is clearly opening itself up to attackers due to ICS becomes more connected with the network and the Internet is very much essential for business needs. Surveys were done by many of the world’s leading security organizations, such as ICS-CERT surveys, which clearly say that the security threats on ICS are rapidly increasing in this digital era.
The threat of Industrial Control System (ICS) mainly classified into two
- Inadvertent
- Deliberate
Various Cyber Security Standards ICS
Many government agencies, various non-profit organizations, and nation-states have developed different standards over the years to overcome threats to ICS. Some of the standards are country-specific, while some others are globally applicable.
To protect the system, networks, and its users in various methods, there are several cyber security standards that are available based on the data.
Some of the common, as well as important standards to protect data, are
- ISA/IEC 62443
- IEC 61508
- NIST SP 800- 82
- ENISA- Protecting Industrial Control Systems
- ISO 27001
- ISA/IEC 62443
ISA/IEC 62443 is a technical report about how to secure industrial automation and control systems (IACS). It is done by international standards and associations. It also provides both normative requirements and supporting guidance to make secure IACS. They clearly define the responsibilities and accountability for all roles such as system suppliers, installing agents, service providers, owners, etc.
- IEC 61508
IEC 61508 is another international standard that is published by the International Electrotechnical Commission. In this standard, they clearly mentioned how to apply, design, install and maintain automatic protection mechanisms known as safety-related systems.
These standards are based on two fundamental principles. They are
1. The safety life cycle is an engineering procedure that is designed based on best practices in order to find and eradicate design mistakes and omissions.
2. To account for the safety implications of device failures, a probabilistic failure method is used.
- NIST SP 800- 82
This standard is mainly used to secure various Industrial Control Systems (ICS), such as Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, Distributed Control Systems (DCS), and other control system configurations like Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), while doing their specific performance, reliability, and safety needs. This standard gives a brief idea about what are the common threats and vulnerabilities of an ICS and also gives remedies to reduce the risks.
- ENISA- Protecting Industrial Control Systems
The current state of Industrial Control System security is described in this study, along with some recommendations for improving ICS security. The recommendations call for the development of national and pan-European ICS security strategies, the creation of a Good Practices Guide on ICS security, the promotion of awareness, education, and research activities, as well as the creation of a common testbed and ICS-computer emergency response capabilities.
- ISO 27001
This is one of the most common requirements that a business must follow while putting in place an information security management system. It is made up of a collection of procedures that spell out the rules and conditions that must be met in order for an organization to be certified to this standard. According to this standard, the business must keep all technology up to date, servers must be free of vulnerabilities, and the organization must be audited at the specified intervals to remain compliant.
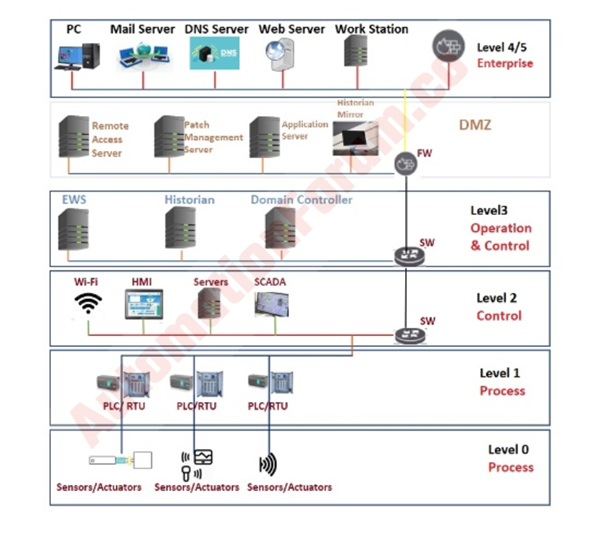
What is the Purdue Model for ICS Security?
The Purdue Reference Model is a part of Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture shortly (PERA) is a reference data flow model developed in the 1990s for Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) which is used to control the entire production by using computers.
End-users, integrators, and vendors can collaborate in integrating applications at key layers of the enterprise network and process infrastructure using the Purdue Reference Model, “95.”
The Purdue Reference Model is used as a concept model for the ICS network which was adopted by ISA-99. The Purdue Reference Model shows all the interdependencies and interconnections of all the main ICS architecture into two zones – Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) and again subdivided these into another six levels from Level 0 to Level 5.
Level 0: Level 0 is referred to as Physical Process. Level 0 includes the physical components such as motors, valves, pumps, sensors, etc.
Level 1: Level 1 is composed of Intelligent Systems that monitor and send instructions to Level 0 devices.
Examples of Level 1 devices are
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
- Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
- Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs).
Level 2: Level 2 is referred to as Control systems. Devices at Level 2 are in control of the system’s overall processes. To supervise, monitor, and manage physical processes, supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) software are used. While the distributed control system (DCS) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are often implemented within the plant, SCADA may manage systems at considerable distances from the physical site of the plants. Basic controls and monitoring are provided by the human-machine interface (HMI) coupled to DCS and PLCs, while SCADA systems gather data and transfer it upstream for recording by the historian in level 3.
Level 3: This is where production workflows are managed. This is used to perform management of batch, data recording, and to control operations and plant performances by using the customized operating system.
Level 3 systems are called manufacturing execution systems (MES) or manufacturing operations management systems (MOMS). This layer also includes databases or historians for storing data from operations. A dedicated backhaul network to the data center or headquarters is often used to communicate between the enterprise and manufacturing levels. Any disturbances at the production level, like at the enterprise level, can result in hours or days of downtime, with a huge potential for revenue loss because it affects the entire manufacturing facility.
Level 4: It’s a Demilitarized zone (DMZ). Systems such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, databases, email servers, and other systems at Level 4 handle the logistics of manufacturing activities while also providing communications and data storage.
Level 5: The enterprise network is at this level. This network, while not an ICS environment, collects data from ICS systems in order to make business choices.
Major Cyber-attacks on Industrial Control Systems
Here we are mentioning some major cyber-attacks that happened in industrial automation networks
Stuxnet
Stuxnet is a computer worm that attacked Iran’s uranium plant in 2010. Stuxnet is believed to have caused significant damage to Iran’s nuclear program by targeting supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. Stuxnet worm mainly affected Siemens PLC.
Attackers have developed standalone and custom malware that targets this site and causes physical damage to equipment at the site. Autonomous malware exploits Zeroday’s vulnerabilities. The service providers transfer the malware to the website on removable media. Antivirus scanners are blind to custom zero-day exploit malware.
Triton Malware
Triton is another malware that was first discovered in 2017 during a petrochemical plant attack in Saudi Arabia. It is considered the world’s most murderous malware. The attack was based on a vulnerability in the computer running Microsoft’s Windows operating system (OS).
Triton malware infects Schneider’s Triconex PLC.
Ransomware
Ransomware is malware that encrypts the victim’s file. Company/user can’t access the encrypted data. To decrypt the encrypted data, users need a decryption key and the cybercriminals or attackers can demand ransom from the victim in exchange for restoring encrypted data. Users have to pay the money to get the decryption key. Attackers normally charge thousands of dollars and are paid in bitcoin or other cryptos.
Another major problem with this attack is that there is no guarantee that you will get the key even if you pay.
How does ransomware work?
There are several ways that attackers can inject ransomware, such as phishing spam, into your computer. Phishing attacks are fraudulent communications that appear to come from a trusted source. The purpose is to trick the recipient into revealing confidential information or to infect the victim’s computer with malware in the form of spyware. Attackers can take over the victim’s computer after downloading and opening the attachment. Some ransomware like NotPetya can take advantage of security flaws to attack machines without scamming people.
How to prevent ransomware?
- Keep your operating system up-to-date.
- Don’t install software from an untrusted source
- Install antivirus software
- Back up your files frequently and automatically
Solutions available for OT network
OT and IT systems are becoming more interconnected day by day. New cyber and operational risks are increasing due to the high dependents on OT/ICS networks. To prevent security threats, you need to be more vigilant and check the devices to find security flaws in real-time. Some of the solutions are
- SMX
- NMS
- SIEM
- Patch Management
- Antivirus Management
SMX- Secure Media Exchange
By monitoring, screening, and documenting the use of removable media throughout industrial facilities, SMX decreases cyber security risk and operational disruptions. SMX gives plant administrators more control and control over how employees and contractors use USB and other detachable media, minimizing cyber risk to process control networks around the world. Critical infrastructures and isolated network environments benefit from SMX’s enhanced threat detection capabilities. For safer process manufacturing, SMX bridges the gap between IT and OT needs. It safely closes security weaknesses while delivering vendor-agnostic threat research updates.
NMS- Network Management System
It is a system that consists of both hardware and software which is designed for monitoring, maintaining, and optimizing a network. But most often an NMS refers to network management software.
NMS performs the following purposes:
Network monitoring – NMS software monitors network hardware and check whether all the devices work properly and alerts the user if any problem occurs.
Device detection – NMS is used to be recognized, configured, and added to the current network if a user connects any new devices. This is called device provisioning.
Performance Analysis – An NMS can analyze the current and historical performance of a network
Device management- By using NMS, we can control multiple devices from a central location. We can configure a new device, modify the current settings based on the performance of a network
Fault management – NMS will automatically divert the traffic if any network issue occurs. This may be based on the preprogrammed protocols. It also sent an alarm to the administrator while rerouting the traffic.
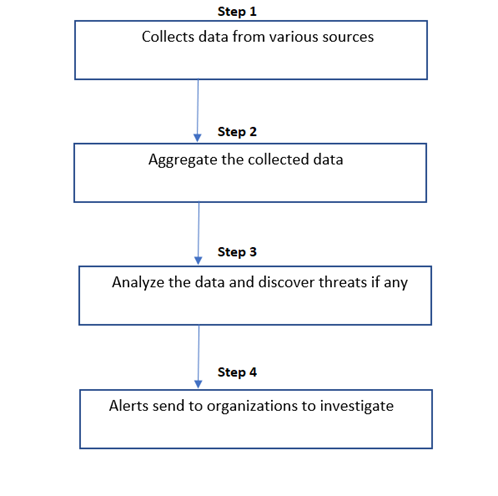
SIEM- Security Information and Event Management
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) is a software system that gathers security information from network devices, servers, domain controllers, and other sources. SIEM collects, maintains, aggregates, and analyses data in order to spot trends, detect dangers, and help enterprises investigate any alarms.
Step 1: Collect the data from various field devices
Step 2: Combine the collected data
Step 3: Analyze these collected data and check there is any threats are there
Step 4: If any threats are found, alerts the authorized person ASAP.
Patch Management
The process of distributing and applying updates to the software after their initial release to solve security issues is called Patch management. These patches are very necessary to make the software error-free and it also referred to as “vulnerabilities” or “bugs”.
Usually, patches are needed for operating systems (OS), various applications, network equipment, etc. After finding the bugs or vulnerabilities in software, a patch can be used to fix it.
Antivirus Management
Installing good antivirus software protects almost every threat on your computer. It automatically updates and scans the machine regularly which helps to find any threats in your system and let know the user if any threats are found.
Benefits of Antivirus
- Consistent security
- Continuous Monitoring and quick response
- Cost-effective
Solutions available in Cyber ??Security for Industrial Automation
The Various types of Cyber security solutions are
Cyber & Malware attack
Anti-malware software is recommended to prevent malware attacks. If this software is installed on a computer then it will help us to find and remove the malware’s if there is any on our machine and it also prevents malware attacks in the future.
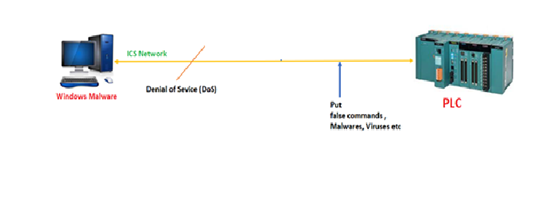
What is DOS and how to prevent it?
DoS or Denial of Service attacks are one of the best attacks since they take down target machines, making it difficult to access their locations or use their online services. Keeping more bandwidth capacity is the simplest approach for countering DoS attacks. If you’re concerned that your company might be a target for DoS attacks, simply maintaining enough server capacity to handle the increased traffic activity can keep the attacks away. Third-party administrations can also help your firm stay online during a DoS attack.
Phishing and the prevention for Phishing assaults
In a phishing attack, a hacker tries to get personal information from you by tricking you into giving it to them. Hackers who are more adventurous may attempt to steal a victim’s government-managed data. A recent phishing attack used Google Docs to trick users into entering their Google login credentials.
The easiest and efficient way to prevent phishing attacks is to make sure the users are aware of both how normal and harmful an attack can be, remind users to keep extra care while checking emails and report any email that has been found suspicious. Apart from this, make sure users are using security features like two-factor authentication for their email accounts.
Cyber security in Industrial Automation and Industrial Control Systems :
Cyber security describes how industrial automation and control systems (IACS) protect themselves from unforeseen events, actions, opportunities, or attacks. Accidents can happen anywhere, including the Internet, company systems, program evaluations, and unauthorized access, and they can have a major impact on health, safety, and the environment.





