Table of Contents

What is an HVAC System?
- HVAC system stands for Heating, Ventilation, & Air Conditioning systems.
- HVAC is a form of an automation system that is used to regulate the air quality and thermal comfort supplied to individuals in the interest of their survival.
- Thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transmission are the basis of HVAC.
- HVAC is a type of automation system, compared to other automation systems available.
- This system warms and refreezes commercial and residential structures.
- HVAC systems are available everywhere such as in houses, and in submarines, to provide environmental comfort.
- These systems, which are growing increasingly popular in new buildings, draw fresh air from the outdoors to produce great interior air quality.
- The process of replacing or circulating air within a room is symbolized by the English letter V called ventilation in HVAC.
- This improves indoor air quality through the elimination of moisture, smoke, smells, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, carbon dioxide, and other pollutants, in addition to regulating temperature and replenishing oxygen.
How Does an HVAC System Work?
According to the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers, an HVAC system takes fresh air from the environment, cools or warms it, and then blows it into an indoor environment.
- An individual room or a whole building structure, such as a house, workplace, school, airport, or even a submarine, might be considered a space.
- A single component of an HVAC system may full-fill two functions.
- The home might have a separate air conditioner.
- Boiler or a heat pump that provides both cooling and heating.
What Does an HVAC System Include?
Heating Unit
- A General HVAC system includes a heating unit, a cooling unit, and a duct to transfer heated or chilled air.
- In most cases, a furnace may be employed as the heating unit in HVAC. The furnace’s efficiency is evaluated by its Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating, which indicates how often fuel is converted into heat irrespective of if it works on natural gas, electricity, or propane.
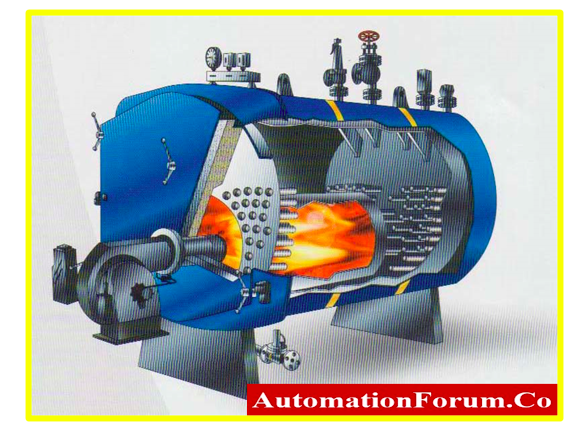
- A furnace with a 95% AFUE rating produces 95% of the fuel it consumes into heat.
- The required minimum AFUE rating is 80%.
- High-efficiency systems, such as those from Carrier, Bryant, and Goodman, have ratings ranging from 95% to 98%.
Cooling Unit

- HVAC systems also include a cooling unit, which is commonly an air conditioner.
- A heat pump that can both chill and heat the air is a cheaper choice in some locations where it does not get cold enough for a boiler.

- In any case, the cooling effect of these units is assessed by their Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), and the cold air they create is circulated throughout the home via ducting.
- For maximum energy efficiency, look for a unit with a high SEER rating. SEER ratings of 20 or above are required for the most efficient devices, while 13 is the minimum.
- An air conditioner must have a SEER rating of at least 14 to achieve the Energy Star certification from the United States government.
- Such systems can also involve ventilation systems that route air out of the house.
- Humidifiers or dehumidifiers control the humidity of the air.
- Air purifiers remove spores, germs, viruses, and other minute particles from the air.
- An HVAC technician can assist you in determining which of these additional components, if any, are appropriate for your needs.
What is Heating Process?
- In HVAC, the heating process is utilized to heat or warm a specific area or space. It employs components such as a boiler, and heat pump.
- It employs three primary heating processes. Such as conduction, convection, and radiation.
- It is essential in cold climates or regions where maintaining heat is essential to survival or any process.
- An HVAC system comprises some form of equipment to generate heat that is used to warm an internal area, such as a furnace, boiler, or heater pump.
- The equipment might be directed towards a specific room, zone, or entire structure. Heating equipment heats an area using various ways (conduction, convection, or radiation) and different types of resources, such as electricity, propane, heating oil, or natural gas.
What is Ventilation Process?
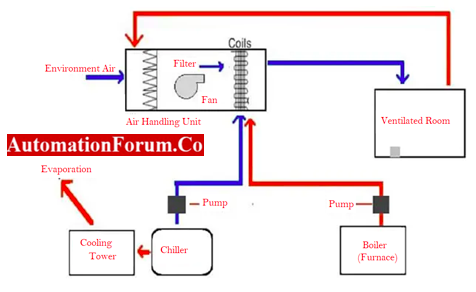
- The ventilation process in HVAC is utilized to maintain the airflow clean and regular, regardless of whether it’s outside or inside.
- Ventilation is a different system from heating and air conditioning, but it works together to maintain the airflow required to properly heat or cool a structure.
- It replaces interior air with outdoor air to ensure a constant supply of fresh air.
- This preserves the air fresh and the surrounding air quality.
- A sophisticated ventilation system is essential for effective HVAC.
- Depending on the heating or cooling system, ventilation can also help to filter the air or maintain the right amount of humidity.
- Car parking spaces are among the most common places where ventilation is employed. When the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by automobiles reaches a specific level, large vent fans are utilized to remove it.
- Adequate ventilation is particularly essential in data centers, where it works in tandem with air conditioning to keep IT infrastructure cool.
- Depending on the kind of equipment and the structure of the data center, a number of ventilation and cooling solutions are used.
What is Air Conditioning Process?
- The HVAC air conditioning process is used to cool a specific area or room.
- It involves the use of air conditioners, chillers, and cooling towers.
- It is required in hot and humid regions or locations where cooling and humidity are essential to survival or any process and must be carefully managed.
- A sophisticated ventilation system is essential. An HVAC system is made up of technology that cools the circulating air. The approach for cooling could differ substantially throughout corporate areas.
- Air conditioning equipment might be located within the building or outside, such as on the roof.
- It may also use water instead of coolant to regulate temperatures. When it is used along with an air conditioning system,
- It may also filter the air and regulate humidity for effective HVAC.
- Data centers depend extensively on air conditioning to guarantee that their IT infrastructure can operate effectively, employing a combination of cooling and ventilation methods.
Classification of HVAC
Each HVAC system has its own characteristics based on a home’s heating and cooling requirements, location, age, existing ductwork, heating and cooling requirements, and other considerations. As a result, an HVAC can adopt a wide range of forms.
HVAC Systems are classified as
- Split system
- Hybrid heat pump
- Ductless mini-split
- Ducted mini-split
- Packaged system
Split System
- A split system, commonly known as a forced-air system, includes one unit inside the home as well as one outside.
- This configuration can include a boiler and an air conditioner, an air handler and a heat pump, or a boiler and a heat pump.
- The ideal setup for your home will be determined by where you reside. For example, in extremely cold areas, the furnace and heat pump combination works well.
Hybrid Heat Pump
- The central heating system in this case comprises an electric heat pump that cooperates with a boiler.
- The heat pump warms the home during warmer seasons such as autumn and spring. When the weather is too cold for a heat pump to function correctly, the boiler swings in.
- This hybrid model, often termed as a dual-fuel system, saves a lot of money because a heat pump costs less to heat a home than a furnace.
Ductless Mini-Split
- According to the Air Conditioning, Heating & Refrigeration Association, a ductless mini-split network comprises an outdoor unit that contains the compressor and condenser and an interior air handler installed to storm the cool air.
- This kind of ductless system is usually used in smaller places such as garages and workshops where a conventional split system is not essential.
- They are not suitable for whole-house applications.
- These systems are typically simple enough for homeowners to install themselves.
Ducted Mini-Split
- A ducted mini-split system transports air into a room from an outdoor compressor and condenser through tubes instead of larger ducts.
- This technique is perfect for buildings with limited space for standard ducting.
- When compared to ductless mini-split systems, ducted mini-splits offer better air circulation.
Packaged System
- A packed system involves the conventional split system components. All units, therefore, are located externally.
- This method is perfect for residences that do not have sufficient size inside for a heating unit.
- Though you might have the space for a split system, you might want to select a packaged system because it’s quiet (everything is placed outside the home) and has cheaper installation costs for installing a single unit.
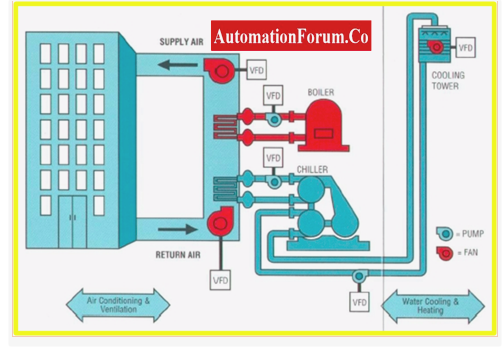
Components of HVAC System
An HVAC System includes
- HVAC Water Chillers
- HVAC heaters
- Hot water generator or furnace
- Chilled water pumps
- Cooling water pumps
- Motor Control Centre
- Cooling Towers
- Piping for refrigerated water or condenser.
- Valves for refrigerated water,& cooling water
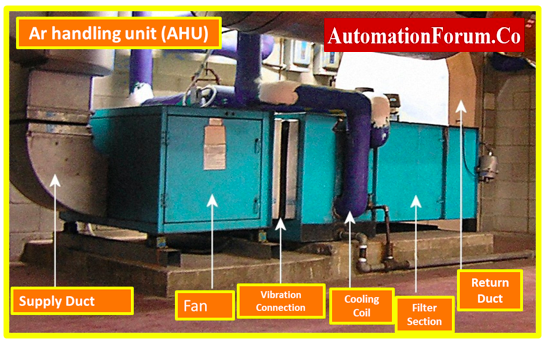
- Air handling units (AHUs),
- Heating coils and cooling Coils
- Ducts in the Ventilation System
- Fan Coil Unit and Thermostats
- HVAC Diffusers and Grills
- HVAC Control & Instrumentation System.
- HVAC Software
What is the difference between HVAC and AC?
- HVAC stands for “Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning” and refers to a system that is used to control the temperature, humidity, and air quality in a building or other enclosed space. HVAC systems typically include both heating and cooling components, as well as ventilation and air filtration systems.
- AC, on the other hand, stands for “Air Conditioning” and refers specifically to the cooling component of an HVAC system. AC systems use refrigerants to cool and dehumidify the air in a space, and they are often used in conjunction with heating systems to provide year-round temperature control.
- In summary, HVAC is a comprehensive system that includes both heating and cooling, while AC specifically refers to the cooling component of an HVAC system.





