- What is DP flow meter?
- To troubleshoot issues with a DP type flow transmitter, follow the methods listed below
- Problem-1: DP-type flow transmitter in an inactive mode without power
- Problem-2: Mismatch between field and PLC/DCS flow values
- Problem-3: The DP flow transmitter does not detect flow
- Problem-4: Unreliable value shown by a DP type flow transmitter
- Problem-5: Value fluctuations in DP type flow transmitters
- Problem-1: DP-type flow transmitter in an inactive mode without power
What is DP flow meter?
Differential-pressure flow transmitters are very common. Most of the time, a DP-type flow transmitter is used to measure the flow of liquids and gasses, which are clean.

DP flow solutions have two parts: a primary element that lowers the pressure and a secondary element (a DP flow transmitter) that measures the difference in pressure.
Differential pressure flow meters, which are sometimes called DP flow meters, use laminar plates, an orifice, a nozzle, or a Venturi tube to create an artificial restriction and then measure the pressure loss of fluids as they pass through the restriction. Bernoulli’s principle says that the drop in pressure across a restriction is equal to the square of the flow rate. The flow rate goes up as the pressure drop goes up. These tough, accurate meters are great for a wide range of clean liquids and gasses.
To troubleshoot issues with a DP type flow transmitter, follow the methods listed below
Problem-1: DP-type flow transmitter in an inactive mode without power
Potential Causes:
- There are a few things that could cause a DP type flow transmitter to lose power, such as a problem with the cable, fuse, or barrier.
- First, check the DP type flow transmitter’s cable connection.

- The right kind of lugs should be used for each connection. Then, use a properly calibrated multimeter to check the voltage.
- Refer the instrument loop drawing, Check the connections in the junction box and the marshalling cabinet if there is no voltage.
- If you find a problem, make sure the cables are tightened properly and/or that the plugs are in the right place.
- Check to see if the fuse in the marshalling cabinet is still good. If the fuse doesn’t work, replace it with another fuse with the same rating.
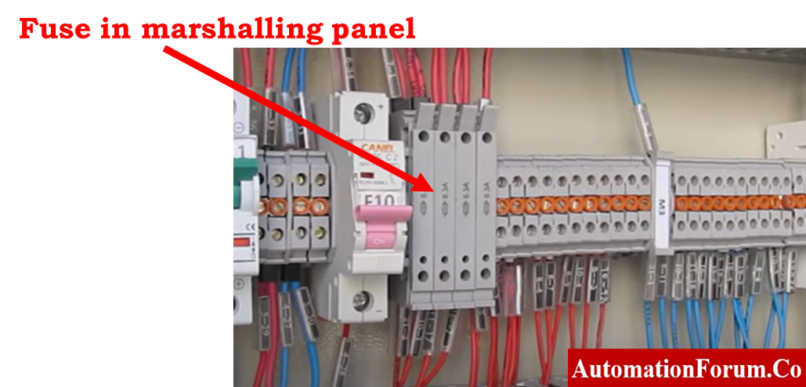
- Check on the barrier. Replace the barrier if it’s broken if it’s malfunctioning. Also, make sure the cable is in good condition.

Problem-2: Mismatch between field and PLC/DCS flow values
Potential Causes:
- The problem of flow value mismatch is often caused by inaccurate range setup on both sides, both in the PLC/DCS/SCADA and the field transmitter.

- Check both the PLC/DCS/SCADA and the field transmitter’s range.

- The flow transmitter’s correct range, which should be set up on both sides, will be listed on the data sheet.
Problem-3: The DP flow transmitter does not detect flow
Potential Causes:
- There may not be any flow in the pipe, therefore check the process system for sufficient flow.
- Possibility of isolation valve(s) being closed or equalization valve being opened, and put the valve(s) in the right place according to the procedure.
- Inadequate transmitter setup, and check instrument datasheet for flow configuration.
Problem-4: Unreliable value shown by a DP type flow transmitter
Potential Causes:
- Examine the condition of the process isolation valves on the flow transmitter of type DP.
- Both the HP side isolation valve and the LP side isolation valve should be open.

- Examine the manifold’s condition. The manifold’s equalization valve should be in the closed position.
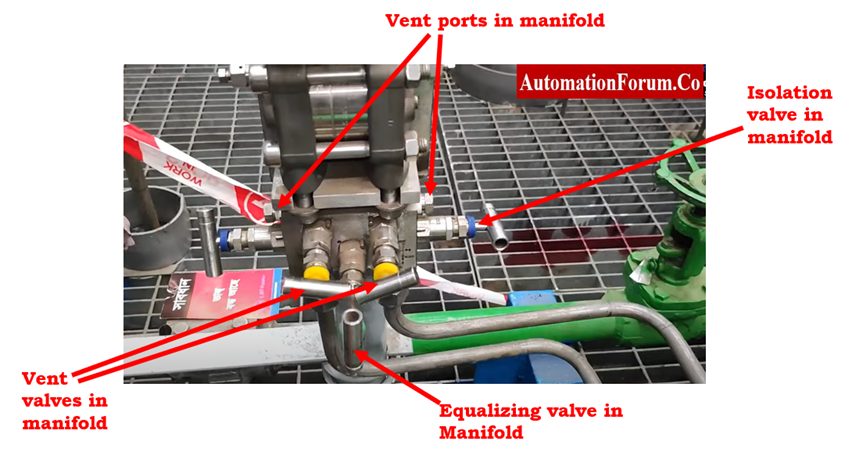
- In the manifold, both of the isolation valves should be open. It is important to correctly fix the vent ports in the manifold.
- Each tubing connection should be examined. All of the fittings have to be leak-free. There shouldn’t be any ruptured tubes. To find the leak, use a snoop liquid leak detector (or any other leak detector).
- After properly isolating the DP type flow transmitter, fix any major or minor tube leaks and/or replace punctured tubes.
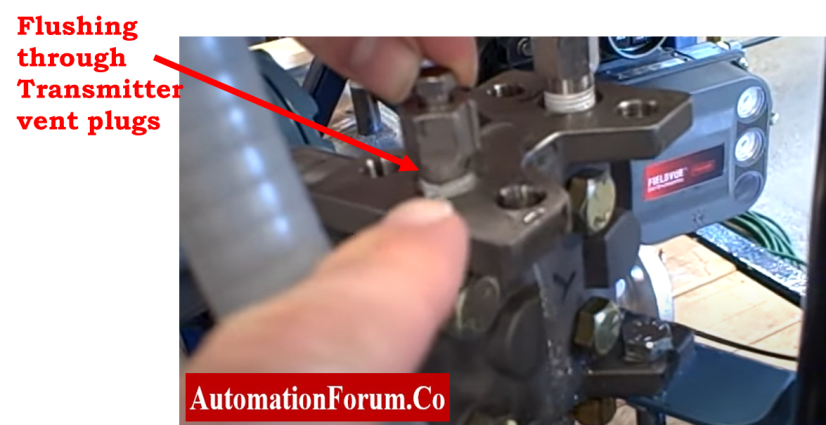
- The tubes can also be clogged. To properly clear out the tube, you need to flush or flush with the drain closed.
- If flushing the tube doesn’t work, you can unclog it with a pump. When using a pump to unclog a tube, the maximum pressure should be 1.5 times the pressure of the process fluid.
- Check whether the HP side of the transmitter is connected to the HP side of the tapes in the line.
- Additionally, make sure the transmitter’s LP side is attached to the LP side of the tapes in the line. If detected reversed, the tubing connection must be corrected.
- The value will not change if any forcing (bypass activation) is applied to either the PLC/DCS or the field transmitter. After receiving the necessary authorization or after completing the interlock restoration process, remove the force.

- A square root function should only be used on one side. Either the PLC/DCS or the field transmitter side. The flow value will be completely inaccurate if the square root is present on both sides.

- If the transmitter is still not reacting correctly, you may use a hand pump or a calibration test equipment, depending on the range, to test its responsiveness.

- Examine the condition of the orifice, venturi, pitot tube, or other basic sensing devices that are used to measure pressure. The line must be isolated for this reason.
- Utilizing the calibrating equipment, calibrate the DP type pressure transmitter; the device’s response will be found to be satisfactory.
- Verify all relevant settings, including LRV, URV, mA range, and device address, if applicable, in accordance with the DP type flow transmitter’s data sheet.
Problem-5: Value fluctuations in DP type flow transmitters
Potential Causes:
- Examine the impulse tubes for leaks. The reading of the DP type flow transmitter might potentially fluctuate as a result of minor tube leakage. Repair and arrest the leakage.
- Adjust the damping value in the transmitter.
- Flush the flow transmitter. The value of the flow will change as a result of any trapped air bubbles in the impulse line.