- What are the major functions of a manifold and when should we use this?
- What are the different types of manifolds?
- What is a 2-way manifold?
- How to use 2 way manifold?
- What is a 3-way manifold?
- How to use a three-way manifold?
- What is a 4-way manifold?
- What is a 5-way manifold?
- How to use a 5-way manifold?
- How to install a manifold to the transmitter?
- How to select a manifold?
- What are the advantages of manifolds?
- What are the applications of manifolds?
What is manifold?
A manifold can be described as a system of headers, branched piping, and valves. It can be used to gather the produced fluids or to distribute the injected fluids. The manifold must provide sufficient piping, valves, and flow controls to safely gather the produced fluids or distribute the injected fluids such as gas, water, etc. This device would be useful for the pressure instruments to do the measurements in the process instrumentation lines. If we utilize the valve manifold in equipment then this equipment can be easily removed for the maintenance and calibration process without shutting down the process.
What are the major functions of a manifold and when should we use this?
- It can reduce the pressure loss between the valves
- A manifold module can provide the interface between the production pipeline, flowline, etc.
- It can provide a safe and convenient method of isolating, blocking, bleeding, and calibrating instruments, meters, and pressure transmitters
- It can do the pressure isolation and equalization
- It can be used to do the differential measurement of the liquids and also it can be used to do the flow control
- It would reduce the cost and time which will be required to do the maintenance and installation of the equipment.
- It would come in handy while customizing the process line
- It can isolate an instrument from the process
- On-site calibration
- It can connect more than two valves so it can be used in confined space
- We can do the calibration of the instrument without shutting down the process
What are the different types of manifolds?
Block and bleed manifolds
It is mostly used for gauge and absolute pressure applications and it is connected to the process by male or female NPT. In this type the low-pressure port is vented to the atmosphere and the high-pressure port is connected to the process. In this type of manifold one valve provides isolation of the instrument and the other one allows for vent, drain, and calibration through the test port.
Conventional manifolds
These manifolds can be used when we need to mount the manifold in the side of the process flange. So this type is used when we don’t want to connect directly to the pressure transmitter sensor. The conventional manifolds are available in 2, 3, or 5-way types.
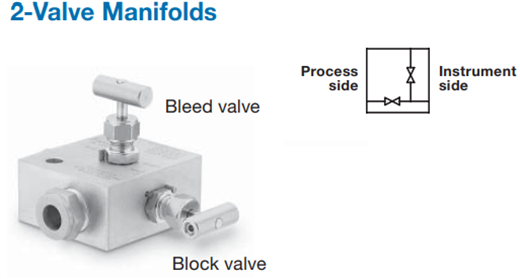
What is a 2-way manifold?
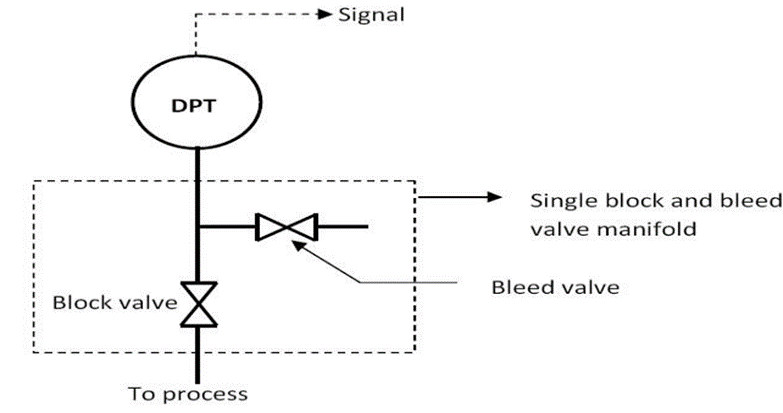
Two-way manifolds are used for Absolute, gauge, and high gauge pressure applications. One valve would provide the instrument isolation and the other one allows the vent drain calibration through the test port. These valves are used as a barrier between the line pressure and the instrumentation equipment. The second valve and the line would provide a vent connection to prevent the line pressure from being locked in the instrumentation and it could also serve as a calibration connection.
How to use 2 way manifold?
These manifolds are mostly used for pressure transmitter, it has one block valve and one test valve. So if we need to calibrate the pressure transmitter then we should close the block valve and then open the drain valve. Then we can connect the drain valve connection to the pressure generator to give the test pressure.
Applications
- Absolute
- Gauge
- High gauge
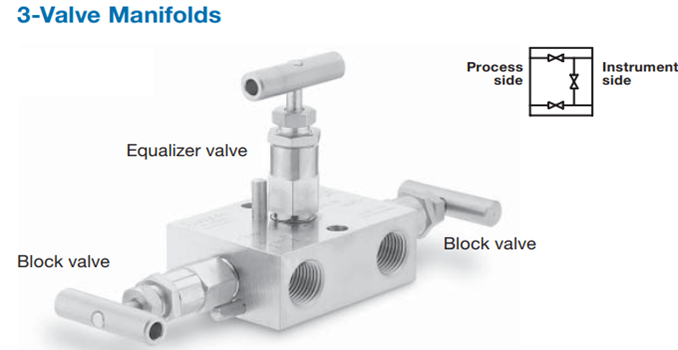
What is a 3-way manifold?
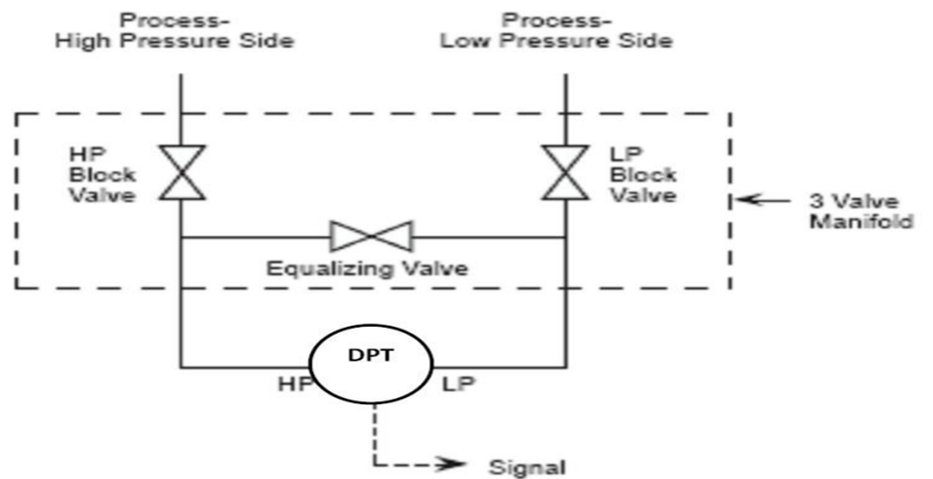
In this type, another valve is added which is the equalizer valve it would be useful for equating the pressure in the transmitter line in case of removing. This type of manifold can be utilized to connect the system impulse lines and the transmitters.
How to use a three-way manifold?
The three-way manifold is composed of two block valves and one equalizer valve. So if we need to check the zero of the differential pressure transmitter then, we need to close the block valve and then open the equalizing valve. This type doesn’t have a test connection.
Applications
- Differential pressure
- Draft range
- High static
What is a 4-way manifold?
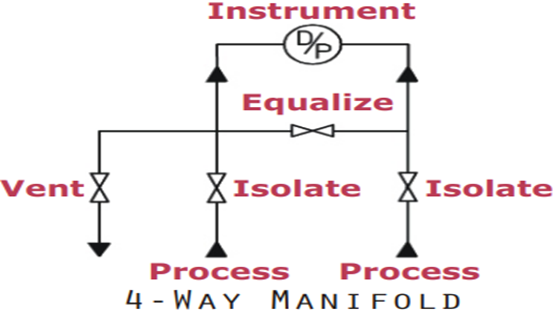
The four-way manifold is used when direct mounting of the differential pressure transmitter is required. These valves would contain two mainline block valves, a single vent valve, and a single equalizing valve configuration. These manifolds are ideal for static instrument applications.
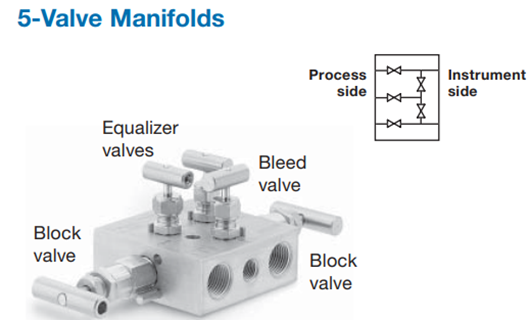
What is a 5-way manifold?
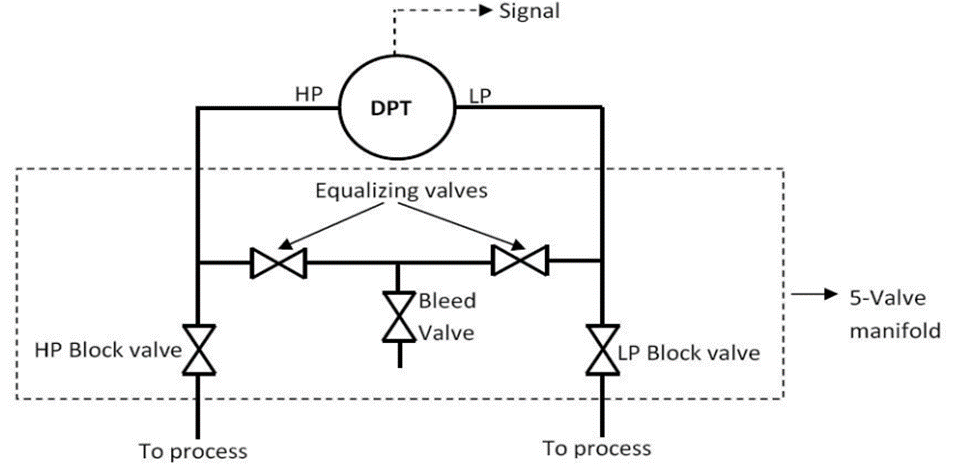
We can use a 5 way manifold for differential pressure transmitters and also these manifolds are designed for remote mounting. These manifolds are composed of two shut-off valves, two equalizing valves, and a vent/calibration assembly in a single assembly. Due to the double equalizing arrangement, these manifolds have very low measurement errors. So by using this manifold we can prevent the measurement error that could occur from equalizer leakage between the high and low-pressure connections. So these manifolds are suitable for custody transfer applications.
How to use a 5-way manifold?
The five-way manifold consists of 2 block valves, 1 equalizer valve, and 2 vents or test valves. So if we need to check the zero of the transmitter then, we need to close the block valve and then open the equalizing valve. If we need to calibrate the transmitter for three or five-point, then after the equalization of the pressure we need to connect the test valve to a pressure generator. This type of manifold is mostly used for the DP transmitter.
Applications
- Differential pressure
- Draft range
- High static
- Multivariable pressure
How to install a manifold to the transmitter?
At first, we need to bolt the manifold to the transmitter then finger tighten the bolts after that do a crossing pattern. First the initial torque value and then the final torque value. We must make sure the manifold which is used can withstand the temperature and pressure of the application.
How to select a manifold?
- We must check the inlet/outlet configuration
- Pressure and temperature ratings
- Packing type
- Disc configuration
- Manifold to system orientation
The manifold would have markings on it and these markings would show all the details mentioned below.
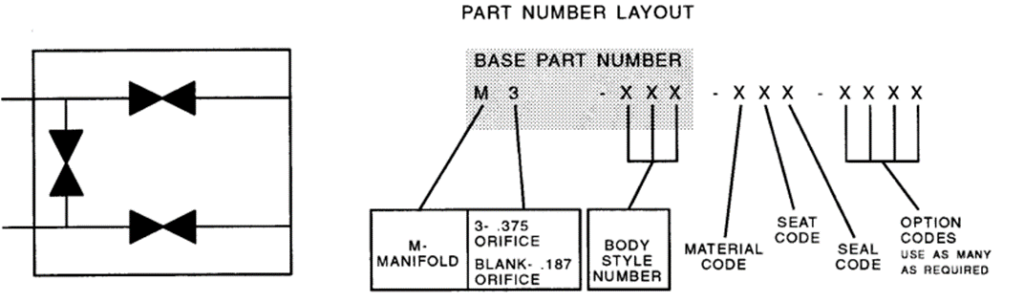
What are the advantages of manifolds?
- It can improve the efficiency of the process
- Pressure loss can be reduced
- Fewer fittings
- Larger diameter connections
- No long hoses or tubing
- Compact size
- System layout would be improved due to the fewer connections
What are the applications of manifolds?
- Oil and gas
- Chemical industry
- Power industry
- Wastewater
- Steel industry
- Pulp and paper industry





