In industrial automation, Profibus is an essential standard for ensuring seamless device communication. Examine essential Profibus interview questions and answers to gain a thorough understanding of this critical fieldbus protocol.
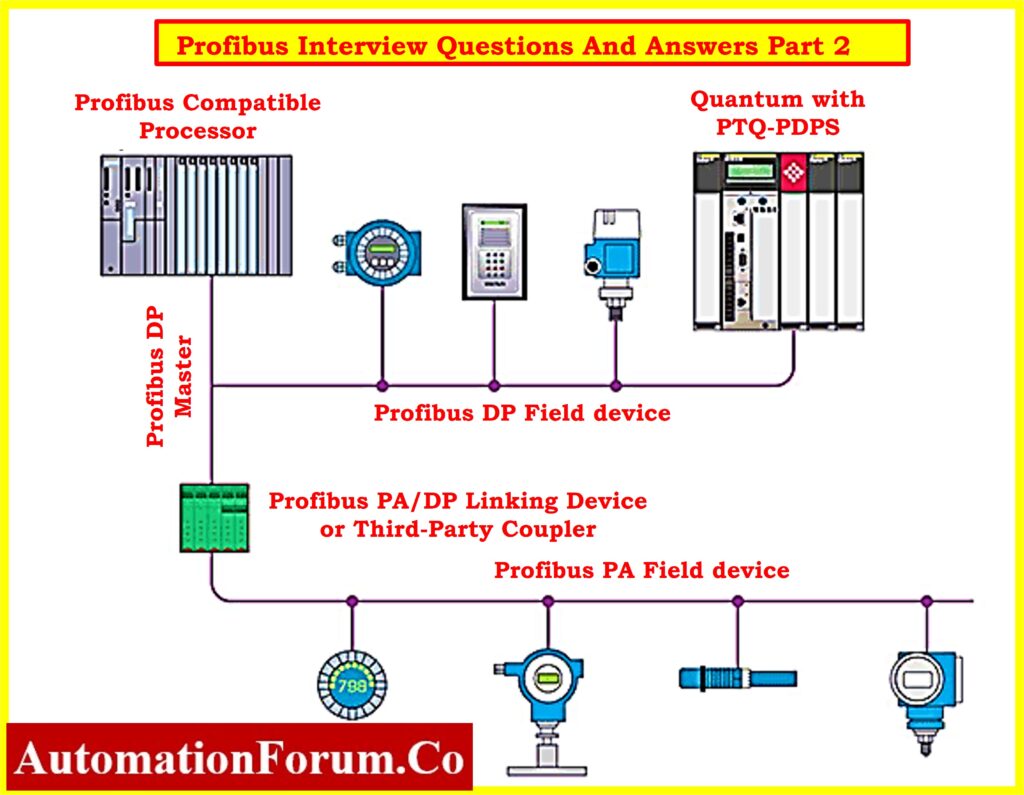
Profibus Interview Questions and Answers – Part 2
1. How is device failure handled by Profibus?
Diagnostic features on Profibus devices allow them to report malfunctions. Redundancy may be utilized in specific circumstances to ensure continuous operations.
2.Can you explain on Manchester Bus Powered’s (MBP) function within Profibus-PA?
Profibus-PA uses MBP technology, which enables power and data transfer over the same pair of wires.
3.How do Profibus network device diagnostics work?
Diagnostic messages are part of the data exchange process in Profibus. Devices offer diagnostic data that the master can interpret to facilitate troubleshooting.
4.In a Profibus network, what does a Class 1 master mean?
A Class 1 master performs an acyclic parameterization and diagnostics in addition to cyclic data exchange with slaves.
5.What constitutes a Profibus DP network’s fundamental components?
The communication link, which is usually a shielded twisted pair cable, the DP master, and the DP slaves are the fundamental components of a Profibus DP network.
6.In Profibus terms, what is an identifier?
An identifier in Profibus is a unique number given to a certain type of device. During the initial setup process, it is utilized to identify the type of device.
7.How does Profibus address conflicts in communication?
Because Profibus employs a token-passing protocol, conflicts are almost eliminated because communication can only begin from the master who has the token.
8.In a Profibus network, how can redundancy be achieved?
By establishing two parallel networks or devices, redundancy in a Profibus network can be accomplished, ensuring uninterrupted functioning in the event of a failure.
9.Can you define a Profibus token?
In Profibus, a token is an individual message type that provides a master the power to start a conversation. Communication is limited to the master carrying the token.
10.In Profibus networks, what are the usual sources of errors?
Faulty devices, wiring issues, improper termination, improper network configuration, and electromagnetic interference can all result in errors in Profibus networks.
11.What are the advantages of process automation with Profibus?
Advantages of Profibus-PA include seamless integration with high-speed Profibus-DP systems, intrinsic safety, power and communication over the same pair of wires, and more.
12.What function does a Class 2 master serve in a Profibus network?
In a Profibus network, a Class 2 master is usually used for configuration, commissioning, and diagnostics.
13.Can you explain on the significance of baud rate in a network using Profibus?
The network’s communication speed is determined by the baud rate. Faster communication is possible at higher baud rates, but network length is limited.
14. How is data security ensured by Profibus?
Error detection algorithms like Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) are included into Profibus. Additionally, it allows safety-related communication using the Profisafe profile.
15. What kind of equipment usually serves as the master in a Profibus network?
In a Profibus network, devices like Distributed Control Systems (DCS), PCs, and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) usually function as masters.
16. How does a set point function in Profibus?
A process’s desired outcome is called a set point. A slave device, such as a drive or controller, receives it often from a master.
17. How is interoperability supported by Profibus?
Profibus facilitates interoperability by using GSD files, which list each device’s features and functionalities, along with defined profiles.
18. What is a Profibus network’s normal topology?
Profibus networks normally have a line topology, however repeaters or hubs can also be used to create tree and star topologies.
19. Describe the various Profibus profiles.
Profibus profiles specify particular features and behaviors for various kinds of applications or devices. Examples are Profisafe for safety-related communication and ProfiDrive for drives.
20. How can a master of Profibus recognize a slave?
A slave’s unique address, which is set during network configuration, is used by a Profibus master to determine it.
21. How may a Profibus network be made longer?
Repeaters and fiber optic cables can be used to increase the length of a Profibus network.
22. In Profibus, what is acyclic communication?
In Profibus, acyclic communication refers to spontaneous or on-demand data interchange, which is frequently used for device parameterization or diagnostics.
23. In Profibus, what is cyclic communication?
In Profibus, “cyclic communication” refers to recurrent, regular data interchange that takes place at predetermined intervals and is usually utilized for data processing.
24. In a Profibus network, what kinds of signals are transmitted?
Profibus represents several forms of process data through the transmission of both digital and analog signals.
25. How is synchronization in multi-master systems handled by Profibus?
Profibus employs a token-passing protocol in multi-master systems to ensure that every master has a turn communicating, maintaining synchronization.
26. Could you describe how the RS485 standard is used by Profibus?
RS485 is commonly used by Profibus-DP for data transfer. Balanced data transmission that is resistant to electromagnetic interference is made possible via RS485.
27. What function does a watchdog serve in Profibus?
A safety feature that keeps a close watch on how a device or network is operating is called a watchdog. It can enter a safe state if it detects a problem.
28. Is it possible to use Profibus in hazardous environments?
Yes, hazardous environments are intended for the usage of Profibus-PA. It makes use of the Fieldbus Intrinsically Safe Concept (FISCO) to ensure secure communication and power.
29. In Profibus, what is the freeze mode?
When configuring or troubleshooting a device, the freeze mode is a unique condition where the output remains constant.
30. How does a master of Profibus manage several slaves?
Using their addresses, a Profibus master communicates with each slave individually. The master controls the order and timing of communication.
31.How can a Profibus network’s performance be observed?
The diagnostic features of the Profibus devices themselves or tools such as ProfiTrace can be used to track performance.
32.How is lost data handled by Profibus?
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) is a feature of Profibus that helps identify data transmission faults. The data can be retransmitted in the event that an error is found.
33. Is it possible to combine Profibus with other networks?
Yes, gateways or proxies can be used to interconnect Profibus with other networks, such Ethernet or Profinet.
34.What does a Profibus watchdog timer do?
A watchdog timer is a fail-safe feature that, in the event that a device doesn’t behave or respond according to plan within a certain period of time, reaches a safe state.
35. How are communication faults handled by a Profibus master?
A Profibus master has the ability to ask for data to be retransmitted if it finds a communication problem. Device diagnostics can also be used to identify and resolve the problem.
36.In Profibus, what is a sync telegram?
In Profibus, a sync telegram is used to synchronize the actions of several devices so that they function simultaneously or in a coordinated manner.
37. How is functional safety supported by Profibus?
Through the Profisafe profile, providing fail-safe communication for safety equipment, Profibus enables functional safety.
38.In Profibus, what does a slot time indicate?
In Profibus, a device’s rights of access to the network are defined by its slot time. This ensures that there is orderly network communication.
39.How can a Profibus device’s firmware be updated?
Software tools supplied by the device the supplier are typically used to upgrade the firmware of Profibus devices via a DP master.
40.What factors need to be taken into account while grounding a Profibus network?
In order to prevent ground loops, profibus networks should be grounded at one point. Usually, grounding is done via the Profibus cable’s shield.
41.How does a bus fault in a Profibus network impact a network?
In a Profibus network, a bus fault could cause problems with communication, resulting in control or data loss. Device malfunctions or wiring problems are among the possible causes.
42. In Profibus, what is the function of a bus terminator?
At both ends of a Profibus network, a bus terminator is used to match the cable’s impedance and stop signal reflections, which can lead to data errors.
43. What does a Profibus alarm mean?
A Profibus alarm is a signal that a device sends out to indicate an error or unusual state. Usually, the master handles it and might make the necessary corrections.
44. What can Profibus’ auto-baud rate detection mean?
With auto-baud rate detection, configuration and integration are made easier by allowing a Profibus device to detect the baud rate of the network when it is connected.
45. Are wireless Profibus networks possible?
When wired connections are used in normal Profibus networks, wireless solutions can be achieved by using wireless gateways or bridges.
46. How is device initialization handled by Profibus?
In Profibus, device initialization is managed by the master, which during startup sets the device’s parameters based on its GSD file.
47.Can SCADA systems be integrated with Profibus?
Yes, centralized monitoring and control are possible when Profibus is coupled with SCADA systems via a gateway or a PLC with Profibus capabilities.
48.In Profibus, what does passive bus topology mean?
Devices connected to the bus through branches are known as passive bus topologies. This is a common topology in Profibus-PA.
49.In Profibus, what is a broadcast message?
A master’s message transmitted to all slaves is called a broadcast message in Profibus. It’s used for data or commands that are universal across all devices.
50.Is it possible to utilize Profibus for motion control?
Yes, motion control is possible with Profibus. For example, the ProfiDrive profile provides an integrated platform for managing drives.
51. How does Profibus ensure device compatibility?
Profibus uses GSD files and standard profiles to ensure device compatibility. A device’s qualities and characteristics are described in a GSD file, which makes it possible for the master to interact and operate it correctly.





