Table of Contents
- What is Serial Communication?
- What is RS-232 Communication Protocol?
- Features of RS-232 Communication Protocol
- Disadvantages of RS-232 Communication Protocol
- What is RS-485 Communication Protocol?
- Features of RS 485 Communication Protocol
- Electrical characteristics of RS-485 Communication Protocol
- Advantages of RS-485 Communication Protocol
- Disadvantages of RS-485 Communication Protocol
- Applications of RS232 and RS485 Communication Protocol
- Main Differences between RS232 and RS485
- Difference between RS 232 & RS 485 Communication Protocol in tabular column
RS-232, RS-422, RS-423, and RS-485 are physical layer serial communication protocols and are used as universal device interfaces. Serial interfaces are extensively used in electronics and embedded systems for remote acquisition of device data or remote control.
What is Serial Communication?
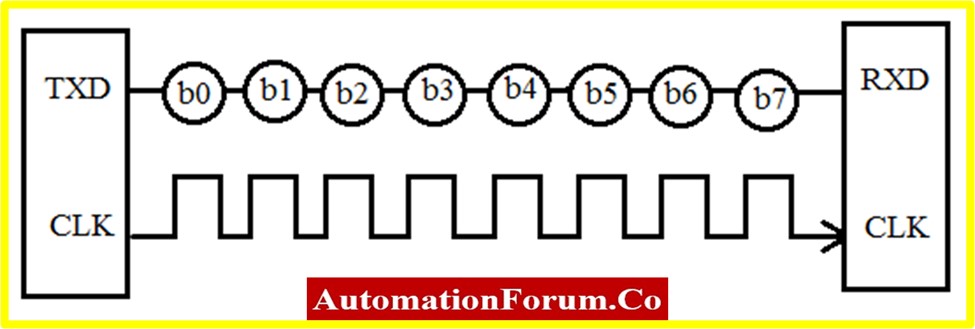
- Serial Communication in telecommunication is defined as the task of sequential data transmission over a computer bus.
- Here, the data is transmitted bit by bit at a time.
- RS-232 and RS-485 are serial interface standards; these standards describe transmission media as a defined set of logic levels, data rates, and timings.
What is RS-232 Communication Protocol?
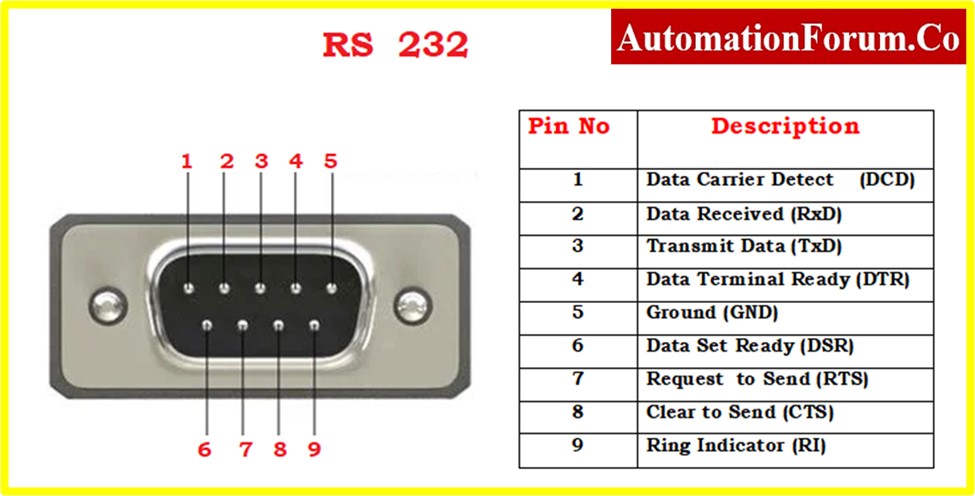
- The term RS-232 stands for “Recommended Standard 232”
- The original number is EIA-RS-232,
- The RS-232 interface was established by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA).
- RS-232 interface acts in accordance with the interface standard for serial data communication.
- RS-232 is universally used in computer serial interface peripheral connections.
- The data transmission rate of RS-232 is 50, 75, 100, 150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 baud per second.
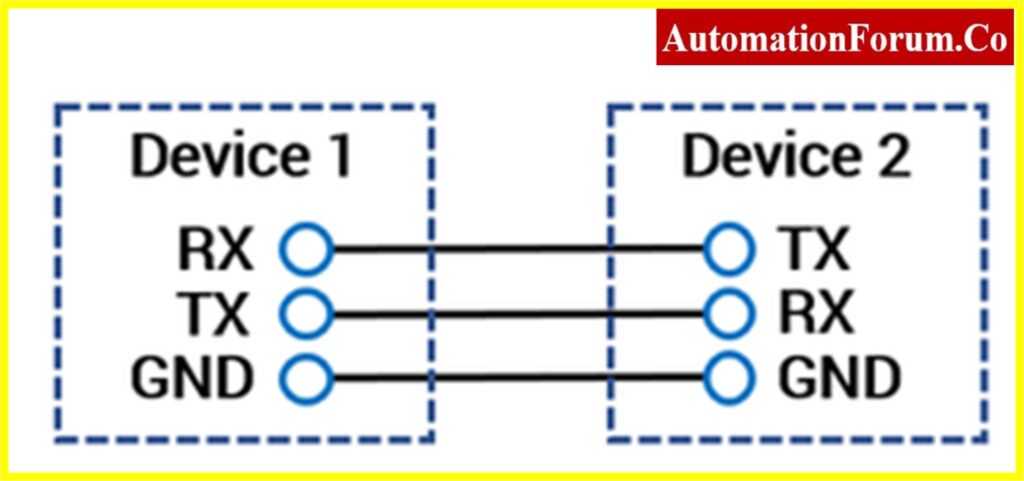
- RS-232 is the simplest form of Serial Communication between two interfaces to bridge two devices normally in medium distance.
- RS-232 can only connect between one transmitter and one receiver.
- In RS-232, the Device 1 Transmitter is linked to the Device 2 Receiver, or vice versa.
- The cable that is used to bridge Device 1 and Device 2 is constructed by using parallel wires or a twisted pair, but the length must be less than 50 feet.
- Both lines are single-ended through ground reference.
- The majority of serial communication devices make use of Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART) integrated circuits to accomplish a communication protocol that transmits 8-bit data through a specified set of start-bits, stop-bits, and parity-bits at defined data rate
- The data is transmitted as ASCII characters with a baud rate of 4800 to 115.200
Features of RS-232 Communication Protocol
- RS-232 is a type of the mainstream serial communication interface.
- Due to the early appearance of the RS-232 interface standard it is unpreventable that there is an insufficiency.
- It has a maximum signal level interface: Due to this, there is a possibility of interface circuit chip damage. The signal line RS-232 interface RS-232 interface is in a negative logic relationship. Since the voltage at logic “1” is -3V to 25V. & the Voltage at logic “0” is +3V to +25V with a noise margin of 2V. Here the receiver is essential to realize the signal of more than +3 voltage as logic “0”, & the signal of below -3 voltage as logic “1”.A Transistor to Transistor Logic level of 5V is a positive logic, & 0V is a negative logic. In this case, we need a level-shifting circuit to link to the TTL circuit which is not compatible with the TTL level.
- Low Data Transmission Rate: The bit rate or data transfer rate is 20Kbps in Asynchronous data transmission, for 51 complex programmable logic device (CPLD) development boards the integrated program baud rate must be 19200.
- This interface makes use of a signal line and a signal return string to establish a common ground transmission form. This standard ground transmission is susceptible to common mode interference, so the noise immunity is weak.
- Limited distance of transmission, it has a maximum transmission distance of about 15 meters (50 feet).
Advantages of RS-232 Communication Protocol
- Very widely use
- Low complexity
- Supports full duplex
- Widespread Compatibility
- Low Cost
- Reliable for Low-Speed Applications
Disadvantages of RS-232 Communication Protocol
- Only supports communication between two devices
- Only works over short distances
- Relatively susceptible to noise
- Inefficient for Multicast Communication
- Obsolete for Many Applications
- Limited Number of Devices
- Low Data Transfer Rates
What is RS-485 Communication Protocol?

- The official name of RS-485 is TIA/EIA-485.
- RS-485 is a bi-directional multi-drop interface that permits data transmission through multiple wires.
- RS-485 was originated to maximize the distance and data limits and to nullify the drawback of RS-232 one-way communication over a 2-Wire interface.
- RS-485 is much faster compared to RS232.
- RS485 makes use of differential signaling for data transmission, which means it uses two wires to transmit signals of opposite polarity.
Features of RS 485 Communication Protocol
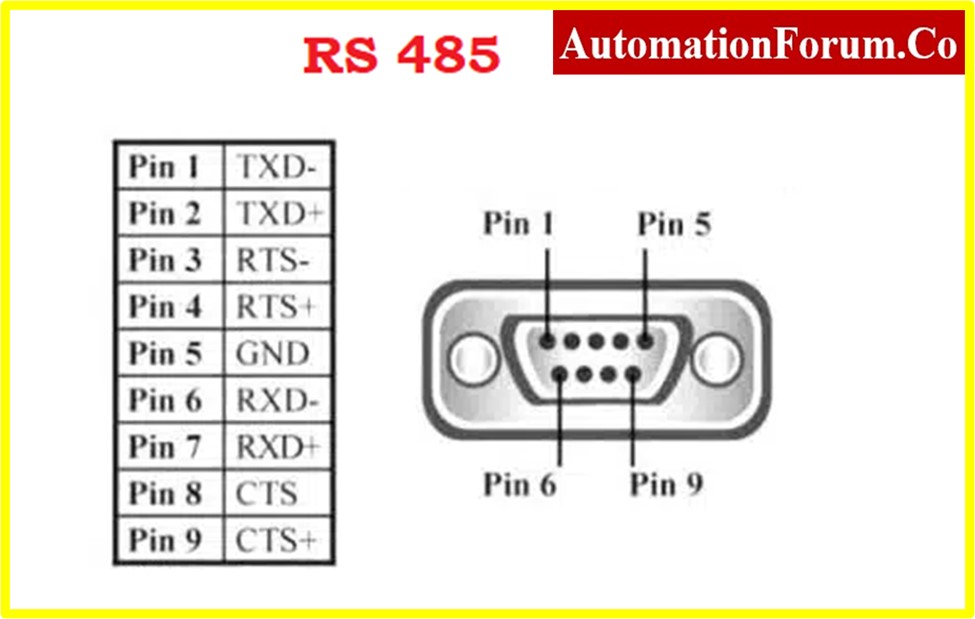
- RS-485 is appropriate for multi-point interconnection hence it saves several signal lines.
- The data transmission rate of RS-485 is high about 10Mbps
- The RS-485 serial bus is extensively used for long communication distances over several kilometers.
- RS-485 might reject common-mode interference through balanced transmitters and differential receivers.
- The sensitivity of the RS-485 bus transceiver is high so that it can detect the voltage signal below 200mV through sensitivity.
- The mode of operation of RS-485 is half-duplex.
- RS-485 transmits only one point at a given time.
Electrical characteristics of RS-485 Communication Protocol
- The interface signal level of RS-485 is lower than RS-232-C.
- Logic 1 or 0 is defined by the voltage difference between the two lines
Logic 1: If the voltage difference between the two lines ranges between +2V to +6V.
Logic 0: If the voltage difference between the two lines ranges between -6V to -2V.
- RS-485 is compatible with the TTL level, which is appropriate to link with the TTL circuit.
- The maximum transmission distance of the RS-485 interface is about 3000 meters.
Advantages of RS-485 Communication Protocol
- Assists several devices on a single bus.
- Less susceptible to noise than RS-232
- Works over longer distances
- Supports faster transfer speeds than RS-232
- Widely Used in Industrial Automation
- Reliable for Outdoor Use
- Standardized Protocol
Disadvantages of RS-485 Communication Protocol
- Not as widely used as RS-232
- Requires termination resistors
- Only supports half-duplex
- Complex Wiring
- Synchronization Required in terms of baud rates and communication protocols
- Susceptibility to Ground Loops
Applications of RS232 and RS485 Communication Protocol
Common applications of RS232 and RS485 are
- Scientific Equipment
- Industrial Wireless Controls
- Computers
- Robots
- Medical Equipment, Etc.
Main Differences between RS232 and RS485
- Immunity to Electrical Noise and Ground Potential
- No. of Transmitters and Receivers
- Data Transmission Speed
Difference between RS 232 & RS 485 Communication Protocol in tabular column
| Specifications | RS 232 Communication Protocol | RS 485 Communication Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage System | Voltage level-based | Differential |
| Actual Devices on single Line | 1 Transmitter, 1 Receiver | 32 Transmitters, 32 Receivers with only one transmitter active at a time |
| Line Configuration | Point-to-point | Multi-drop |
| Maximum Operational Distance | 15M (50 Feet) | 1,200M (3000 Feet) |
| Data Transmission Rate | 1MBit/s | 10MBit/s |
| Mode | Full Duplex | Half Duplex or Full Duplex |
| Output Voltage (Max) | +/-25V | -7V to +12V |
| Receiver Input Resistance | 3 to 7 k? | 12 k? |
| Receiver Input Voltage | +/-15V | -7V to +12V |
| Receiver Sensitivity | +/-3V | ±200mV |
| noise immunity | noise immunity is less | noise immunity is high |
| Signaling | uses single-ended lines or unbalanced signaling | uses a balanced differential signaling technique |
| Signal Wires | Two: TX (transmit) and RX (receive) | Two: A and B (differential pair) |
| Ground Reference | Shared ground reference | Common ground reference for all devices |
| Data Rate (Baud Rate) | Typically lower (up to a few Mbps) | Typically higher (up to 10 Mbps or more) |
| Applications | Legacy applications, short-distance point-to-point communication | Industrial automation, building automation, HVAC control, access control, outdoor applications, long-distance multi-point communication |





