- What kinds of materials are used for making instrumentation cables?
- Low Smoke Zero Halogen
- Characteristics of Zero Halogen Cables
- Polyurethane(PU)
- Most important characteristics of polyurethane cable
- Polyethylene (PE) and Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Insulation
- What is cross-linking in Polyethylene Cable?
- Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Steel Wire Armor
- What are commonly used armor materials in steel wire armor?
- Conductor
- Metal Braid
- Main purpose of cable braiding
- Metallic Tape
- What are the three main components of an instrumentation system?
- What type of Cables are used in Instrumentation?
- What is an instrumentation cable?
- What wire is used for instrument cables?
- How to select an instrumentation cable Guide for Process Instrumentation?
- Compare Power Cable and Instrument Cable
An instrumentation cable is an essential component that plays a significant part in most power plants and in process industrial sectors. The instrumentation cable conveys electrical signals of the lower level to and from electronic controllers to indicate, regulate, & monitor these electrical signals.
Generally, an instrument cable is considered the best cable for efficient signal transmission, because this cable offers higher protection against electrical interference.

What kinds of materials are used for making instrumentation cables?
- Instrumentation cables can be manufactured from various materials, usually, this depends upon insulation material & Shielding.
- Usually, instrumentation cable is made by using several non-conductors for low-energy transmission.
Low Smoke Zero Halogen
- Zero Halogen materials like Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl2), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I), & Astatine (At) makes an instrument cable highly durable.
- In making these cables, the amount of these halogens used is of minimum quantity. For Example, Poly-urethane, Poly Vinyl Chloride ingredient halogens in cable insulation that do not emit smoke and have fewer halogens during burning.
- This type of insulation in instrumentation cables is essential to assure human safety from dangerous hazards.
- Here it is important to consider the installation of this type of cable in a region where safety is predominant to avoid the emission of toxic and corrosive substances and to minimize the emission of smoke in an occurrence of a fire.
Characteristics of Zero Halogen Cables
The essential characteristics of zero halogens cables are
- These cables do not emit toxic & corrosive substances.
- Prevent pollution in the environment.
Polyurethane(PU)
- Polyurethane(PU) is also a type of insulating material that is suitable for applications where the cables are subjected to minimum mechanical load.
- Compared to rubber, these Polyurethane cables exhibit better resistance to chemical reactions.
- The following are the best chemical characteristics
- Better resistivity against mineral oils, many solvents, & non-alcoholic benzene
- Provides better resistance when stored in water.
- This polyester-based polyurethane cable may come in danger of decomposition via microbial activities for being exposed to heat or moisture for a long period of time.
Most important characteristics of polyurethane cable
- It has good tensile strength,
- Better bending radius,
- Higher flexibility at low temperatures, and
- Good resilience.
Polyethylene (PE) and Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Insulation
- Polyethylene (PE) is a polymer made of thermoplastic substance widely used as insulating material in instrument cables.
- This Polyethylene is a type of insulator with three-dimensional molecular bonding structures, & is considered superior heat, & moisture resistant.
- The fiber can withstand any type of catastrophe or disaster including UV exposure.
- The cable construction consists of stranded copper conductors similar to PVC cables to provide better electrical conductivity.
What is cross-linking in Polyethylene Cable?
- Cross-linking in Polyethylene cable is a chemical reaction where polymers chain to form a kind of three-dimensional network.
- After cross-linking the chemical properties of the polymer differs
- Here, the cable insulation in this polyethylene is made from XLPE that resists temperature above 90 Degrees Celsius.
- But, polyethylene is a thermoplastic material that resists a limited temperature of around 70 Degrees Celsius
- A cable bending scratch exceeds 15 times its outer diameter.
Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Poly Vinyl Chloride is a thermoplastic insulating material,
- Usually, this Poly Vinyl Chloride material is prepared by a chemical process called polymerization of several polymers.
- Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC) insulated cables are the ideal option, & are used over a wide range in every industrial sector because of their idealized properties.
- This PVC offers better resistance to flames, fires, water, and heat, and is tough & powerful to abrasions and moisture.
- The weight of PVC is very light compared to others, and resistant to corrosion, weather, and chemicals.
- To provide a better performance, these PVC cables must be reliable, with high tensile strength,
- These PVC cables offer maximum protection against electromagnetic interference.
- PVC cables are suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Steel Wire Armor
- Steel wire armored cable is composed of steel wire conductors of high strength, assembled with a layer of insulating material.
- To increase the mechanical strength of the cable, this mechanical armored layer needs to be added to any cable structure.
- Armor enhances the ability of its anti-erosion and is suitable for rough environments.
- The armor safeguards the conductor from the cause of mechanical impact.
What are commonly used armor materials in steel wire armor?
- Commonly used armor materials in steel wire armor are Steel threaded wire, steel tape, and aluminum tape.
- The permeability of steel tape and steel wire armor layer is very high, and exhibits excellent magnetic shielding effect, to prevent low-frequency interference.
- The steel wire armored cables yield better mechanical strength and anti-erosion properties.
Conductor
- Basically, conductors are the substance that allows something to pass through them.
- Conductors are the kind of materials used in making Instrumentation cables.
- Copper, Aluminum, & Steel are considered good conductors since they offer better conductivity, & are highly durable
Metal Braid
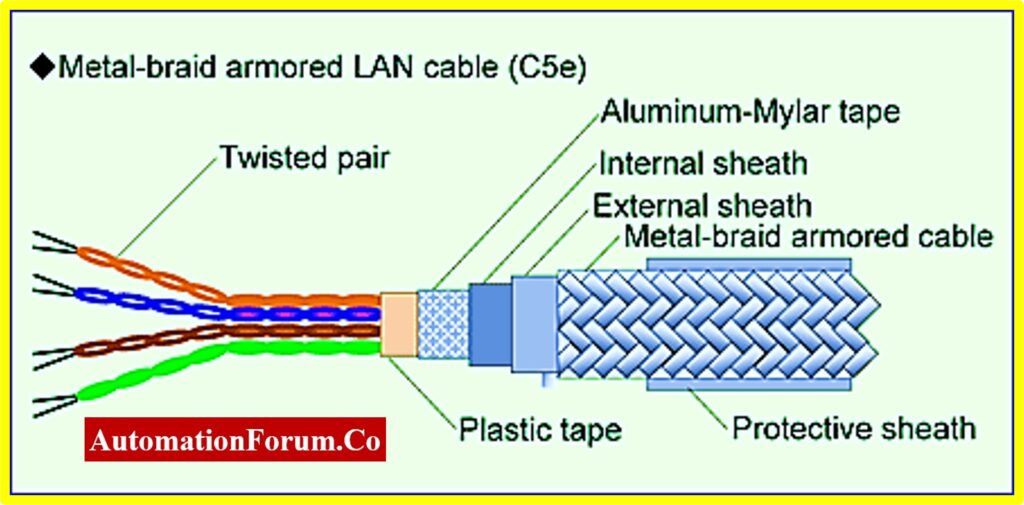
- Braiding resembles interlaced threads that permit metal braid to bend and stretch without twisting it.
- Metal Braid is manufactured by conductors such as copper, tinned copper, or aluminum that offer excellent electrical conductivity, & deliver an electrostatic shield for signal integrity protection.
Main purpose of cable braiding

- To protect the cable from electromagnetic interference.
- To provide better mechanical strength.
- Metal braid maintains the flexibility of the cables.
- Braiding safeguards the cable from hot surfaces and abrasion.
- It prevents damage from laboratory animals like mice, and squirrels.
Metallic Tape
- Along with Metal Braid, this Metal tape is used as an alternative source.
- Silver plated copper furnishes excellent protection against high frequency hence it is the most common material.
- On the other hand, this metal braid shelters about 70 to 90% of the cable.
- Mica-coated cable uses mica tape as an insulator.
- Its conductor is swaddled with insulating tape and the fiberglass strands are stranded on the above surface of the mica tape, & shielded with Poly Tetra Fluoro Ethylene or space resin.
- This Mica tape cable resists a temperature of up to 500°C.
- Since this Mica tape offers better resistance to high-temperature insulators,
- Mica tape also offers better electrical cable, incredible heat resistance and good dielectric strength.
What are the three main components of an instrumentation system?
An instrumentation system includes
- The sensor,
- Analog Signal Processing circuits,
- Analog to Digital converter,
- Digital Processor.
What type of Cables are used in Instrumentation?
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Optical Fiber Cable
- Fieldbus Cable
- Profibus Cable
- Thermocouple Compensating Cable
What is an instrumentation cable?
- Instrumentation cables single pair or multi-pair cable elements
- These cables are designed to convey electrical signals.
- These cables are used to connect field instruments In process industries or in power plants to monitor, & control the process,
- An instrumentation cable transmits signals generated by the transducer to controllers through panels.
What wire is used for instrument cables?
41-36 gauge copper wire.
How to select an instrumentation cable Guide for Process Instrumentation?
The selection of instrumentation cable for Process Instrumentation depends upon
- Instrument Type
- Length of Cable Run
- Electrical Interference
- Environmental Conditions Identification
- Direct Burial
- Cable Design
- Packaging.
Compare Power Cable and Instrument Cable
Power Cables transmit and distribute electrical power signals of high voltage; they may be single or three-phase.
An instrumentation cable in industrial automation & other signal control applications transmits signals generated by the transducer to controllers through to panels.





