Table of Contents
- Applications of SCADA
- What is SCADA?
- Applications of SCADA include
- 1. Electricity Generation, Transmssion, and Distribution Systems:
- 2. Manufacturing Industries or Plants:
- 3. Food & Pharma Production:
- 4. Telecom & IT-based systems:
- 5. Water Treatment Plants, Sewage Treatment Plants, & Supply Management:
- 6. Traffic Controls:
- 7. Lift & Elevator Controls:
- 8. Buildings & Society Environments:
- 9. Oil & Gas Systems:
- 10. Mass Transit & Railway Traction:
- SCADA in Power transmitting Systems
- Some of the applications are
- Benefits of SCADA for Power Systems
- The general features of a SCADA substation system are
- Additional features of the substation control system
- SCADA for Power Utility Network
- Features of Power Network Utilities
- Objectives of SCADA
- The application of SCADA
- SCADA Advantages
- Frequently asked Questions
Applications of SCADA
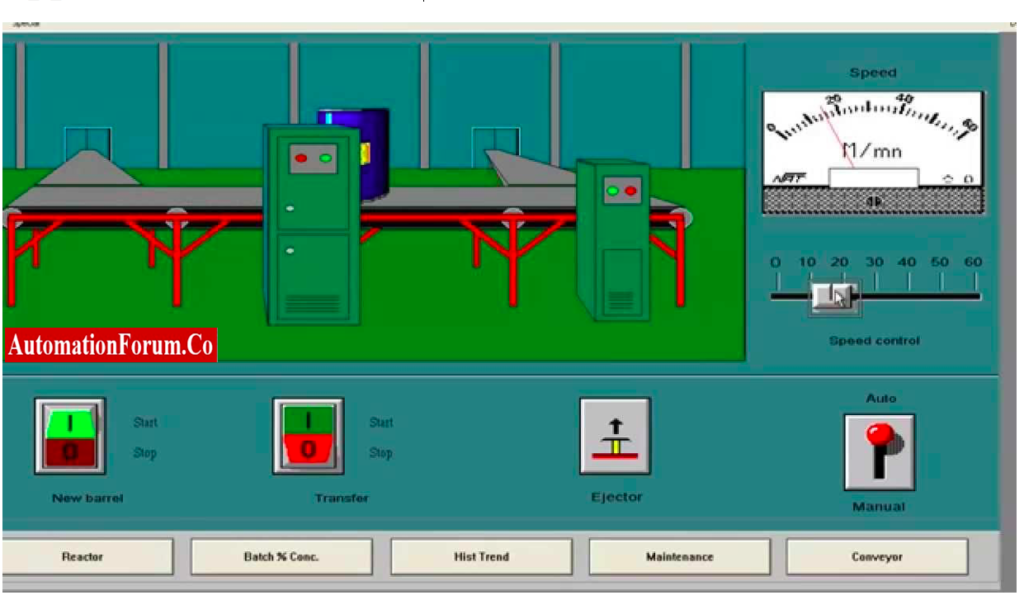
What is SCADA?
- SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition.
- SCADA is a computer-based system to analyze real-time production data. SCADA monitors and manages alarms, and programs for automatic responses triggered by system parameters.
- SCADA system is a very essential tool for process automation.
- It helps to be aware of potential network issues.
- It makes informed decisions to respond accordingly on time.
- It is a type of remote monitoring system to manage and control equipment to eliminate human error.
- SCADA is widely used in various sectors such as chemical, gas, water, communications, and power systems.
- SCADA is a combination of software and hardware elements for process industries to

- Process Control & monitor in real-time from a remote location
- Analysis & calculation of complex processes & maintaining control signals accordingly.
- Data Acquisition, Historical Data Logging, Archiving & Retrieving
- Trend & Alarm Generation
- Recipe Management in Process & Chemical Industries
- Report Generation
Applications of SCADA include

1. Electricity Generation, Transmssion, and Distribution Systems:
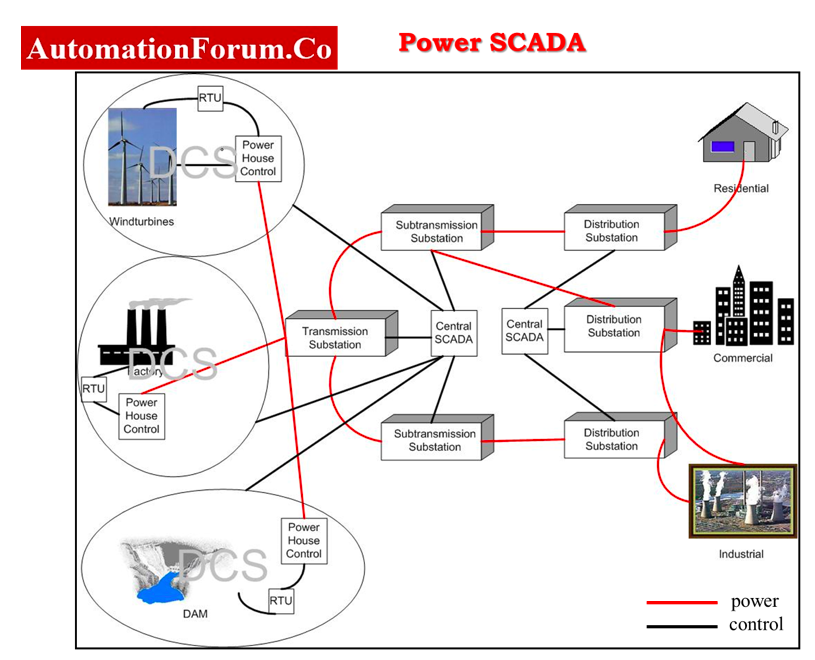
- SCADA systems are used in electric power generation plants, transmission areas, and distribution systems.
- SCADA systems monitor each and every phase of the generation of electricity from fuel input to electrical output.
- SCADA systems can also be used to monitor and control electrical switchboards, Grids, and transmission lines.
- SCADA monitors and controls the actual electrical power being transmitted over long distances.
- This system responds to load fluctuations instantaneously.
2. Manufacturing Industries or Plants:
- A SCADA helps in managing various raw materials or inventory items, to control automated systems in synchronous order.
- SCADA precisely controls every plant operation to ensure all systems run smoothly and meet productivity targets.
- SCADA tracks the number of units produced, & measures process values such as temperature, pressure, and humidity at various production phases.
- It also controls assembly line robots.
3. Food & Pharma Production:
- SCADA system monitors and controls all stages of the production unit.
- Controls the exact mixture of required ingredients.
- Monitors the time and temperature required to manufacture & process food & beverages or pharmaceutical products.
- SCADA documents data to prove the production meets the industrial standard and government regulations.
4. Telecom & IT-based systems:
Managing different Radio Frequency based systems, communication mediums, and large communication systems such as logging data and information through an antenna using a SCADA system is very easy.
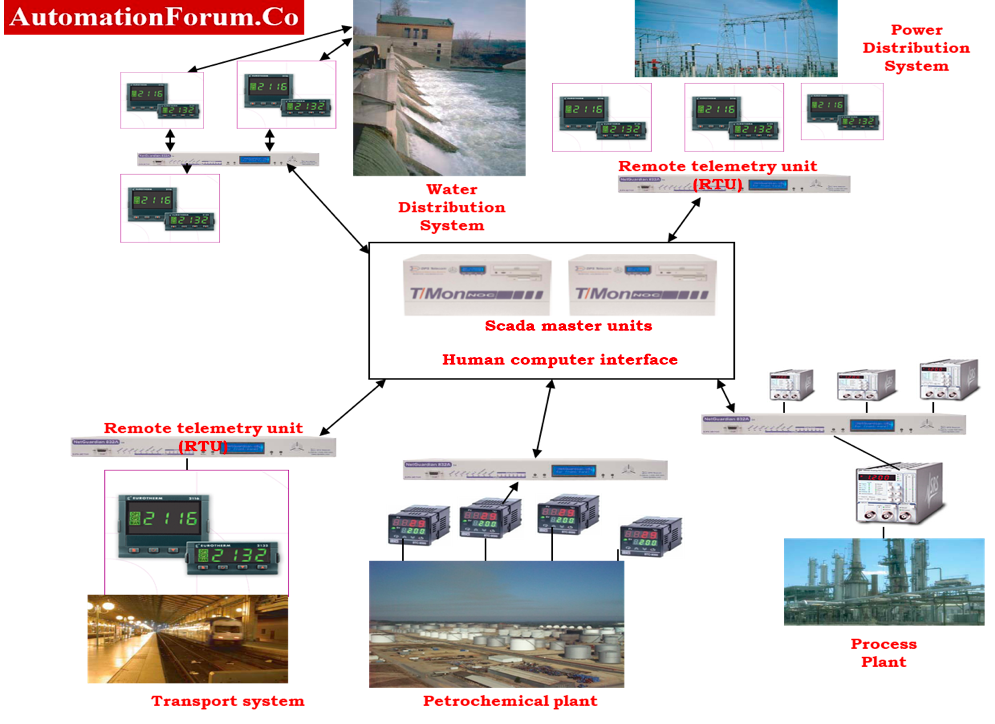
5. Water Treatment Plants, Sewage Treatment Plants, & Supply Management:
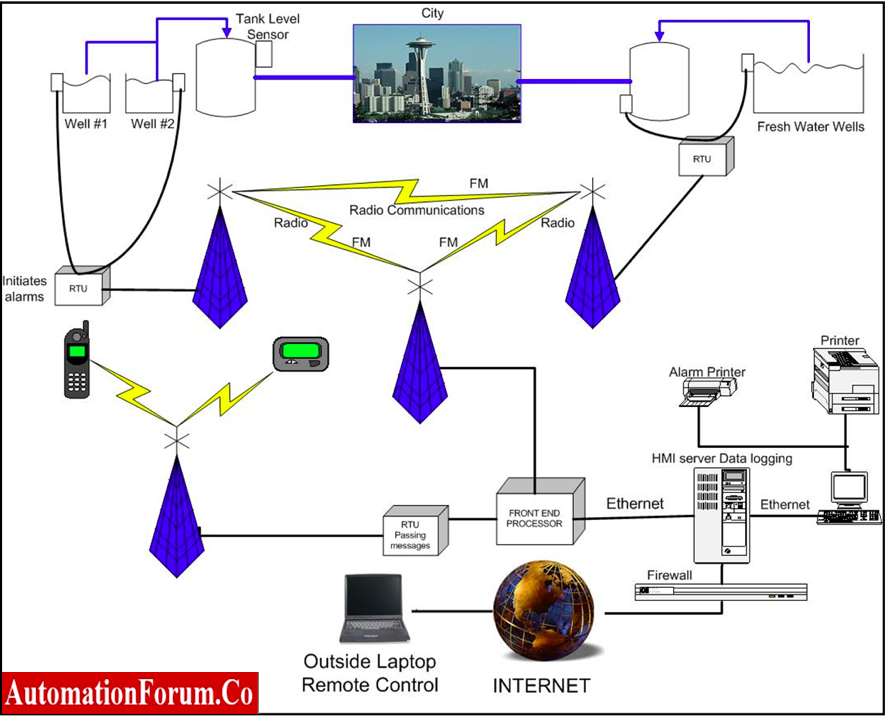
- Municipal Corporations and other government sectors are using SCADA for monitoring, controlling, and regulating the level and flow of water in dams & reservoirs.
- SCADA system monitors and controls the water being pumped from bore wells and treated at WTP.
- This system controls flow rate sensors and contaminant sensors.
- This controls the booster pump to regulate the water pressure supplied to the process.
6. Traffic Controls:
- In metropolitan cities, SCADA regulates traffic signal lamps, detects signals out-of-order, & controls traffic flow.
- In railway systems, on-road systems, & airlines the traffic flow is controlled by the SCADA system.
7. Lift & Elevator Controls:
SCADA system can also be used to lift and control elevators in commercial malls and in large industries.
8. Buildings & Society Environments:
Facility managers use SCADA to control High Voltage AC, refrigeration units, lighting, and entry systems.
9. Oil & Gas Systems:
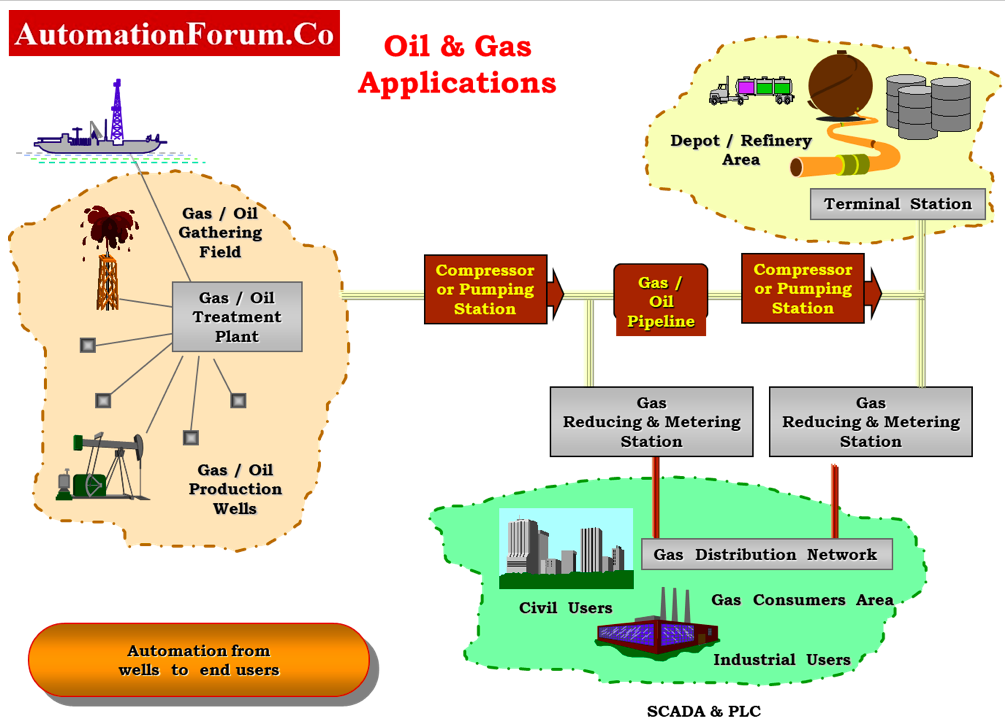
- SCADA system monitors wells and pumping sites, pumping pressure, pipeline flow, and compressor stations.
- It detects irregularities to prevent catastrophic events from occurring for safety.
10. Mass Transit & Railway Traction:
- Transport authorities use the SCADA system to
- Control supply of electricity to subways, trams, and trolley buses.
- To automate traffic signal indication for railways.
- To track and locate trains and buses.
- To control railway crossings.
- SCADA protocols also regulate electricity in remote locations.
SCADA in Power transmitting Systems
- Re-routing services for station maintenance
- Service Restoration
- Protective relay interface/interaction
- Voltage regulation management
- Load tap changer control
- Transformer management
- Real-time modeling.
- Automatic control of circuit isolation.
- collective switch control display
- Interface real-time single-line displays
- On-line operation and maintenance logs
- Automatic system diagnostics through system alarm management.
Some of the applications are
- Comprehensive operational planning and control
- Fuel resource scheduling
- Optimum power flow
- Network security
- Economic dispatch
- Generation dispatch control
Benefits of SCADA for Power Systems
- Improved quality of service
- Improved reliability
- Reduced operating costs
- Maintenance /Expansion of customer base
- Ability to defer capacity addition projects
- High-value service providers
- Improved information for engineering decision
- value-added services
- Flexible billing option
- Improved customer information access
- Reduced system implementation costs
- Reduced manpower requirements
The general features of a SCADA substation system are
- Substation parameter monitoring
- Controlling electrical network components remotely
- Safety tagging
- High-resolution time stamping
- The sequence of event reporting for post-event analysis
Additional features of the substation control system
- Demand side management
- Volt/VAR control
- Preventive maintenance
- Fault detection isolation and restoration.
SCADA for Power Utility Network
- Power Utility Network (PUN) software provides an electrical utility with tools to enhance system operation at a very low cost.
- The PNU software consumes real-time SCADA data.
- PNU logic is a combination of both mathematical and logical techniques.
- The present scenario is to produce and distribute quality power at the minimum investment.
- Proper operation of the electrical network & having real-time data about the network helps to achieve the required goal.
- PNU provides the user with a host of applications to distribute automation.
Features of Power Network Utilities
- Component Modeling
- State Estimation
- Bad Data Suppression
- Contingency Analysis
- Fault Isolation/Islanding
- Load Shedding
- Volt/VAR Scheduling
- Dispatcher Power Flow
- Short Circuit Analysis
- Network Topology Processor
Objectives of SCADA
There are many objectives of the SCADA System.
- Improves overall System efficiency such as capital & energy.
- Increases penetration of energy sources along with renewable energy sources.
- Reduces energy requirements at generation and transmission sections
- Increases sequence to essential loads.
The application of SCADA
- In power plants, the SCADA serves the invaluable safety and protection
- This system attempts to solve the fault that occurred and restore power quickly when a fault is experienced in a transmission line.
SCADA Advantages
- Receiving real-time information to monitor equipment
- Remote industrial control
- Storage of performance data for later analysis
- It allows for dynamic maintenance and reduces downtime
Frequently asked Questions
What are the four types of SCADA?
The SCADA systems are classified into four types
- Monolithic SCADA system,
- Distributed SCADA system,
- Networked SCADA system, and
- I-o-T SCADA system.
What is an example of SCADA?
Basically, SCADA systems control and monitors physical processes. General examples of SCADA are
- Transmission of Electricity,
- Transportation of Gas & Oil in Pipelines,
- Water Distribution,
- Traffic Lights.
What are the four functions of SCADA?
The four primary functions of the SCADA system are:
- Data Acquisition,
- Network Data Communication,
- Data Presentation,
- Data Control.
What language is SCADA?
- Most SCADA systems are now programmed using standard interfaces.
- Basically, C, or a derived programming language is used as a SCADA language.
What is the main function of SCADA?
The basic function of SCADA systems are
- Collects field information,
- Transfer it to the main computer.
- Displays the process information as a graphical representation.





