- What is a Smart Sensor?
- Working Principle of Smart Sensor
- What are the basic components included in a smart sensor?
- What are the main basic functions of Smart Sensors?
- Block Diagram of Smart Sensor
- Describe various types of Smart Sensor
- Classification of Level Sensor
- Advantages of Smart Senor
- Disadvantages of Smart Senor
- Applications of Smart Sensors
- What is a Smart Sensor?
- What is a Sensor?
- What is the purpose of the sensor?
What is a Smart Sensor?
- A smart sensor is a high-tech electronic device that unites conventional capabilities for sensing along with data processing, transmission, and, in certain instances, the ability to make decisions.
- It was developed to garner data from the surroundings, analyze it, and communicate it to a network or centralized system for assessment and subsequent action.
- A smart sensor is a device that, unlike a typical sensor, is capable of measuring physical values and offering an output proportional to the noticed value.
- Smart sensors are able to perform data analysis on the amount being measured using a built-in computing resource and utilize the results to take steps to improve the efficiency of the automation process.
- Smart sensors can also convey greater accuracy readings.
- The smart sensor has computational abilities to filter out all noise signals and transforms the measured signal into a re-useable digital format by eliminating the need for a transducer to be present as in a conventional sensor.
- Smart sensors consist of some built-in communication features that permit the user to exchange data & information for suitable communication with external devices through internet protocol.
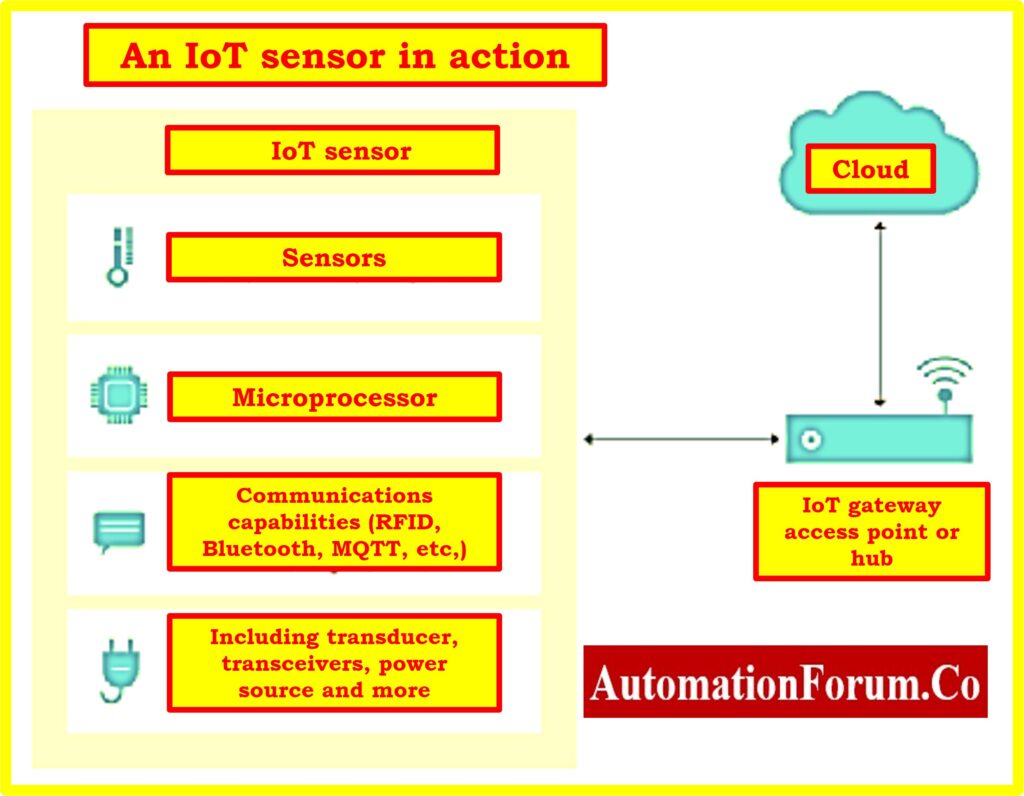
- For this purpose, these smart sensors are said to be essential components of the Internet of Things (IoT) and industry. 4.0
- Smart Sensor enables the huddle of real-time data, facilitates automation, and optimization, and bestows Internet of Things (IoT) systems development.
- A smart sensor is an electronic device that receives an input signal from the physical environment and achieves predetermined functions by using specific input & then processes the data through built-in computing resources.
- A smart sensor is an electronic device that monitors and regulates various environments including smart grids, battlefield reconnaissance, exploration, and many science applications.
Working Principle of Smart Sensor
- Smart sensors function by occupying data and information from physical environments & varying their physical properties such as speed, temperature, pressure, and mass, into equivalent electrical signals.
- These smart sensors consist of a type of microprocessor called a Digital Motion Processor (DMP)
- This DMP permits the smart sensor to execute on-board rectifying of data like filtering noise otherwise performing different kinds of signal conditioning.
What are the basic components included in a smart sensor?
The Smart sensors typically include the following components shown below
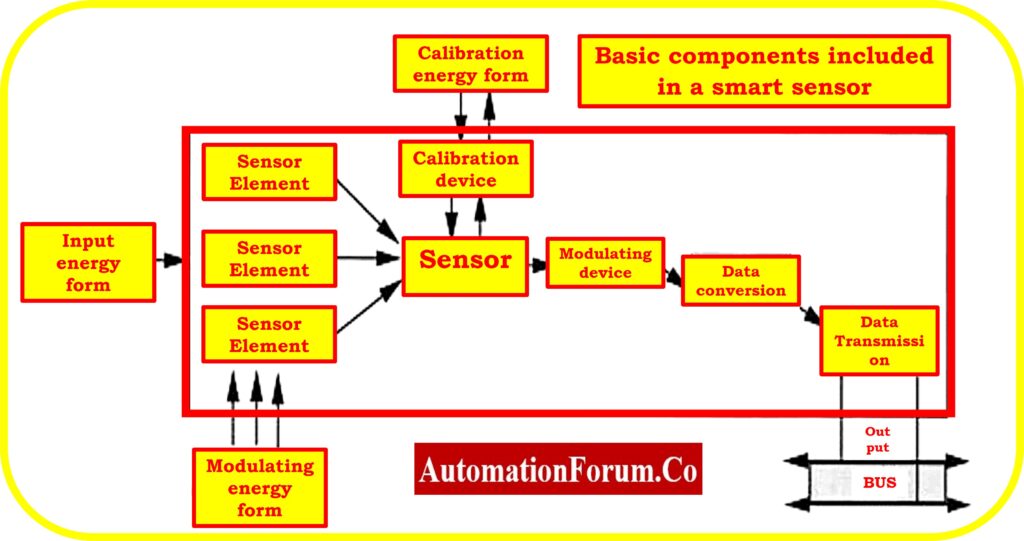
- Sensing Element:
- Sensing Element detects and measures physical variables such as temperature, pressure, light, humidity, motion, and chemical concentrations.
- A thermometer or more specialized gas or image sensor is considered a standard sensor that may be used as the sensing element.
- Signal Conditioning Unit:
- This component builds up the sensing element’s initial information for further analysis.
- It might involve boosting, filtering, or transforming sensor output to digital format.
- Microcontroller or Microprocessor:
- These microcontrollers or Microprocessors are considered the Heart & Brain of the smart sensor.
- It interprets the conditioned data, provides computations, performs algorithms, and regulates the sensor’s overall operation.
- Communication Interface:
- A smart sensor consists of communication facilities to convey the collected data & information to other devices or systems.
- This can be wired through Ethernet, Universal Serial Bus, or wireless such as Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth communication protocols.
- Power Supply Unit:
- The smart sensor consists of a power source for efficient operation.
- The power sources may be battery units through cabled power connections or energy harvesting types of equipment such as solar panels or vibration-based generators.
- Data Storage and Processing Units:
- Some smart sensors are able to store data and can perform initial data processing.
- These are used in some situations where there is no continuous network connectivity available, or when real-time decisions are required to be made at the sensor level.
What are the main basic functions of Smart Sensors?
The smart sensors perform four main basic functions such as
- Measurement
This action is done by sensing physical signals and transforming them into proportional electrical signals to assist in monitoring, & measuring these process variables.
- Configuration
Configuration function is an essential feature that permits the smart sensor to detect the position during installation.
- Verification
The verification function employs continuous monitoring of sensor behavior by using various supervisory circuits.
- Communication
This communication feature permits the smart sensor for swapping the received data with the primary microcontroller or microprocessor.
Block Diagram of Smart Sensor
The below-shown schematic represents the block diagram of the smart sensor
Block Diagram

- Sensing Unit
The sensing unit senses the physical parameters of the process and transforms them into equivalent electrical signals.
- Conditioning Unit
The conditioning unit monitors and regulates the sensed signal to meet the requirements of higher-level operations without sagging any data.
- Analog to Digital Converter
Analog to Digital Converter transforms the received analog signal into proportional digital format & conveys the same to the microprocessor.
- Local User Interface
The local user interface (LUI) is a panel-mounted device that permits the building operators to monitor and to regulate the control equipment.
- Application Algorithm
The application Algorithm rectifies the signal received from smart sensors based on the application program loaded previously to generate desired output signals.
- Memory Unit
The Memory Unit stores the processed media for further requirement.
- Communication Unit
The communication unit transmits the output signals generated by the application algorithm or microprocessors to the main station
This unit also receives user commands from the key station to execute specific tasks.
Describe various types of Smart Sensor
Based on physical parameters these Smart Sensors are categorized into various types
- Level Sensors

- A level sensor is a kind of smart sensor for monitoring and maintaining a level of the liquid present in a large container or storage device.
- The sensor produces a data signal based on the level of liquid sensed in it and transforms it into an equivalent electrical signal.
- Generally, these level sensors are mainly used in various industries such as automotive, manufacturing, and also in household applications.
Classification of Level Sensor
Level sensors are further classified into
- Point Level Sensor: this sensor defines whether a liquid has executed an exact point within a container
- Continuous Level Sensor: This sensor delivers accurate measurements for liquid level.
- Temperature Sensors

- Temperature sensors measure the temperature of process fluid such as liquid temperature, air temperature, or solid matter temperature.
- These Temperature Sensors come with various principles to determine temperature namely RTDs, NTC thermistors, thermopiles & thermocouples.
- Generally, these temperature sensors are used in
- Medical Devices,
- Computers,
- Automobiles,
- Cooking Appliances &
- Industrial Machinery Equipment.
- Pressure Sensors

- A pressure sensor or pressure transducer that converts physical signal to proportional electrical output signal.
- Pressure Sensors are available based on capacity, size, sensing technology, & mode of measurement.
- Infrared Sensors

- An infrared sensor emits a light wave to sense some kind of object in the surroundings to determine the heat, & motion of an object.
- Generally, Infrared Sensors consist of a transmitter known as IR LED, & a receiver known as an IR photodiode.
- These Infrared Sensors are used in
- Night Vision Devices,
- Radiation Thermometers,
- IR Tracking,
- IR Imaging, Etc.
- Proximity Sensors

- Proximity Sensors sense the presence of objects without any physical contact just by using light, sound, IR, or electromagnetic fields.
- These are used in collision avoidance & collision warning systems.
- Generally, These Proximity Sensors are used in
- Consumer robotics,
- Process industries
- Automotive vehicles sense another object during parking.
Advantages of Smart Senor
The advantages of the smart sensor are
- Small in Size
- Simple Design
- Easy to Use
- High Performance
- Low, & Easy to Maintain
- Self-Calibration
- Self-Assessments
- High Reliability
- High Speed of Communication
- Reduced down time
- Fault tolerant systems
- Adaptability for self-calibration and compensation
- Lower weight
Disadvantages of Smart Senor
The disadvantages of the smart sensor are
- High complexity
- Requires both sensors & actuators
- Easily stolen
- Gets damaged badly
- Costly
Applications of Smart Sensors
Smart Sensors are used in various sectors including
- Industrial Automation,
- Environmental Monitoring,
- Healthcare,
- Transportation,
- Smart Homes.
What is a Smart Sensor?
Smart Sensor is built with a Digital Motion Processor that accepts input signals from external sources.
What is a Sensor?
A Sensor is a normal sensor built without a Digital Motion Processor.
What is the purpose of the sensor?
A sensor measures the physical signal & transforms it into equivalent electrical signals for further processing





