- What is an industrial thermometer?
- How do you calibrate an industrial thermometer?
- Purpose and Scope
- Tools required for calibration
- Safety
- Temperature gauge calibration setup
- Calibration procedure
- Recording calibration
- Completion of calibration
- Sample calibration report
- Standards in Industrial Thermometer Calibration
- Calibration Tolerances and Limits
What is an industrial thermometer?
The gas-actuated, bimetal, or expansion principle is used in the operation of temperature gauges. They have a measurement range of -200 to +700 °C. Moreover, all instruments can be used in thermowell.

The thermal condition of a homogeneous substance is measured by thermometers. The measuring system and the body that will be measured must be as close as feasible. The most common measurement techniques rely on physical and material properties that change with temperature.
How do you calibrate an industrial thermometer?
Purpose and Scope
This method contains directions for calibrating a temperature gauge using a dry bath temperature calibrator and a standard reference thermometer. These instructions are included in the procedure.
Tools required for calibration
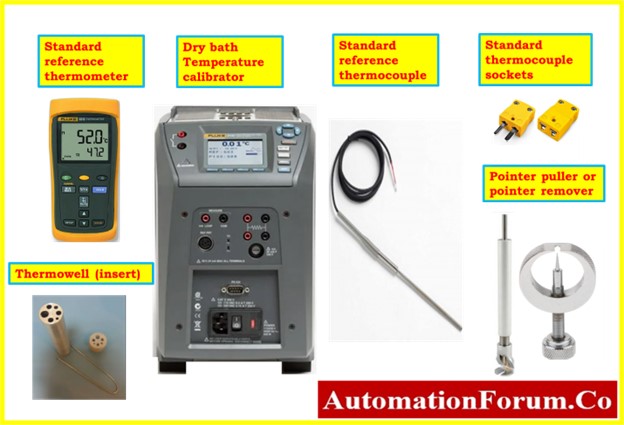

- Necessary hand tools.
- Multimeter.
- Pointer puller or pointer remover.
- Dry bath temperature calibrator.
- Standard reference digital thermometer.
- Soft cloth for cleaning.
- Thermowell
Safety
- To avoid any flow of fluids or gasses that could result in damage or harm, it is essential to stop the process and isolate the pipe before attempting to remove the temperature gauge.
- Depressurizing the pipe after the process has been stopped is crucial to preventing any potentially harmful unexpected releases of pressure. This can be accomplished by progressively releasing the pressure by opening a valve downstream from the temperature gauge.
- To remove the gauge from the pipe, you might require a wrench or other equipment, depending on the type of connection. Make careful to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations for appropriate removal methods.
- Examine the temperature gauge after disconnecting it to check for any wear or evidence of damage.
- Please check the link provided below for details on fundamental safety, general advice, and specifics on calibrating operations in process industries.
Basic Safety and General Considerations for Process Industries Calibration Process
- To stop any leaks or discharges of fluids or gasses after the temperature gauge has been removed, the pipe must be sealed. Installing a plug or cap over the pipe entrance will do this.
- While removing a temperature gauge from a process pipe, it’s crucial to adhere to all safety precautions and instructions to avoid accidents or injuries. For future reference, make sure to note the removal, as well as any repairs or replacements, in a maintenance record.
- Only in the event that the thermowell is present is it permissible to remove the temperature gauge without first isolating the system.
- If it is not installed, it is considered a shut-down task; otherwise, the technique to be used is described below to calibrate the temperature gauge.
- Make sure that the temperature gauge is completely removed from the working environment.
- Use the proper PPE, such as gloves, safety glasses, and a face mask, while working in a process area to protect oneself from dangerous chemicals and to adhere to safety requirements.
Temperature gauge calibration setup
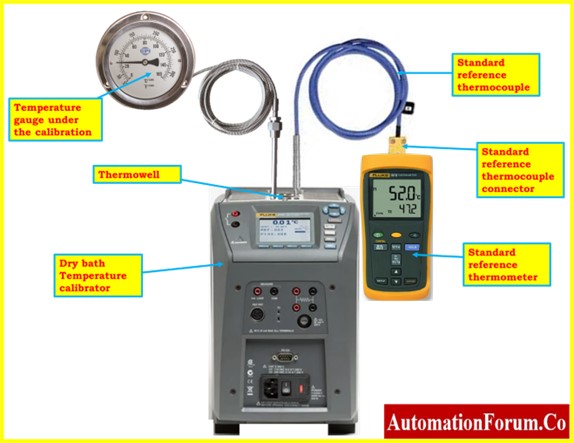

- A dry bath calibrator, a thermowell of a sufficient size for a temperature gauge, a standard reference thermometer with the appropriate range and accuracy, a power source extension, compensating cables, and the connections required to connect the reference thermometer are the tools you will need.
- Make sure the equipment is clean and free of any debris or residue that could affect the accuracy of the calibration.
- Turn on the dry bath calibrator by plugging it into an electrical outlet.
- Verify that the device is operating properly and that the temperature control is set to the appropriate range.
- As you place the temperature gauge into the dry bath calibrator with the suitable thermowell, make sure the sensing element is entirely submerged in the bath and not in contact with the walls or bottom of the container.
- Use the standard reference thermometer to gauge the temperature of the dry bath calibrator in the same location as the temperature gauge.
- Make sure the thermometer has been calibrated and has the appropriate accuracy and resolution for the calibration by inspecting it.
- Observe the reading on the thermometer in comparison to the temperature that was displayed on the dry bath calibrator.
- If there is a difference, adjust the dry bath calibrator’s temperature properly and observe the temperature change before taking another reading with the thermometer.
- The setup is ready for calibration if the thermometer and dry bath calibrator are steady and the temperatures coincide.
Calibration procedure
How to calibrate the temperature gauge?
- The type of temperature gauge that will be calibrated should be taken into consideration while setting the dry bath temperature calibrator.(like range lock)
- Adjust the dry bath calibrator’s set temperature as necessary depending on the type of temperature gauge being used.
- Never go above the temperature range of the thermometer; always check the documentation and the dial scale to determine the capacity.
- Allow the temperature gauge and dry bath calibrator enough time, typically several minutes, to stabilize at the same temperature.
- Observe the temperature gauge’s indication, the dry bath calibrator’s reading, and the reference thermometer’s indication at the reference temperature.
- Repeat the process for a variety of different reference temperatures ranging from 0% to 100% on the temperature gauge’s scale in order to calibrate it.
- Please read the manufacturer’s instructions before starting the calibration procedure as it may differ depending on the specific calibrator.
- Make the appropriate adjustments to the gauge if there is an inaccuracy in the reading.
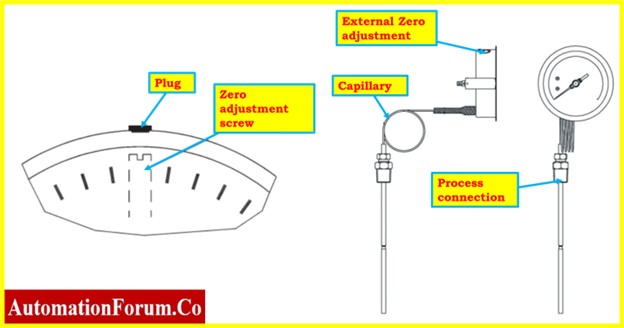
- Remove the plug at the top of the casing on the thermometer that has an external adjustment option, and then use the screwdriver to rotate it until the pointer is pointing at the desired temperature on the scale.
- Please consult the temperature gauge manufacturer’s instructions before making any corrections to avoid making any further mistakes.
Recording calibration
- Add inputs in both the upscale and downscale temperature directions from the test calibrators. These inputs should correspond to the output values that are indicated on the temperature gauge.
- Recalibration is necessary if the output value of the temperature gauge does not fall within an acceptable range. Again, if the output values deviate from the permitted range, a replacement temperature gauge needs to be mounted.
- If every temperature gauge output value (+/- %) is within accepted limits, no additional calibration is necessary.
- The blank calibration report’s as found/as left column should be filled in with the temperature gauge output values.
Completion of calibration
- When the calibration has been successfully finished, attach the calibration label to the temperature gauge.
- After the calibration is complete, clean the apparatus, store it somewhere safe, and record the calibration data for later use.
- Remove the calibrators from their connections.
- Reinstall the temperature gauge in the processing area.
- Make sure the workplace is tidy.
- De-isolate the equipment.
- Make sure the temperature gauge is working properly before putting it back into use.
Sample calibration report
The following image demonstrates how the calibration of the temperature gauge sample report which was carried out using a thermometer and a dry bath temperature calibrator, with a standard thermocouple serving as the reference.
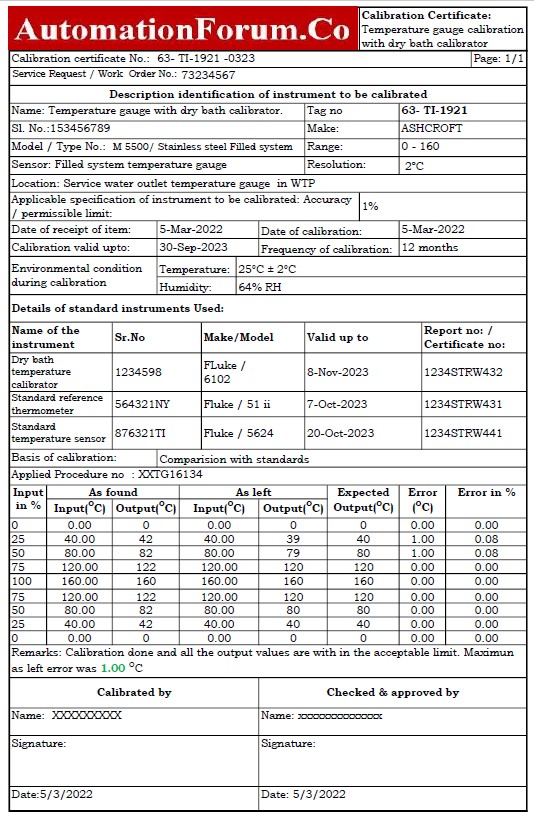
The link below will allow you to obtain the Excel template that was used to create the temperature gauge calibration report.
Standards in Industrial Thermometer Calibration
It is essential to consult specific guidelines from recognized bodies like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). These standards will cover additional calibration guidelines, temperature sensor types, uncertainty analysis, and traceability requirements.
Some key standards to refer to include:
- IEC 60751 – Industrial platinum resistance thermometers and sensors.
- ASTM E2877 – Guide for Digital Contact Thermometers Calibration.
- ISO 17025 – General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories.
Refer to these standards for additional precision, handling techniques, and accuracy levels required during calibration of industrial thermometers.
Calibration Tolerances and Limits
Define acceptable tolerances for thermometer accuracy and any limits that would require recalibration or replacement.
Traceability of Calibration Standards
Ensure that all reference instruments used for calibration are traceable to national or international standards, such as NIST or equivalent bodies, to guarantee the accuracy of calibration results.
Click here for more Instrument Calibration Procedures





