Table of Contents
Orifice Plate Pressure Taps
These allow the flow transmitter to tap into the pipe to measure maximum & minimum pressure levels within the flow rate.
What are the types of pressure tapings allowed in the orifice plate?
There are six different types of pressure taps used in affiliation with orifice plates
Flange Taps
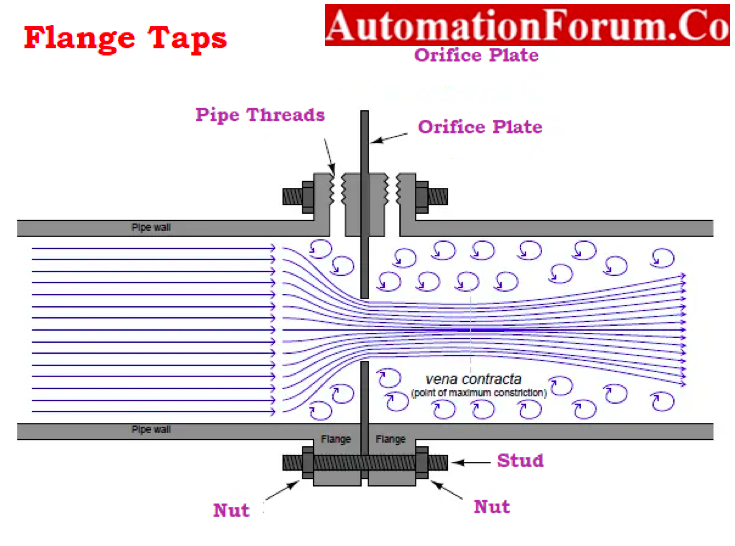
- The most popular taps are flange taps and radius taps.
- For pipes having a diameter greater than 2 inches, flange taps are positioned one inch upstream and one inch downstream of orifice plates.
- They cannot be employed for pipes smaller than 1.5 inches in diameter and are not advised below 2 inches.
Vena-Contracta Taps
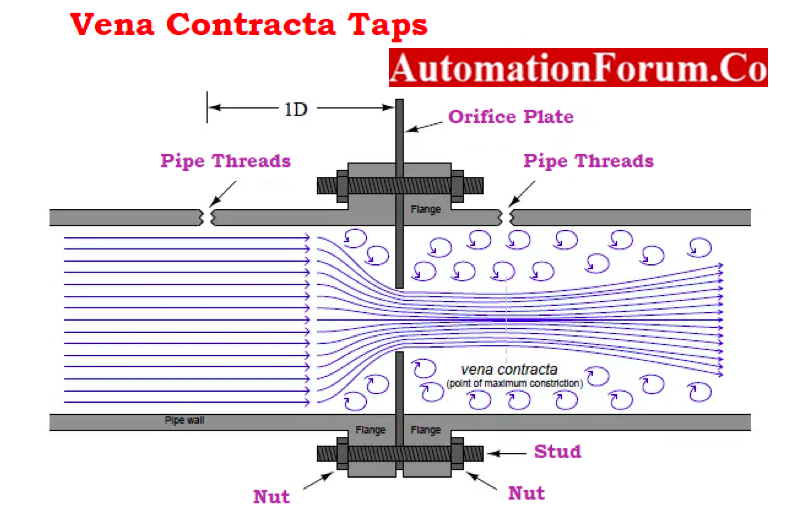
- To achieve the maximum pressure difference, vena-contractive taps are positioned one pipe upstream and the downstream tap is positioned at the point of minimum pressure.
- These taps are identical to flange taps and are designed for smaller pipe diameters.
Radius Taps
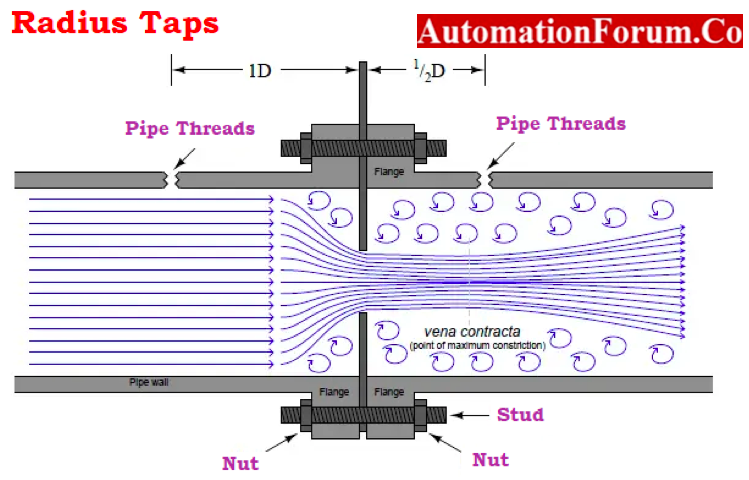
- Radius taps are more formalized taps that maintain one radius of a pipe up to one diameter of pipe upstream, but the downstream tap is 50% diameter of the pipe downstream.
- For pipe sizes of 6 inches or greater, these vena-contractive and radius taps are both recommended.
Pipe Taps or Full Flow Taps
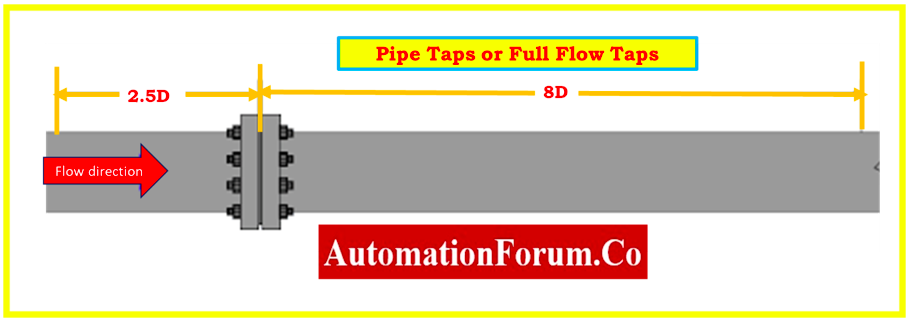
- Pipe taps are located 2.5 pipe diameters convergent and 8 pipe diameters divergent, with the high-pressure flow taps located 2.5 pipe diameters upstream.
- Because the taps really aren’t closer to the flange that includes the orifice plate, the exact place is not significant, and measurement error is considerable.
Corner Taps

- Corner taps are analogous to flange taps since the pressure tap is positioned within the orifice plate’s edges on either side.
- In Europe, these taps are employed for all pipe diameters, while in North America, these are utilized on pipe sizes below 2 inches.
Elbow Taps
- An orifice plate isn’t utilized with elbow taps.
- When the fluid moves around an elbow, it depends on the pressure difference.
- These taps are extremely inaccurate, yet they’re inexpensive, with easy installation.
Classification of Orifice Plates
Types of Orifice Plates

Concentric type Orifice Plate with centrally bored
- The square-edged, concentric punched design is the most typical orifice plate.
- It is used for an extensive variety of applications, involving clean liquids, gases, and steam circulation.
- Stainless steel is often used.
- Other materials, including nickel and monel are utilized for corrosive resistance.
- This type of orifice plate is extremely accurate.
- Nevertheless, it is not advised to be applied to slurries or highly corrosive operations.
Eccentric Orifice Plate (Hole is off-center)
- Eccentric bore orifice plates vary from concentric bore orifice plates because the aperture is off-center, or eccentric.
- The bore’s position avoids the accumulation of solid materials, making it suitable to measure fluids containing suspended solid particles.
- Eccentric bore orifice plates are more ambiguous, particularly in comparison to the concentric orifice.
Segmental Orifice Plate
- The segmental punched orifice plates have a hole that is a concentric circle segment.
- In gas flow applications, the segmental hole, like the eccentric orifice plate design, must be offset downward.
- Generally, These Segmental bores are utilized only to measure liquids or gases that also carry non-abrasive contaminants such as sewage treatment, steel, chemical, water conditioning, paper, and petrochemical industries.
Quadrant Edge Bore
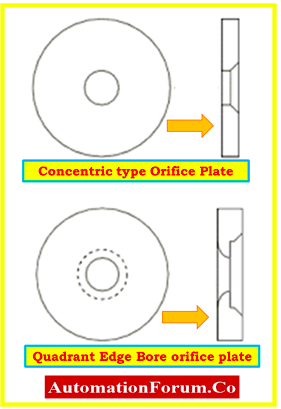
- The quadrant edge bore is an orifice with a round inlet edge.
- The convergent side of the quadrant edge bore is carved like a flow nozzle, while the divergent side operates as a sharp edge orifice plate.
- This design is suggested for measuring the flow of viscous fluids like heavy crudes, syrups, and slurries.
- With a Reynolds Number less than 10,000, the quadrant edge bore develops a relative constant coefficient.
Integral Orifice Plates
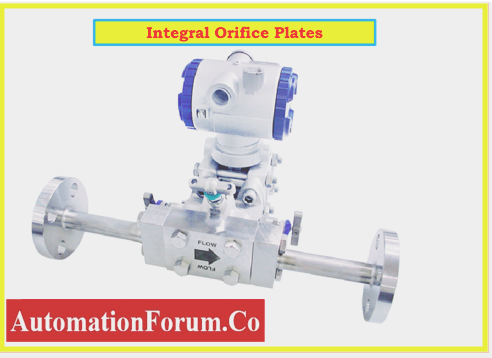
- Integral orifice plates are yet another kind of orifice meter used only for minimal flow rates.
- These are merely small tubes that you’re able to mount directly to the differential pressure transducer.
- A choice of buying some orifice & transmitters within the tube to link the higher cavity section to the lower cavity section.
- In applications such as chemical dosing systems, which need a high level of flow rate precision, these instruments are utilised for the exact measurement of low flow rates.
Ring Type Joint (RTJ) Orifice Plates

- The RTJ-type orifice plate features an important gasket for installation among ring-type joint flanges.
- It is based on proven technology.
- It doesn’t have moving parts.
- Ring Type Joint is applicable for high-temperature and pressure applications.
- Orifice plates are well suited for clean liquids, gases, and low-velocity steam flows.
- Plate thicknesses are ascertained by line size and pressure difference and should be enough to avoid flexion under operational conditions.
Conditioning Orifice Plates consists of Four Bores

- Orifice plates are manufactured by stainless steel 316, but for higher temperature, & pressure applications or for corrosive applications these plates are available in Mono or Hastelloy
- A typical orifice plate has a beveled or conical shape.
- The narrow side contains a sharp edge that may face upstream towards the flow.
- The marking on the orifice plate must also face upstream.
- Orifice plates must normally be installed at least 4-5 pipe diameters from a curve or elbow.
- One can buy straightening veins to eliminate straight-run needs. Orifice plates are simple to set up and maintain.
- They are accurate and can be used with a wide range of pipe diameters. In engineering textbooks and other materials, there’s a huge collection of information on how fluids engage with an orifice plate.
- Orifice plates contain sharp edges that can degrade over time by sludge and corrosive liquids, which will introduce measurement inaccuracy. The entire installation cost may even be significant, even though typically an orifice plate is approximately $100-$300.
- The flange and maintenance requirements are considerably greater, in addition to the energy dissipation cost incurred by restricting the flow.





