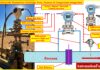
What is SCADA?
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. SCADA is a system of supervision, control and data processing in real time. SCADA components include Master Station, telecommunications media and Remote Station / Remote Terminal Unit.

SCADA relates to a system that collects data from multiple sensors in a factory, plant or other distant places and then sends it to a central computer to manage and control the data.
How a SCADA works?
SCADA is a system for obtaining real-time data from both Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) or other communication sources in the field, so that network operators allow supervision of network operations and control of breaker equipment load from a distance (remote operation).

Hardware Architecture:
SCADA system consist of two basic layers:
- Client layer: Handles the man-machine interaction
- Data server layer: Handles most of the process of data control activities. The data servers communicate with devices in the field through process controllers.
Software Architecture:
The SCADA system comprises of a software program that provides trend, diagnostic data, and manages information such as scheduled maintenance procedure, logistic information, comprehensive schematics for a specific sensor or machine, and

This implies that the operator can represent the scheme in a schematic manner
Interfacing:
Development of OPC client features for SCADA for open and standard access to devices.
There still seems to be a shortage of
- An Open
Data Base Connectivity (ODBC) interface forarchive / log information, but not for the database configuration. - An ASCII import/export facility for configuration data.
- A library of APIs that support C, C++ and Visual Basic (VB) for RTDB, log and archive access to information.
SCADA System working:
Most control actions are performed automatically by remote terminal units (“RTUs”) or by programmable logic controllers (“PLCs”).

PLC controls the industrial process, but the SCADA system can enable operators to change the setpoints and alarm conditions.
Data acquisition begins at the RTU or PLC level and includes meter readings and equipment status reports that are communicated to SCADA as required.

Data is then compiled and formatted in such a way that a control room operator using the HMI can make supervisory decisions to adjust or override normal RTU (PLC) controls
In order to allow trend and other analytical auditing, data can also be supplied to a historian, often based on a commodity database management system.
HMI (Human Machine Interface):
Human Machine Interface is

In
The functions of the HMI are as follows:
- View / monitor the condition of the distribution system.
- Enter or change data.
- Navigate between SCADA functions.
- Monitor and control the Distribution Network System equipment.
- Monitor and control the distribution network system configuration.
Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)

RTU is also referred to as Remote Station, which is a device placed in a substation in the form of a processor that functions as a receiver, processor and forwards information from the equipment being monitored and sends it to the master station or receives instructions from the master station
Major applications of SCADA system:
- Fault Detection, which provides fault information through the operation of protective equipment, so that fault detection can be quickly identified and the point of disturbance can be immediately identified.
- Isolation, namely the ability to localize networks is disrupted by utilizing tele control facilities for network maneuvering or manipulation.
- Restoration, which is the ability to restore the network condition to its normal position before it is disturbed after the interference is repaired by
tele control facilities to control network equipment such as cubicles, LBS, reclosers orsectionalizers