What is Three Phase?
A typical technique of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution is three-phase electric power. It is a form of polyphase system that is utilised by electrical grids all over the world to transfer power. Large motors and other heavy loads are also powered by it. Because it utilises less conductor material to transfer electrical power, a three-phase system is usually more cost effective than an identical single-phase or two-phase system at the same line to ground voltage.

What is 3 phase wiring?
In most cases, distribution install a single-phase energy meter in domestic areas because there is less load (consumer unit for house). If the limit is exceeded, a 3-phase energy meter for consumer units should be installed. In home locations, 3-phase electrical wiring is recommended when the load exceeds what is required for house.
In this three-phase electrical wiring installation, most families only connect single phase loads.
- Light points,
- Fans,
- Television,
- Air-Conditioner, etc.
As can be seen, the overall load exceeds the single-phase electrical wiring installation limit, demanding the use of a three-phase distribution wiring system.
What is 220v 3 phase wiring?
Single-phase loads (210-230V) are distributed throughout the phases of a three-phase system to balance the load and make the most use of wires and transformers. The three phase wires have the same voltage to the system neutral in a symmetrical three-phase four-wire wye system. The voltage between line conductors is three times the voltage between phase conductor and neutral.
VLL =? 3VLN
The neutral wire is shared by all currents returning from the customers’ premises to the supply transformer.
Any three-phase load, such as a three-phase motor, requires all three phase wires to be connected, however only two (any two) phase wires of a three-phase system can supply a single-phase load. The power in a delta system is typically 240 or 480 volts. One of those voltages is the single-phase power available at the time. For most uses, single-phase power at only 240 volts isn’t practicable; we need 120/240-volt, single-phase power.
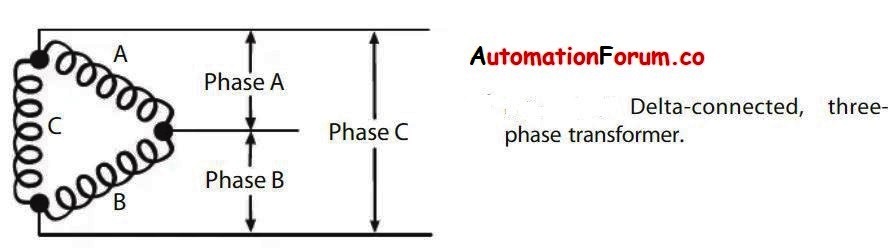
The transformers in the diagram below are the same as in the previous one, but one of the secondaries has been tapped at the middle. If the basic voltage is 240 volts, the secondary tapped at the midpoint in the diagram below will give 120/240-volt single-phase power that can be used alongside the three-phase power. The midway where the tap is made is also grounded to a grounding electrode, although this is not illustrated in the image below. This results in a stable system.

A neutral wire is run from the junction of the three secondaries in a wye-connected arrangement. Any circuit connected to all three wires, A, B, and C, has a three-phase voltage of 208 volts. Wires A and B (or B and C, or A and C) have a single-phase voltage of 208 volts. The voltage between the neutral wire N and either A, B, or C would consequently be expected to equal 208 or 104 volts, however this is incorrect. A wye-connected, 208-volt, three-phase system has a voltage of 120 volts between the neutral and any hot wire.
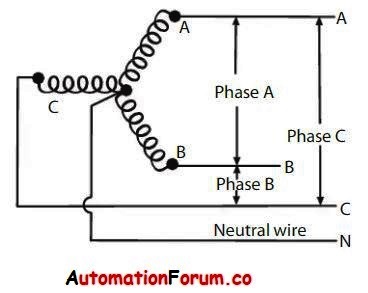
At first inspection, this appears to be incorrect, because if the voltage between wires A and B is 208 volts, the voltage between the neutral wire and either A or B should be half that, or 104 volts, rather than the 120 volts indicated previously. Remember that in a three-phase circuit, each phase’s voltage peaks or reaches its maximum at a distinct moment. The voltage in secondary A is 120 volts at the moment, while secondary B is 88 volts, resulting in a voltage of 120 + 88 or 208 volts across wires A and B. It’s worth noting that 208 = 120?3
As a result, the system has the advantage of allowing three-phase power at 208 volts, single-phase power at 208 volts, and single-phase power at 120 volts to be sent across only four wires (including a grounded neutral).
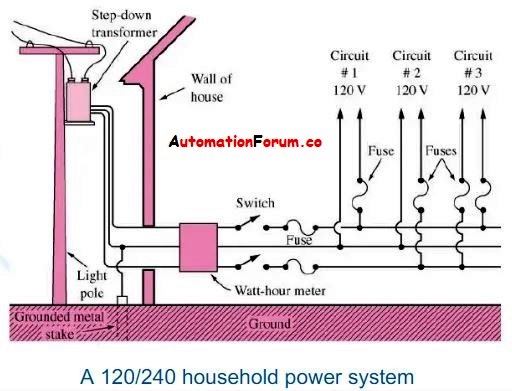
- Three wires of the wye-connected system (the grounded conductor and any other two wires) are provided in a home instead of the usual 120/240-volt, three-wire system, providing 120 volts for lighting and 208 volts (instead of the usual 240 volts) for water heaters and similar large loads.
- All four wires (the three phase wires plus the neutral) are used in bigger setups. This is a 208Y/120-volt three-phase, four-wire system. The windings’ neutral point (where all three windings are connected) is grounded.
In the case of a three-phase wiring system,
440V – line-to-line voltage
240V – line to neutral voltage
- 440V from L1 to L2
- 440V from L2 to L3
- 440 V from L3 to L1 and
- 240V from L1 to N
- 240V from L2 to N
- 240V from L3 to N
Features of 220v 3 phase wiring:
The salient features of 3 phase wiring are:
- Extremely sensitive in conductivity
- Work is carried out in accordance with the availability of phases.
- Circuit with a low cost and high reliability
- Manpower has been completely eliminated
- Up to 7A of large domestic loads can be handled.
Application:
This type of wiring can be applicable in:
- Residential uses for protection of equipment,
- Commercial purpose like flour mills, small storage refrigeration etc.
- Schools, colleges and office use to avoid frequent tripping.





