PLC:
A PLC, or programmable logic controller, is a rugged computer used in industrial automation. These controllers have the ability to automate a particular procedure, a machine feature, or even an entire manufacturing line.
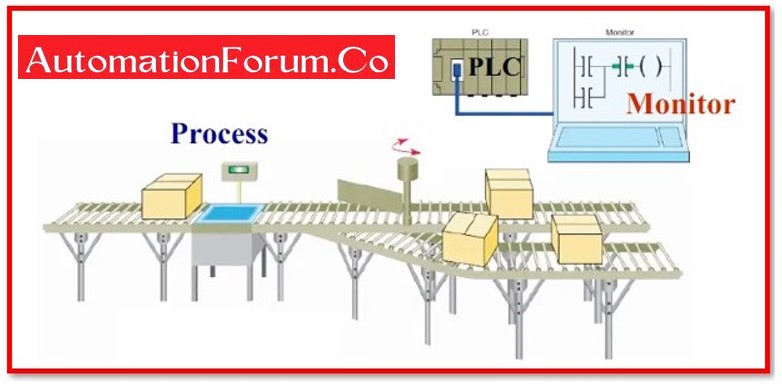
How does a PLC function?
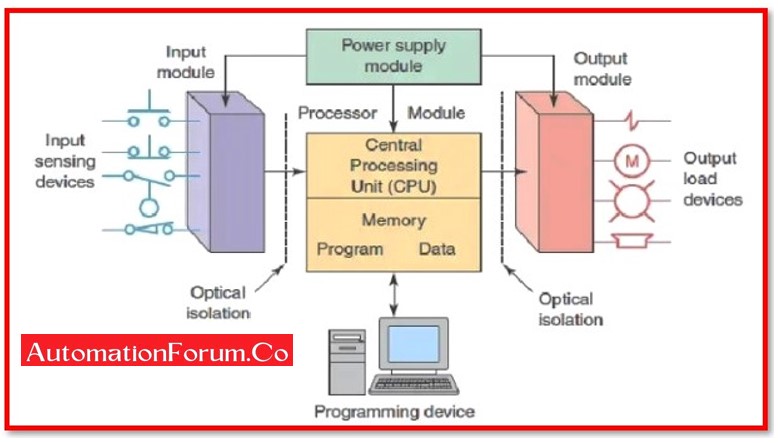
The PLC collects data from attached sensors or input devices, processes the information, and then initiates outputs based on preset settings.
A PLC has a variety of functions depending on the inputs and outputs, including the ability to start and stop processes automatically, monitor and record run-time data such as machine productivity or operating temperature, and more. Programmable logic controllers are a versatile and dependable control technique that may be applied to virtually every application.
Types of PLC:
There are 4 different types of PLC:
- Fixed integrated PLC:Fixed integrated PLCs have a single unit that houses both the controller and the IO.
- Distributed PLC:A network connects the controller and input/output devices.
- Soft PLC: Instead of using a specific controller, a general-purpose computer runs the PLC as a programme.
- Modular PLC: A modular PLC contains separate modules for the controller and IO that are inserted into a chassis.
Based on hardware setup Most commonly used PLC are: Fixed PLC and Modular PLC.
FIXED INTEGRATED PLC:
The Fixed I/O PLC is the most popular name for this kind of PLC.Actually, “Fixed I/O” stands for Fixed “Input/Output.” When purchasing Compact PLCs, users will observe that the microcontroller itself houses both the PLC’s input and output parts.
In other words, the manufacturer determines and fixes every form of output or input. Additionally, with this kind of PLC, the number of inputs and outputs may not be increased.
Small-scale applications are controlled or carried out using these PLC types. A small package houses the processor, power supply, memory, inputs, and outputs. These PLCs typically have set numbers of inputs and outputs, such as 8, 16, 24, 32, and 40 inputs and 4, 8, 16, 32, and 40 outputs. The amount of inputs, outputs, and memory configurations vary according on the manufacturer and model. Inputs include analogue and digital inputs, while outputs include digital and analogue outputs. The primary benefit of fixed type PLCs is their reduced price. The lack of flexibility with fixed type PLCs is one of their drawbacks.Additionally, certain versions require the replacement of the complete system if any component malfunctions.
Advantages of Fixed PLC:
- Fixed PLCs can only store a certain amount of data. This is due to the fact that every component is contained within a single entity.
- Fixed PLCs may be substantially less expensive.
Disadvantages of Fixed PLC:
- Less memory is frequently built into fixed PLC than into their modular equivalents. Fixed PLC have a fixed number of inputs and outputs since they are manufactured with I/O components already installed.
- Because the system is put together as a whole, it is difficult to fix if one component breaks. Longer downtimes may result from this for repairs.
- Fixed PLC cannot do more complex tasks as a result. The pre-assembled feature of fixed PLC has the additional drawback that repairs could be more difficult.
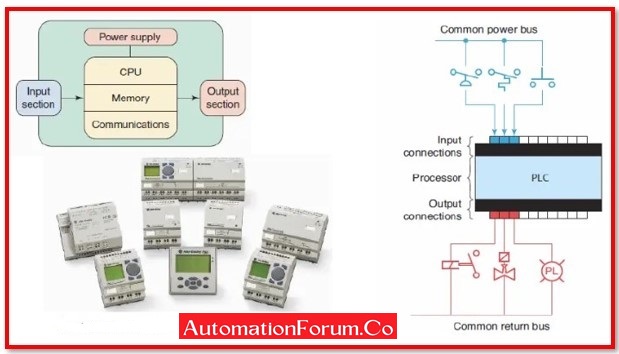
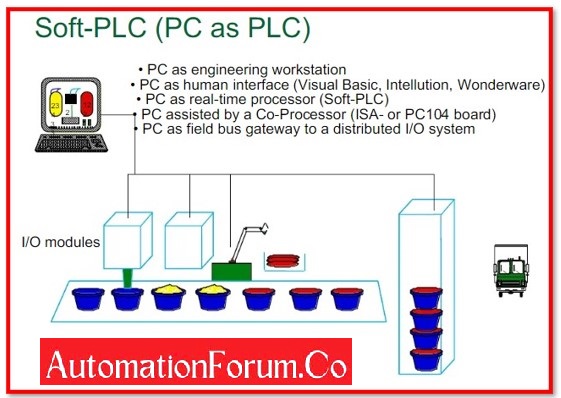
SOFT PLC:
A programmable logic controller, or PLC, often known as a fully complete embedded computer, can be created using a software technology called a soft PLC. It combines high performance computer networking, data management, and computational capabilities with discrete, PID, and analogue I/O control offered by PLCs. As a result, soft PLCs provide reliable operation, incredibly quick and deterministic programme scan durations, a great set of instructions, clear data table memory, an unlimited number of user programmes, and above all, an open architecture platform that enables users to connect to a variety of I/O systems, networks, and other devices.
A soft PLC needs to be implemented under the proper system requirements in order to function properly. An Ethernet port, USB port, parallel port, or user-specified port, 32 MB RAM, 386 or higher compatible CPU, 64 MB disc, I/O ports or interface cards, as well as other communication interfaces like the COM ports, are among the minimum software and hardware requirements.
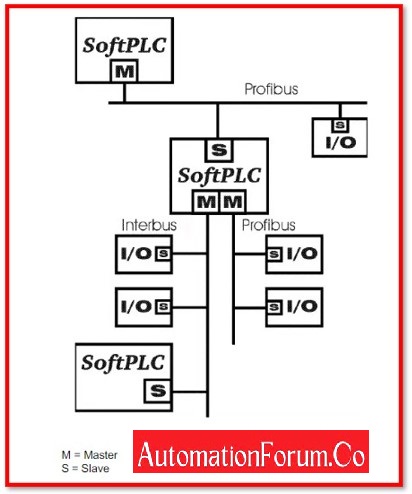
Soft PLCs combine the following operations:
- PLC’s
- Data monitors
- Information Gateways
- Embedded computing.
Advantages of Soft PLC:
- Soft PLCs can assist in lowering production costs. They foster efficiency, which leads to more output and, ultimately, higher profits.
- With benefits including simpler configuration and maintenance, Soft PLCs support a variety of programming languages. They are therefore the ideal choice in high-volume industrial settings where frequent updates are necessary.
- In keeping with current industry requirements, a Soft PLC device offers sophisticated security solutions. To prevent unwanted access, for instance, enables you to modify access restrictions to production data.
Disadvantages of Soft PLC:
- There is no other software included beside Soft PLC.
- Not every application requires for Soft PLC, and vice versa, due to the potential addition of needless programming costs.
Distributed PLC:
A network connects the system’s distributed controllers together. The MIMD structure is used to implement a multiple core controller architecture that uses independent bit and word units. By using a semaphored memory system in its basic form, the calculation process is effectively synchronised. The suggested compiler automatically divides up the programme into several processing units. A graph-based representation of the standard programme is utilised for distribution and scheduling purposes. Selected standard languages can be combined into an independent graph-based form thanks to a developed conversion model. Utilizing PFGA devices, the distributed controller architecture has been prototyped, allowing for precise implementation and performance assessment. Token passing-based deterministic protocol was used to implement the data exchange.
Advantage of Distributed PLC:
- Compared to other systems, the Distributed PLC system requires less and simpler wiring.
- The distributed PLC is capable of remote control.
- The connected system receives a quick response from the distributed PLC.
Disadvantages of Distributed PLC:
- The high-speed implementation of distributed PLC does not work.
- The distributed PLC costs more when used infrequently.
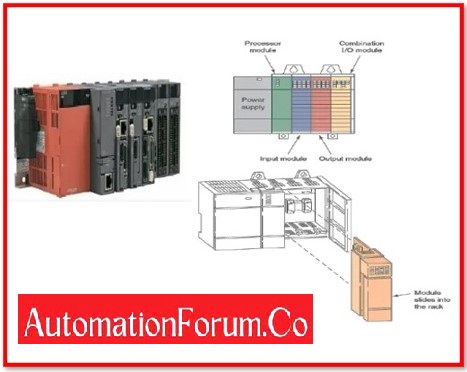
Modular PLC:
The term “modular” refers to a form of PLC that enables various expansions of the PLC system through the use of modules.
Due to the independence of each component, modules usually make it simpler to use the programmable logic controller and provide more functionality like more I/O units.
To build a PLC control system, you must manually connect the power supply, communications module, and input/output module since they are all independent of the microcontroller itself.
The rack-mounted or rack mount PLC is a type of modular PLC. All connections are centralised in a rack mount PLC because the communications module of the PLC is housed in the rack itself.

Separate modules can be put into the compartments that make up this sort of PLC. A rack, a power supply unit, a CPU module, an input, and an output make up the modular basic control. It has an operator interface for running programmes and keeping track of things. The rack has the modules hooked in. These PLCs are employed in industrial settings. Depending on the PLC brand and type, the input and output racks can be upgraded as needed and have more storage capabilities. This form of PLC has the benefit of allowing for industry scaling without the need for downtime, but it also costs more than compact PLCs. The modular PLC is simpler to maintain than the compact PLC.
Advantages of Modular PLC:
- The memory and data storage capacity of modular PLCs are significantly greater.
- The modular PLC is more useful since it can handle more complicated procedures.
- In order to develop and adjust processes for smooth expansion, modular PLCs were created.
- Modular PLCs can quickly identify problems and rectify them while continuing to run some processes.
- Modular PLC has higher long-term economic security.
Disadvantages of Modular PLC:
- Reduced space efficiency caused by modular PLC.
- When modules fail, modular PLC might increase troubleshooting cost.
- Configuration complexity increases as a result of modular PLC.
- Because modular PLC have low IP ratings, enclosures are required.
- Maintaining more spare inventory on-site for modular PLC
- Modular PLC I/O racks promote centralised rather than distributed I/O, which is certainly not standard way in the modern world.





