- What is calibration?
- What are calibration standards?
- What is calibration point?
- What is calibration error?
- Why calibration is important?
- How frequently we need to calibrate instruments?
- What is the difference between QC and Calibration?
- Why is calibration necessary?
- What is Calibration Adjustment?
- Instrument Calibration
- Calibration vs. Verification: Understanding the Terminology
- What are the advantages of calibration?
What is calibration?
Calibration is the process of comparing the reading of one instrument or equipment with a standard instrument. The reference instrument is already calibrated and referenced to a known set of parameters. The reference instrument should itself be directly traceable to equipment that is calibrated. Calibration is done to minimise any type of uncertainty in measurement by ensuring the accuracy of test equipment. For most standard organisations accuracy ratio will be 3:1. The main objective of calibration is checking the accuracy of the given instrument and determining the traceability of measurement.
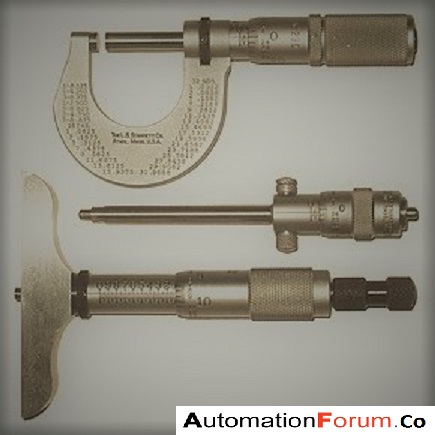

The above diagram shows a micrometer. The main parameter for calibration is the accuracy of the scale. A calibrated slip gauge is used for calibrating the scale. For checking flatness and parallelism a calibrated optical flat is used.
What are calibration standards?
In simple words, calibration is the process of matching the standard value of the instrument to the master value (true value) of the instrument. IIM & TE item is taken as standard reference for calibration.
The below table shows the different valve type and common test standard:
| VALVE TYPE | COMMON TEST STANDARD |
| Cast Iron gates | API 598, MSS SP-70* |
| Control valves | ISA-S75, FCI 70-2 |
| Pressure relief valves | ASME PTC 25, API 527 |
| Cryogenic valves | BS 6364, API 598 |
| Steel ball valves | API 598 |
| Steel butterfly valves | API 598 |
| Cast iron checks | API 598, MSS SP-71* |
| Cast iron plugs | API 598, MSS SP-78* |
| Bronze gates, globes and checks | MSS SP-80* |
| Pressure seal valves | ASME B16.34* |
| Steel valves larger than NPS 24” | ASME B16.34* |
| Pipeline valves | API 6D* |
| Cast iron globes | API 598, MSS SP-85* |
What is calibration point?
Calibration point is a single source for calibration of wide range of instruments in electronics traceable to NABL (NATIONAL ACCREDITATION BOARD FOR TESTING AND CALIBRATION LABORATORIES).
What is calibration error?
Most calibration errors are some combination of hysteresis, zero, span, linearity errors. The zero error always accompany with other type of errors. The efficient identification and correction of instrument calibration errors are important. A hysteresis calibration error occurs when the response of the instrument become different to the increasing input compared to the decreasing input. Hysteresis errors are always caused by some mechanical friction on moving element such as bellows, levers, bourdon tube etc. The output of an instrument with hysteresis problem always lags behind the changing input, because friction always acts in a direction opposite to relative motion.Technicians, perform a single-point calibration test as a qualitative indication of its calibration. If the instrument performs within the specification, then it is good. If not, the instrument definitely need to be re-calibrated.
Why calibration is important?
Due to normal wear and tear, the accuracy of almost all measurement devices decreases. The accuracy may degrade over time to time. Also a hazardous manufacturing surrounding may cause damage to the accuracy of the instrument, sometimes it may be degraded due to long use. In short,these all factors results in improper functioning of the manufacturing unit. The quality of the products also reduced if there is no accuracy in measurement devices. For proper functioning, calibration is an important process to be done regularly.
How frequently we need to calibrate instruments?

What is the difference between QC and Calibration?
Qc (Quality Control) make sure that the instrument is working properly. While calibrators give a reference point to adjust the instrument. If the working is improper; if QC is out of the specified range, calibrators are used to adjust the instrument to make it into the specified range.
Why is calibration necessary?
Industrial processes need calibration for multiple essential purposes:
Accuracy deteriorates naturally with time which decreases reliability. Several commercial sectors enforce mandatory calibration procedures to fulfill their legal regulatory requirements.
Quality Assurance functions as an essential foundation for any quality management system through calibration procedures.
The accuracy of financial transactions depends directly on exact measurement results in addition to impacting operational costs.
Manufacturing processes maintain consistency and reliability through product quality management.
The operation provides dual protection for workforce members and customers through its prevention of measurement hazards.
Correct measurement methods enable organizations to reduce waste while upholding environmental accountability.
Apart from these standards there exist specific industry requirements that might need calibration services.
For detailed safety guidelines, general recommendations, and calibration procedures in process industries, refer to the provided link:
What is Calibration Adjustment?
The process of modifying measuring devices through calibration adjustment brings device readings near reference standards while it is commonly known as adjustment or trimming.
A standard reference serves as the basis to make comparisons against an instrument during its calibration procedure.
An adjustment procedure should be performed as a way to fix measurement errors when discrepancies are discovered during the calibration process.
The procedures for calibration and adjustment function as different operations. Measurement devices undergo calibration to perform comparison routines which do not involve changes to their design.
Modification of the device happens through adjustment processes to match the specified standard.
The term “calibration” is informally used interchangeably with adjustment by some people although most formal definitions demonstrate these two processes as different sequential operations.
Click here for Collection of Instrument Calibration Activity Calculators for Accurate Adjustments
Instrument Calibration
The ability to maintain accurate measurements depends heavily on instrument calibration as an essential procedure. Instruments need to be set correctly to produce readings within defined acceptable parameters.
The main goal of calibration exists to minimize and eliminate all factors producing imprecise measurements which constitute a vital element in instrumentation design.
All instruments use different calibration procedures yet testing samples against known standards referred to as calibrators constitutes the basis of this process.
When measurements from the instrument match these reference values a direct connection between the measurement technique and the known standards is formed.
Through calibration the instrument acquires the ability to yield better results than its natural capabilities permit. Business practice dictates that instrument range assessments require a limited number of calibrators at special measurement locations instead of all prospective values.
The process of increasing calibrator numbers would boost accuracy but organizations need to evaluate the time commitment required to make this improvement happen.
The process requires selecting between high performance standards and increased calibration work requirements.
The manufacturer-provided calibration specifications represent the optimal points for measuring devices to operate since such a deployment minimizes the system’s internal measurement errors.
Click here for Downloadable Instrumentation Calibration Report Preparation Templates
Calibration vs. Verification: Understanding the Terminology
The fields of metrology differentiate verification from calibration even though people often interchange their definitions when dealing with liquid delivery devices. The procedure of volume verification for pipettes or automated liquid handlers involves a traceable measured volume to check their accuracy.
Verification determines passing or failing status through a comparison between measured errors and predetermined tolerance margins. Results from verification testing show that the instrument must keep errors within the established tolerance boundaries.
The verification process follows a scheduled basis which laboratory requirements dictate and adaptable checks can occur when specific needs emerge. An interim verification or quick check serves as a specific need verification procedure. Before critical tasks and suspected malfunctions verification serves as necessary preventative checks.
What are the advantages of calibration?
- Calibration is proof that the instrument is working properly.
- Increases the confidence of instrument user.
- Calibration fulfils the requirement of traceability.
- Increases power saving and cost saving.
- Reduced rejection and failure rate, hence gives higher productivity.
- Interchangeability.
- The improved product quality and service quality leading to satisfied customers.
- Increases safety.
These are the benefits or advantages of calibration.
Click here for more Instrumentation Calibration Procedures





