Control Valve
Troubleshooting Guide for On-Off / Shutdown Valve Operation: Common Issues and Solutions
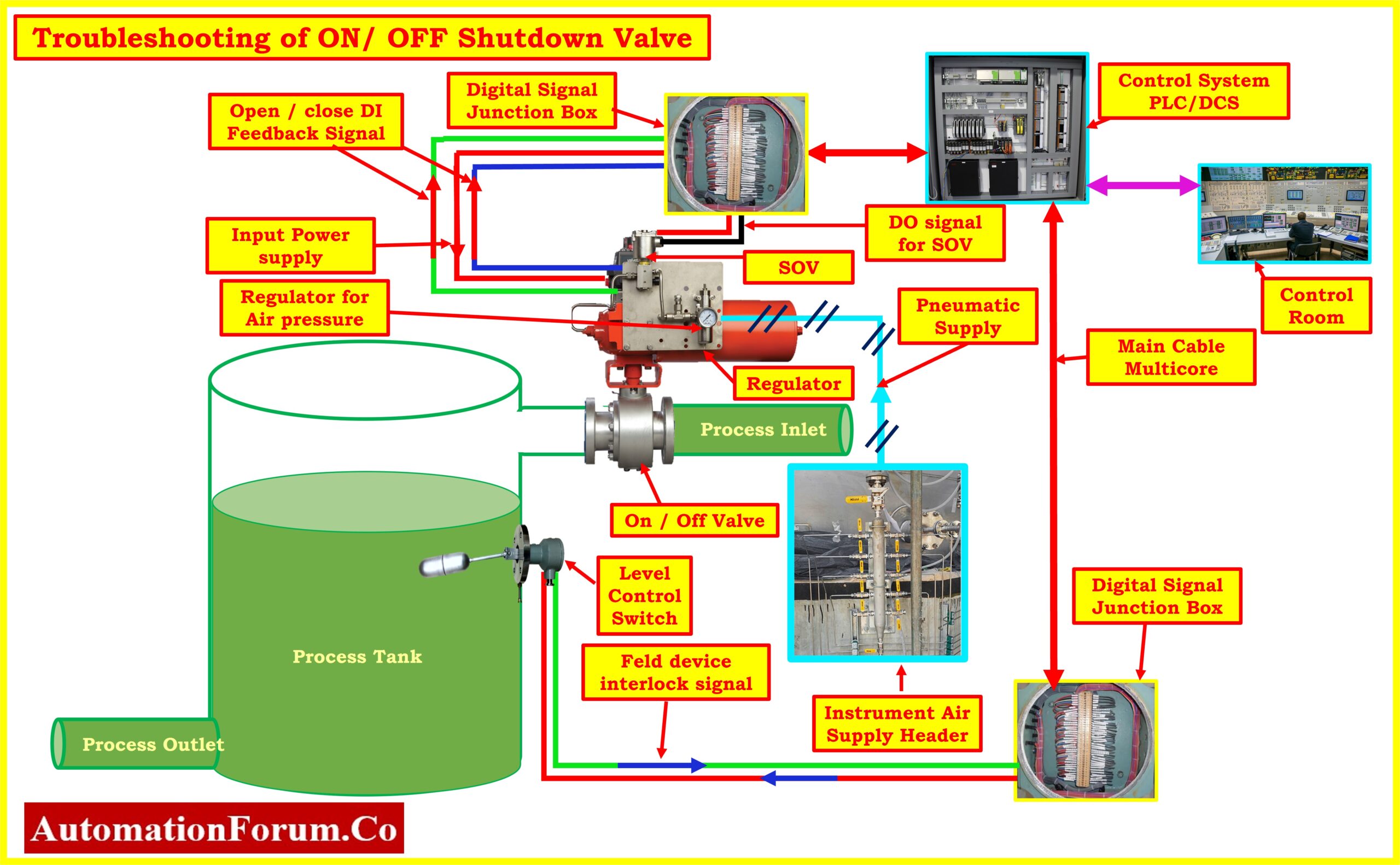
Table of Contents
- Problem No.1: On-Off Valve Feedback output signal Issue
- Problem No.2: On-Off Valve is not fully opening or closing and gets stuck in between
- Problem No.3: On-Off Valve Not Opening or Closing and not responding
- Common On-Off Valve Problems
- Problem No:1 Leaking
- Problem No:2 Sticking
- Problem No:3 Corrosion
- Problem No:4 Broken Handle
- Problem No:5 Faulty Seals
- Problem No:6 Malfunctioning Actuator
Troubleshooting on-off/shutdown valves involves diagnosing and resolving issues affecting their feedback signal, movement, and responsiveness. This comprehensive guide outlines step-by-step procedures and solutions for three common problems encountered in valve operation.
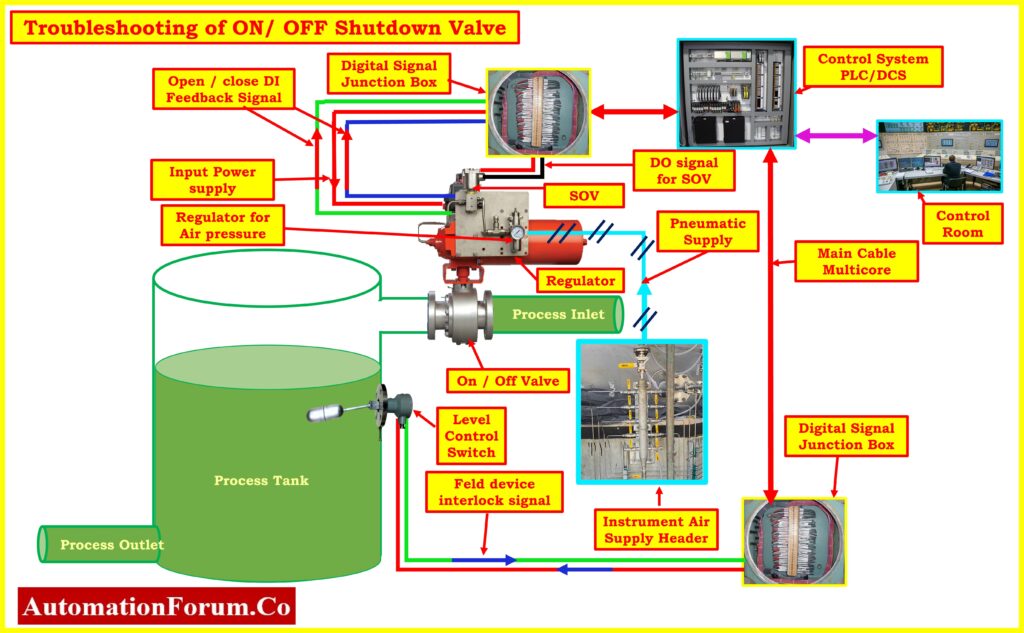
Problem No.1: On-Off Valve Feedback output signal Issue
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Misalignment between Command and Field Position: Discrepancy between the command sent to the valve and its actual position. | Verify alignment between command and field position, recalibrate if necessary. |
| Electrical Issues: Blown fuse or faulty wiring disrupting voltage supply to feedback mechanism. | Check for blown fuses in loop, replace to restore proper voltage supply. |
| Faulty Limit Switch or Proximity Sensor: Malfunctioning feedback components providing inaccurate readings. | Replace malfunctioning components with new ones for accurate feedback readings. |
| Barrier in Marshaling Cabinet: Faulty barrier affecting signal isolation and integrity. | Install new barrier in marshaling cabinet to ensure proper signal isolation. |
| Forced Feedback: Manual override or forced signals interfering with feedback mechanism. | Investigate and remove any manual overrides or forced signals to allow accurate feedback reading |
| Digital Input Channel Fault: Faulty channel processing feedback signals inaccurately or not at all. | Replace faulty channel with new one, configure for proper processing of feedback signals. |
| Loose Wiring or Junction Box Issues: Loose connections or faulty junction box causing intermittent signal transmission. | Inspect wiring connections and junction box for looseness or damage, tighten or repair as necessary to ensure uninterrupted signal transmission. |
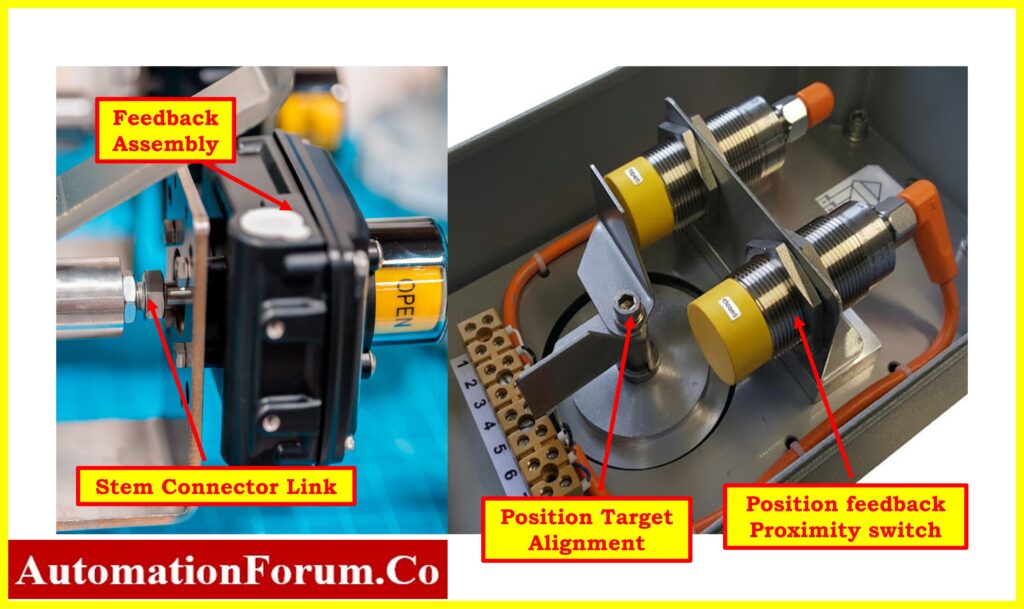
Problem No.2: On-Off Valve is not fully opening or closing and gets stuck in between
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Incorrect Instrument Air Pressure: Improper air pressure settings may prevent the valve from fully opening or closing. | Verify air pressure settings according to the datasheet specifications and adjust if necessary. |
| Instrument Air Tubing Leak: Leakage in the air tubing can result in insufficient pressure to operate the valve properly. | Identify and repair any leaks in the instrument air tubing to ensure proper pressure supply to the valve. |
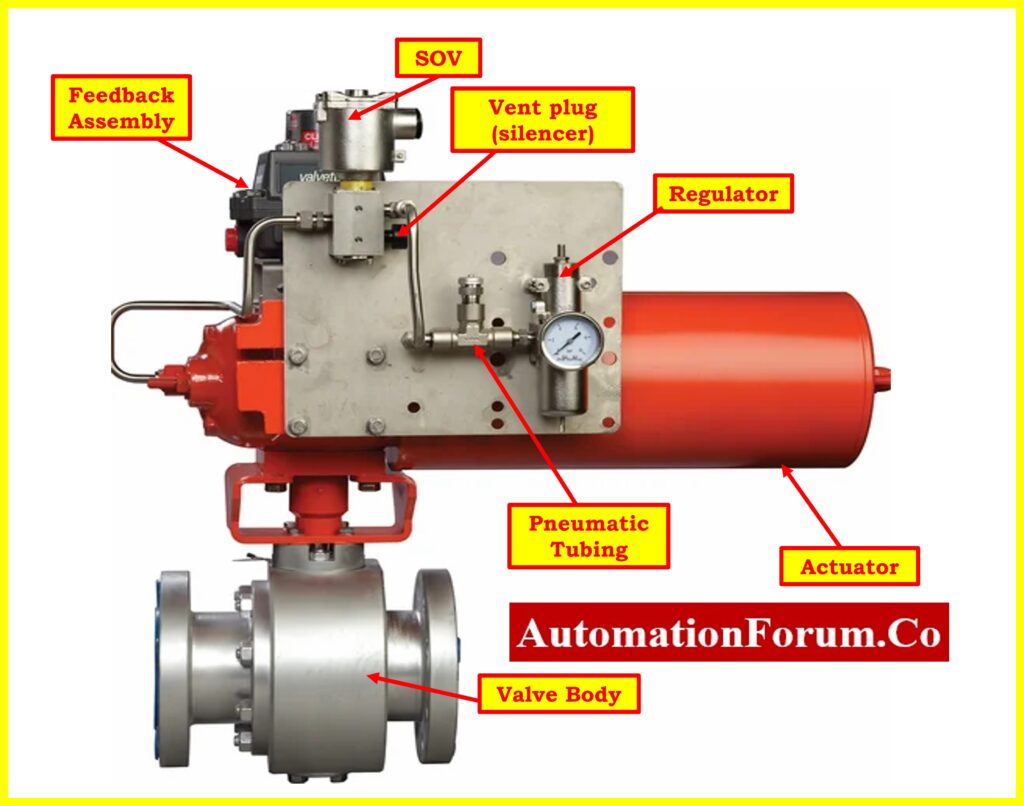
| Passing Actuator: A malfunctioning actuator may allow air to pass through, preventing proper valve operation. | If the actuator is passing, either replace or overhaul it to restore proper functionality. |
| Faulty SOV: A defective solenoid-operated valve (SOV) can hinder the valve’s full opening or closing. | Investigate the condition of the SOV and replace it if found faulty to enable full valve movement. |
| Misadjusted Limit Stop Bolt: Improper adjustment of the limit stop bolt in the actuator or gearbox may restrict the valve’s movement. | Ensure proper adjustment of the limit stop bolt in the actuator or gearbox to allow full valve opening and closing. |
| Stuck Valve Body: Accumulation of debris or mechanical issues can cause the valve body to become stuck in between open and closed positions. | Apply direct air to the valve to attempt to free a stuck valve body by cycling it several times. If the issue persists, consider performing a comprehensive overhaul of the valve to rectify any underlying mechanical issues and restore optimal performance. |
Problem No.3: On-Off Valve Not Opening or Closing and not responding
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Presence of Interlock: A safety interlock system may prevent the valve from operating. | Check for any active interlocks and resolve them to enable valve operation. |
| Malfunctioning Interlocking Device: A malfunction in a level switch or pressure switch producing digital input signals can disrupt valve operation. | Inspect and troubleshoot malfunctioning interlocking devices. Repair or replace them as necessary to restore proper function and enable valve operation. |
| Latching Solenoid Valve: If the SOV is of the latching type, ensure that the latching system is functioning correctly. | Verify the functionality of the latching mechanism and make necessary adjustments or repairs if needed. |
| Locked Handwheel: A latched handwheel can prevent valve operation. | Check the handwheel and ensure it is not latched. If it is, release the latch to allow valve operation. |
| Lack of Voltage: Absence of voltage to the solenoid valve can hinder its operation. | Verify voltage supply to the solenoid valve. Replace blown fuses in the marshaling cabinet if necessary. |
| Faulty Relay: A faulty relay in the marshaling cabinet can disrupt signal transmission. | Inspect and replace any faulty relays in the marshaling cabinet. |
| DO Channel Issue: Rarely, a fault in the digital output (DO) channel can affect valve operation. | Change the DO channel if necessary and configure it properly. |
| SOV Coil Resistance: Abnormal resistance in the SOV coil can impede its function. | Measure and replace the SOV coil if resistance is outside acceptable limits. |
| SOV Body Condition: Issues such as passing or a stuck plunger in the SOV can prevent valve operation. | Inspect the SOV body and replace if necessary. |
| Instrument Air Pressure: Incorrect instrument air pressure settings may affect valve operation. | Check and adjust instrument air pressure according to datasheet specifications. |
| Instrument Air Tubing Leak: Leakage in the instrument air tubing can lead to insufficient pressure for valve operation. | Identify and repair any leaks in the instrument air tubing to ensure proper pressure supply to the valve. |
| Passing Actuator: A malfunctioning actuator may allow air to pass through, affecting valve operation. | Inspect and replace or overhaul the actuator if necessary to restore proper function. |
| Stuck Valve Body: Mechanical issues or debris accumulation can cause the valve body to become stuck. | Apply direct air to the valve and cycle it several times to attempt to free a stuck valve body. If unsuccessful, consider performing a proper overhaul of the valve. |
| Loose Connection in Junction Box (JB): Loose electrical connections in the JB can disrupt signal transmission. | Inspect the JB for any loose connections and tighten or repair them as necessary to ensure uninterrupted signal transmission and proper valve operation. |
| Air Regulator and Instrument Air Header Problems: Issues with the air regulator or instrument air header may affect air supply to the valve. | Inspect and repair or replace faulty air regulator or instrument air header components to ensure proper air supply to the valve. |
| SOV and Vent Plug Issues: Problems with the solenoid-operated valve (SOV) or blocked vent plug can valve operation. | Inspect and repair or replace faulty SOV or vent plug components to ensure proper valve function. |
| Manual Mode Loop: If the operator has placed the loop in manual mode, it may prevent automatic operation of the valve. | Communicate with the operator and switch the loop back to automatic mode to enable normal valve operation |
| Forced Signal from PLC or DCS: A forced signal from the PLC or DCS system may override normal operation of the valve. | Investigate the PLC or DCS system settings and remove any forced signals to allow the valve to operate according to its control logic. |
Common On-Off Valve Problems
Common issues with on-off valves can disrupt operations and compromise system integrity. Leaks, sticking, corrosion, broken handles, faulty seals, and malfunctioning actuators are among the prevalent problems. Effective maintenance and preventive measures are essential for mitigating these issues and ensuring smooth valve operation.
Problem No:1 Leaking
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Seals within the valve may degrade over time due to wear and tear, leading to leaks. | Regularly inspect seals and replace damaged ones promptly. |
| Improperly tightened fittings can result in gaps through which fluid may escape. | Ensure all fittings are properly tightened to prevent leaks at connection points. |
| Corrosive substances in the fluid or environmental factors can corrode valve components, compromising their integrity. | Implement protective measures such as coatings to prevent corrosion of valve components. |
| Excessive pressure can exceed the sealing capacity of the valve, causing leaks to occur. | Monitor and control pressure within recommended limits to prevent seal failure. |
| Extreme temperatures can cause expansion or contraction of materials, affecting the tightness of seals and leading to leakage. | Employ temperature management techniques to mitigate the effects of extreme temperatures on seal integrity. |
Problem No:2 Sticking
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Accumulation of dirt, debris, or scale within the valve can obstruct its movement, causing sticking. | Regularly clean valve internals to remove dirt, debris, or scale buildup. |
| Insufficient lubrication of moving parts can increase friction, leading to sticking or binding. | Ensure proper lubrication of all moving parts to reduce friction and facilitate smooth operation. |
| Corrosion of internal components can cause rough surfaces that impede smooth valve operation. | Implement corrosion prevention measures such as protective coatings or materials. |
| Misalignment of valve components can lead to interference and hinder proper movement. | Ensure proper alignment of valve components to prevent interference and sticking. |
| Malfunctioning actuators may fail to provide sufficient force to open or close the valve effectively. | Check and repair actuators as needed to ensure they provide sufficient force for valve operation. |
Problem No:3 Corrosion
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Contact with corrosive fluids or gases can degrade valve materials over time. | Apply protective coatings or treatments |
| Absence of protective coatings or treatments leaves valve components vulnerable to corrosion. | Use corrosion-resistant materials |
| Environmental factors such as humidity or temperature fluctuations | Monitor and control environmental conditions |
Problem No:4 Broken Handle
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Excessive force applied to the handle during operation can cause it to break. | Upon identification of a broken handle, it should be promptly replaced to ensure continued operation of the valve. |
| Continuous use over time can lead to material fatigue and eventual failure of the handle. | Train personnel on proper handling techniques to minimize stress on the handle during operation. |
| Mishandling or rough operation of the handle can weaken its structure and cause it to break prematurely. | Select handles made from robust materials capable of withstanding mechanical stress and wear for improved longevity. |
Problem No:5 Faulty Seals
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Seals degrade over time due to continuous use and exposure to operating conditions. | Regular inspection and replacement of seals can prevent leaks and ensure proper sealing. |
| Seals may not be installed correctly, leading to gaps and leaks. | Proper installation techniques should be followed to ensure a secure and effective seal. |
| Chemicals present in the process fluid can deteriorate seal materials. | Select seals compatible with the process fluid and operating conditions to maximize performance and longevity. |
| Operating conditions exceeding seal limits can cause degradation and failure. | Maintain operating conditions within specified limits to prevent premature seal failure. |
Problem No:6 Malfunctioning Actuator
| Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Faulty wiring, connections, or electrical components can lead to actuator malfunction. | Inspect wiring and connections for damage or loose connections, and repair as necessary. |
| Damage to internal components such as gears, pistons, or springs can impair actuator operation. | Disassemble the actuator, inspect internal components for damage, and repair or replace as needed. |
| Insufficient lubrication or cleaning can lead to mechanical wear and eventual failure of the actuator. | Develop and adhere to a maintenance schedule that includes lubrication, cleaning, and inspection of the actuator to ensure optimal performance and longevity. |





